Final ID: P1002
MIND Diet, Circulating Inflammatory Biomarkers, and Cognitive Function: A Prospective Study
Abstract Body: Background: Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegeneration Delay (MIND) diet was associated with better cognitive outcomes, but the role of inflammation in this association was rarely explored.
Methods: We included 3777 Health and Retirement Study participants (mean age=65.3 years, 59.0% female) who completed the food frequency questionnaire in 2013 and assayed for 18 inflammatory markers in venous blood in 2016. The inflammatory markers included 5 cytokines and 4 other proteins in serum and 9 blood cell measures. Cognitive function was assessed using the 27-unit modified Telephone Interview of Cognitive Status (TICS-m) in 2016, 2018, and 2020. We used linear regression models to assess the associations of the MIND diet score with inflammatory markers and performed mediation analysis to whether they mediate the MIND-cognitive function association.
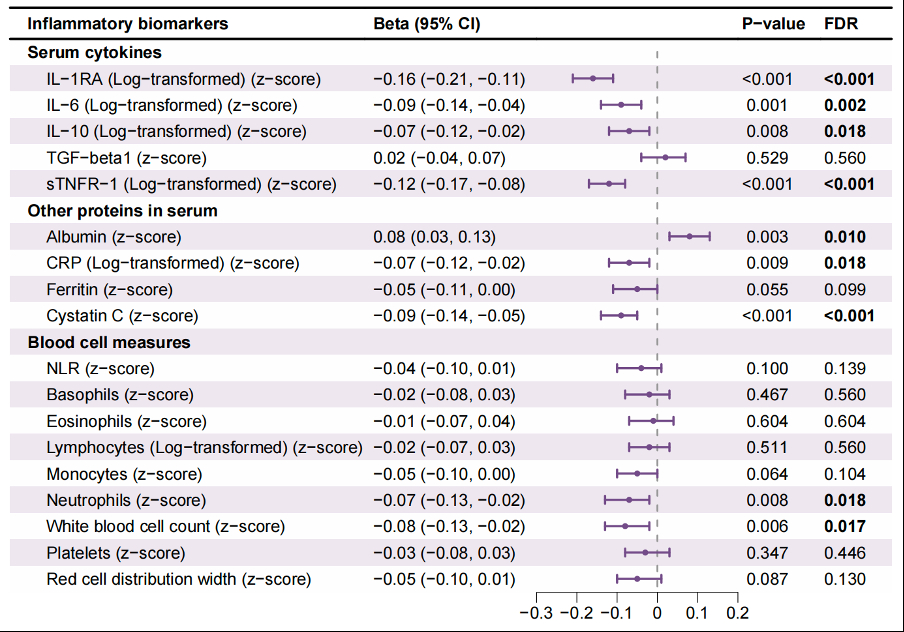
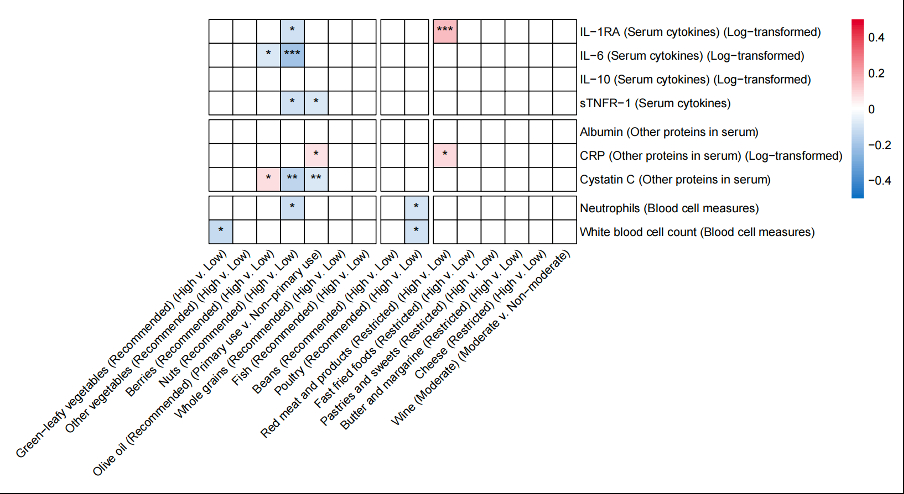
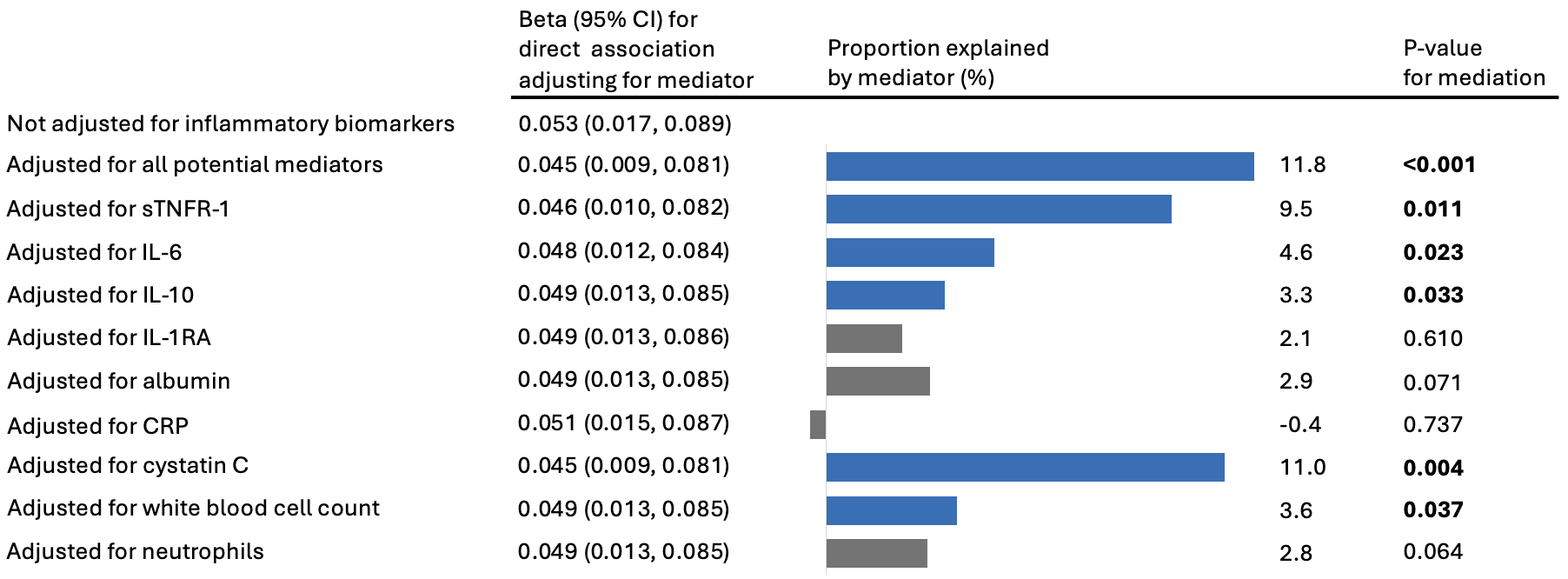
Results: During the 7-year follow-up, higher MIND diet score indicating higher compliance to the MIND diet was significantly associated with better cognitive function (beta per 3-unit increment with global cognitive function z-score=0.05, 95% CI: 0.02-0.09). Higher MIND score was also related to lower levels of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), IL-6, IL-10, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (sTNFR-1), C-reaction protein (CRP), cystatin C, neutrophils, and white blood cell count and higher level of albumin (false discovery rates<0.05). Among them, higher levels of IL-6, IL-10, sTNFR-1, cystatin C, neutrophils, and white blood cell count, and lower level of albumin were inversely associated with cognition in later waves (P-values<0.05 for all). Further, the association of the MIND diet with cognitive function was significantly mediated by cystatin C (11.0%), sTNFR-1 (9.5%), IL-6 (4.6%), white blood cell count (3.6%), and IL-10 (3.3%). Collectively, these markers mediated the MIND-cognition association by 11.8% (p<0.001).
Conclusion: Adherence to the MIND diet is associated with a panel of circulating systemic inflammatory markers that have been extensively investigated in Alzheimer’s disease. These peripheral blood-based biomarkers significantly mediate the MIND-cognition association and may serve as potential targets or intermediate outcomes of dietary intervention for cognitive health.
