Final ID: P1169
Postpartum Care in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: Exploring Factors Affecting Follow-Up
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) increase long-term cardiovascular risk, yet adherence to postpartum follow-up is poor, particularly among women facing socioeconomic barriers. This study explores how factors such as race, social determinants of health (SDOH), substance use, and admissions to NICU correlate with postpartum follow-up and adherence to current cardiovascular screening recommendations.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that disparities in race and SDOH influence postpartum follow-up and adherence to screening guidelines. Additionally, we hypothesize that high-risk factors such as NICU admissions may contribute to lapses in follow-up care.
Methods:
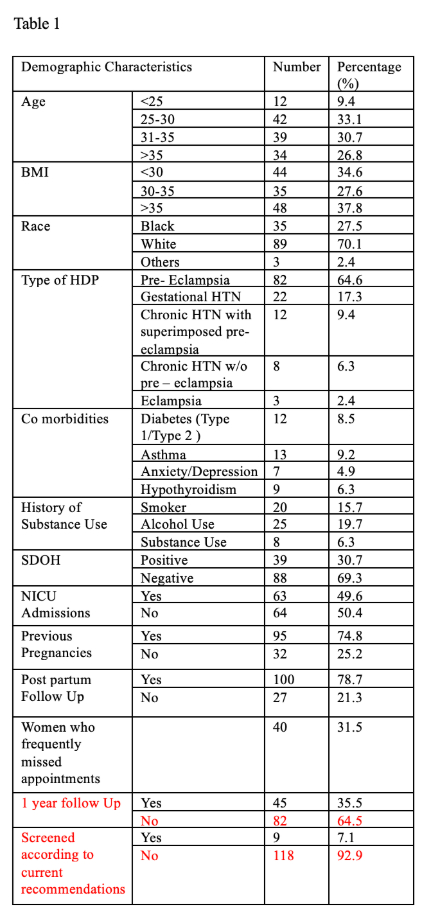
A retrospective review of 173 women with HDP diagnosis was conducted between July 2021 (after the easing of COVID-19 restrictions) and July 2024 at a community hospital. Thirty-one women were excluded due to incomplete records or HDP history prior to 2021. An additional fifteen women were excluded as it has not been one-year post-delivery. Data on postpartum follow-up, prior co-morbidities, race, alcohol use, NICU admission, and SDOH were collected (Table 1). Adherence to screening was assessed per AHA and ACOG recommendations.
Results:
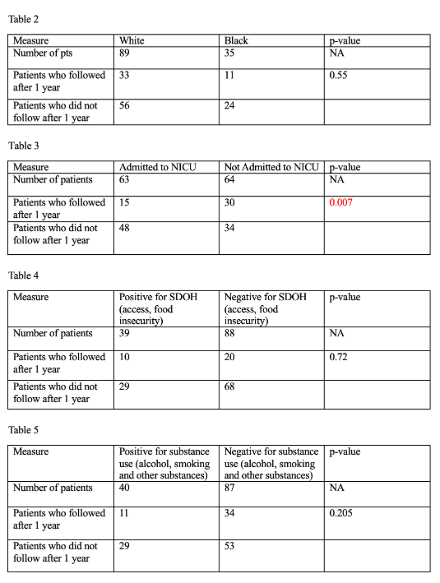
Of the 127 women included in the study, 70.1% were White, and 27.5% were Black. In total, 21.3% had no postpartum follow-up and 31.5% frequently rescheduled appointments. Screening adherence was poor, with only 14% having some recommended labs drawn one year postpartum. Only 6.3% of women were screened with all five recommended labs (BMP, HbA1C, TSH, urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio, lipid panel). Chi-square analysis was performed for race, SDOH, NICU admission, and substance use. It was noted that NICU admission significantly impacted follow-up, with only 24% of women with babies admitted to NICU following up (p=0.007). Race, SDOH, and substance use did not significantly impact follow-up rates (p>0.05). (Table 2-5)
Conclusion:
There is a significant gap in postpartum follow-up and screening, particularly among women with babies requiring NICU care. This could be explained by complex post-natal care but has a significant impact on maternal health outcomes. While race and SDOH did not significantly affect follow-up, targeted interventions for high-risk populations are necessary to improve cardiovascular outcomes.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) increase long-term cardiovascular risk, yet adherence to postpartum follow-up is poor, particularly among women facing socioeconomic barriers. This study explores how factors such as race, social determinants of health (SDOH), substance use, and admissions to NICU correlate with postpartum follow-up and adherence to current cardiovascular screening recommendations.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that disparities in race and SDOH influence postpartum follow-up and adherence to screening guidelines. Additionally, we hypothesize that high-risk factors such as NICU admissions may contribute to lapses in follow-up care.
Methods:
A retrospective review of 173 women with HDP diagnosis was conducted between July 2021 (after the easing of COVID-19 restrictions) and July 2024 at a community hospital. Thirty-one women were excluded due to incomplete records or HDP history prior to 2021. An additional fifteen women were excluded as it has not been one-year post-delivery. Data on postpartum follow-up, prior co-morbidities, race, alcohol use, NICU admission, and SDOH were collected (Table 1). Adherence to screening was assessed per AHA and ACOG recommendations.
Results:
Of the 127 women included in the study, 70.1% were White, and 27.5% were Black. In total, 21.3% had no postpartum follow-up and 31.5% frequently rescheduled appointments. Screening adherence was poor, with only 14% having some recommended labs drawn one year postpartum. Only 6.3% of women were screened with all five recommended labs (BMP, HbA1C, TSH, urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio, lipid panel). Chi-square analysis was performed for race, SDOH, NICU admission, and substance use. It was noted that NICU admission significantly impacted follow-up, with only 24% of women with babies admitted to NICU following up (p=0.007). Race, SDOH, and substance use did not significantly impact follow-up rates (p>0.05). (Table 2-5)
Conclusion:
There is a significant gap in postpartum follow-up and screening, particularly among women with babies requiring NICU care. This could be explained by complex post-natal care but has a significant impact on maternal health outcomes. While race and SDOH did not significantly affect follow-up, targeted interventions for high-risk populations are necessary to improve cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Heart-pounding Case of Cardiomyopathy in Pregnancy
Tran Linh, Everitt Ian, Vaught Arthur, Barth Andreas, Minhas Anum
Altered vasorin and angiotensinogen/vasorin ratios correlate with vascular reactivity in women with preeclampsiaMurugesan Saravanakumar, Tubinis Michelle, Saravanakumar Lakshmi, Sinkey Rachel, Kaushik Teshi, Tita Alan, Jilling Tamas, Berkowitz Dan