Final ID: P1028
Prospective associations of optimism and cynicism with Life’s Essential 8: The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: Hostility and Optimism are traits known to be associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, important gaps remain in understanding the behavioral and biological mechanisms of these associations among multi-ethnic midlife women transitioning through menopause. We aim to assess the associations of optimism and cynicism with Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) and its components.
Methods: Participants were from the SWAN study, a multi-ethnic longitudinal study of the menopause transition. Optimism and cynicism were assessed at baseline and visit 1 via the Life Orientation Test (0[low]-18[high]) and the Cook-Medley Cynicism scale (0 [low] – 13 [high]), respectively. The total and component-specific LE8 scores (0[worst]– 100[best]), including dietary health, physical activity, sleep quality, nicotine exposure, blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids and body mass index (BMI), were measured 5 years after baseline. Linear regression models adjusting for demographics and menopause related variables (listed in figure) were used to test the associations of quartiles of optimism or hostility in relation with each LE8 outcome separately.
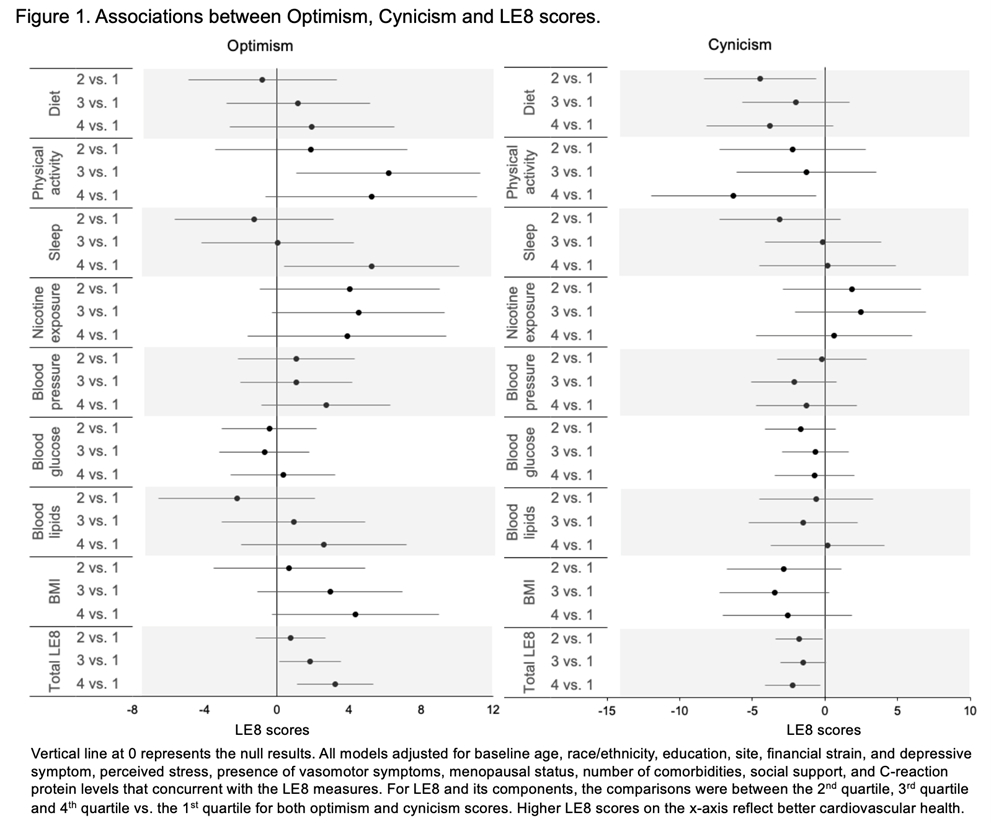
Results: A total of 1,907 women (mean (SD) baseline age: 45.9 (2.7) years; 48% White, 27%% Black, 9% Chinese, 7% Hispanics, 10% Japanese) with available data on main predictors and outcomes were included in the analysis. Compared women with the lowest quartile of the optimism scores, women in the highest quartile had 3.3 (95% CI: 1.1-5.3) points higher total LE8 scores (p-trend= 0.0005). Conversely, women in the highest quartile of hostility had 2.2 (0.4-4.1) points lower total LE8 scores (p-trend= 0.075) than women with the lowest quartile of hostility. Of the 8 components, higher optimism scores were associated with better sleep and physical activity scores, whereas higher hostility scores were associated with lower physical activity and diet scores, Figure 1. An analysis accounted for both traits together showed similar results compared to the analysis of the two traits separately.
Conclusion: Optimism was positively associated with total LE8 scores, while cynicism was negatively associated with total LE8 scores. Optimism and cynicism play more important roles in health behavior components than health measures components.
Supported by NIH/DHHS {Grants U01NR004061; U01AG012505, U01AG012535, U01AG012531, U01AG012539, U01AG012546, U01AG012553, U01AG012554, U01AG012495, and U19AG063720}.
Methods: Participants were from the SWAN study, a multi-ethnic longitudinal study of the menopause transition. Optimism and cynicism were assessed at baseline and visit 1 via the Life Orientation Test (0[low]-18[high]) and the Cook-Medley Cynicism scale (0 [low] – 13 [high]), respectively. The total and component-specific LE8 scores (0[worst]– 100[best]), including dietary health, physical activity, sleep quality, nicotine exposure, blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids and body mass index (BMI), were measured 5 years after baseline. Linear regression models adjusting for demographics and menopause related variables (listed in figure) were used to test the associations of quartiles of optimism or hostility in relation with each LE8 outcome separately.
Results: A total of 1,907 women (mean (SD) baseline age: 45.9 (2.7) years; 48% White, 27%% Black, 9% Chinese, 7% Hispanics, 10% Japanese) with available data on main predictors and outcomes were included in the analysis. Compared women with the lowest quartile of the optimism scores, women in the highest quartile had 3.3 (95% CI: 1.1-5.3) points higher total LE8 scores (p-trend= 0.0005). Conversely, women in the highest quartile of hostility had 2.2 (0.4-4.1) points lower total LE8 scores (p-trend= 0.075) than women with the lowest quartile of hostility. Of the 8 components, higher optimism scores were associated with better sleep and physical activity scores, whereas higher hostility scores were associated with lower physical activity and diet scores, Figure 1. An analysis accounted for both traits together showed similar results compared to the analysis of the two traits separately.
Conclusion: Optimism was positively associated with total LE8 scores, while cynicism was negatively associated with total LE8 scores. Optimism and cynicism play more important roles in health behavior components than health measures components.
Supported by NIH/DHHS {Grants U01NR004061; U01AG012505, U01AG012535, U01AG012531, U01AG012539, U01AG012546, U01AG012553, U01AG012554, U01AG012495, and U19AG063720}.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Are Associated with Incident Peripheral Artery Disease, Results from the Women’s Health Initiative.
Jackson Elizabeth, Leblanc Erin, Haring Bernhard, Harrington Laura, Allison Matthew, Eaton Charles, Lamonte Michael, Hovey Kathleen, Andrews Chris, Wells Gretchen, Manson Joann, Levitan Emily, Spracklen Cassandra, Wild Robert
Assessing Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding the American Heart Association’s Framework for Cardiovascular Health in PediatricsOrtiz Robin, Chan Debra, Nita Abigail, Heffron Sean, Nagpal Nikita, Duh-leong Carol