Methods: We included 3777 Health and Retirement Study participants (mean age=65.3 years, 59.0% female) who completed the food frequency questionnaire in 2013 and assayed for 18 inflammatory markers in venous blood in 2016. The inflammatory markers included 5 cytokines and 4 other proteins in serum and 9 blood cell measures. Cognitive function was assessed using the 27-unit modified Telephone Interview of Cognitive Status (TICS-m) in 2016, 2018, and 2020. We used linear regression models to assess the associations of the MIND diet score with inflammatory markers and performed mediation analysis to whether they mediate the MIND-cognitive function association.
Results: During the 7-year follow-up, higher MIND diet score indicating higher compliance to the MIND diet was significantly associated with better cognitive function (beta per 3-unit increment with global cognitive function z-score=0.05, 95% CI: 0.02-0.09). Higher MIND score was also related to lower levels of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), IL-6, IL-10, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (sTNFR-1), C-reaction protein (CRP), cystatin C, neutrophils, and white blood cell count and higher level of albumin (false discovery rates<0.05). Among them, higher levels of IL-6, IL-10, sTNFR-1, cystatin C, neutrophils, and white blood cell count, and lower level of albumin were inversely associated with cognition in later waves (P-values<0.05 for all). Further, the association of the MIND diet with cognitive function was significantly mediated by cystatin C (11.0%), sTNFR-1 (9.5%), IL-6 (4.6%), white blood cell count (3.6%), and IL-10 (3.3%). Collectively, these markers mediated the MIND-cognition association by 11.8% (p<0.001).
Conclusion: Adherence to the MIND diet is associated with a panel of circulating systemic inflammatory markers that have been extensively investigated in Alzheimer’s disease. These peripheral blood-based biomarkers significantly mediate the MIND-cognition association and may serve as potential targets or intermediate outcomes of dietary intervention for cognitive health.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Albuminuria with Cognition in Midlife: The CARDIA study
Chang Ning-shan, Vivek Sithara, Yaffe Kristine, Guan Weihua, Launer Lenore, Seegmiller Jesse, Schreiner Pamela, Sedaghat Sanaz, Shlipak Michael, Jacobs David
Age at First Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation and Longitudinal Cognitive DeclineWang Yujie, Wang Bin, Cao Han, Tang Mingkun, Yao Chen, Zhang Ping, Li Dong