Final ID: P1137
The associations between maternal cardiovascular health scores during pregnancy and growth status of 0-2 years old infants: A birth cohort study
Abstract Body: Objective: Many maternal factors during pregnancy have been suggested to influence the physical development of offspring, while the overall effects haven’t been comprehensively evaluated. We aim to revise the Cardiovascular Health (CVH) metrics for pregnant women, a composite health indicator recommended and updated by the American Heart Association in 2022, and to explore its association with growth status within age 2 years based on a birth cohort.
Methods: Pregnant women in 20-28 weeks of gestation were recruited in Guangzhou, China, from 2017 to 2018, and their offspring were followed up until 2 years old. Maternal behavioral factors were collected by standardized questionnaires, including diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure, and sleep. Maternal biochemical data were extracted from medical records, including weight, blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipid. Higher scores indicating better health (ranging from 0 to 100), three of the eight metrics were specifically adapted for pregnant women. Pre-pregnancy BMI and pregnancy weight gain were used to evaluate weight status. The Chinese Healthy Diet Index and the standard of the Chinese Guidelines for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus were applied to assess diet and blood glucose. Infants’ length and weight were repeatedly measured at 1, 3, 6, 8, 12, 18, and 24 months, and weight-for-length z-scores (WAZ), length-for-age z-scores (LAZ), body mass index z-scores (BAZ), and weight-for-age z-scores (WLZ) were calculated. The generalized estimating equation was conducted to explore the association between maternal CVH scores and infants’ growth status.
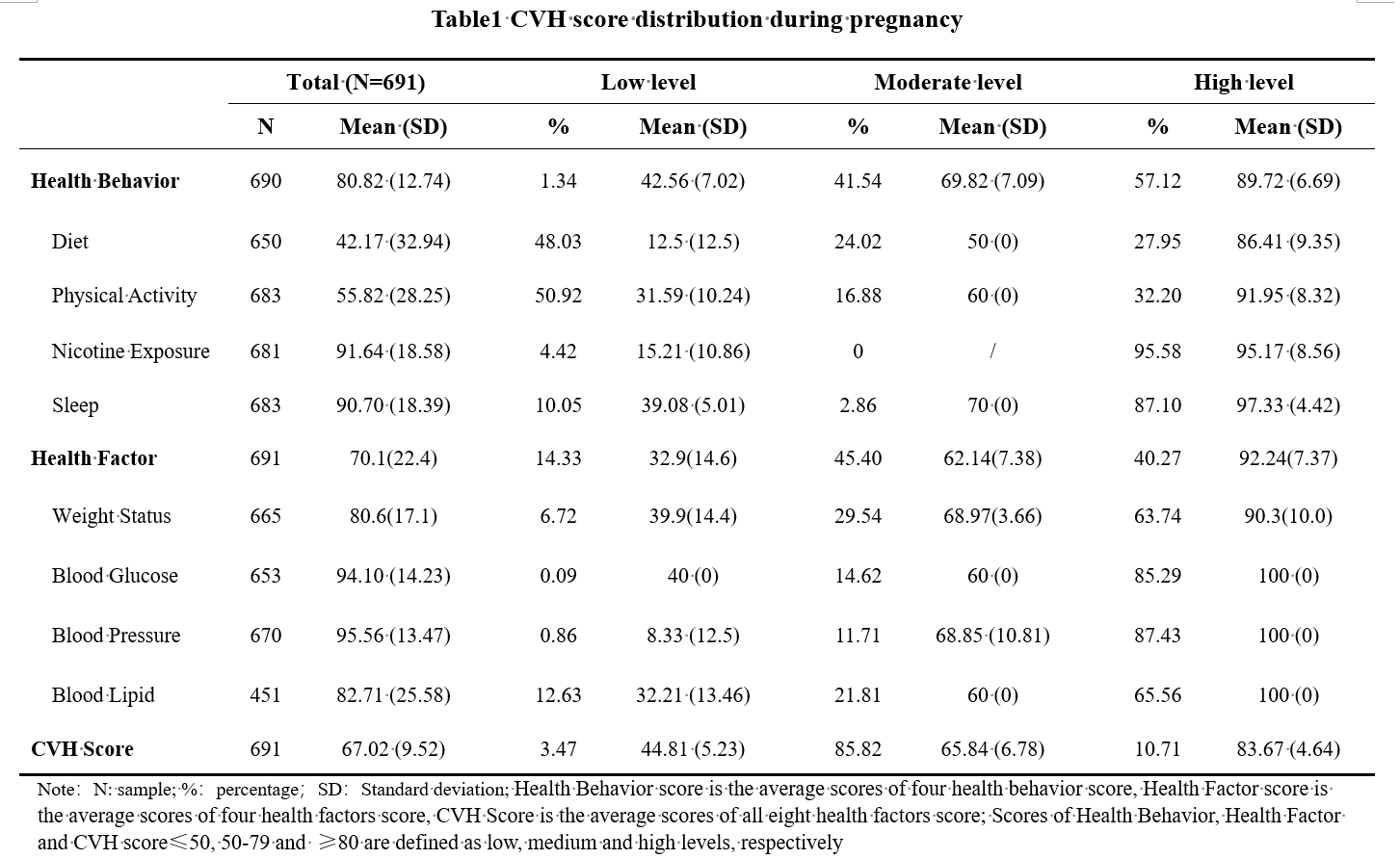
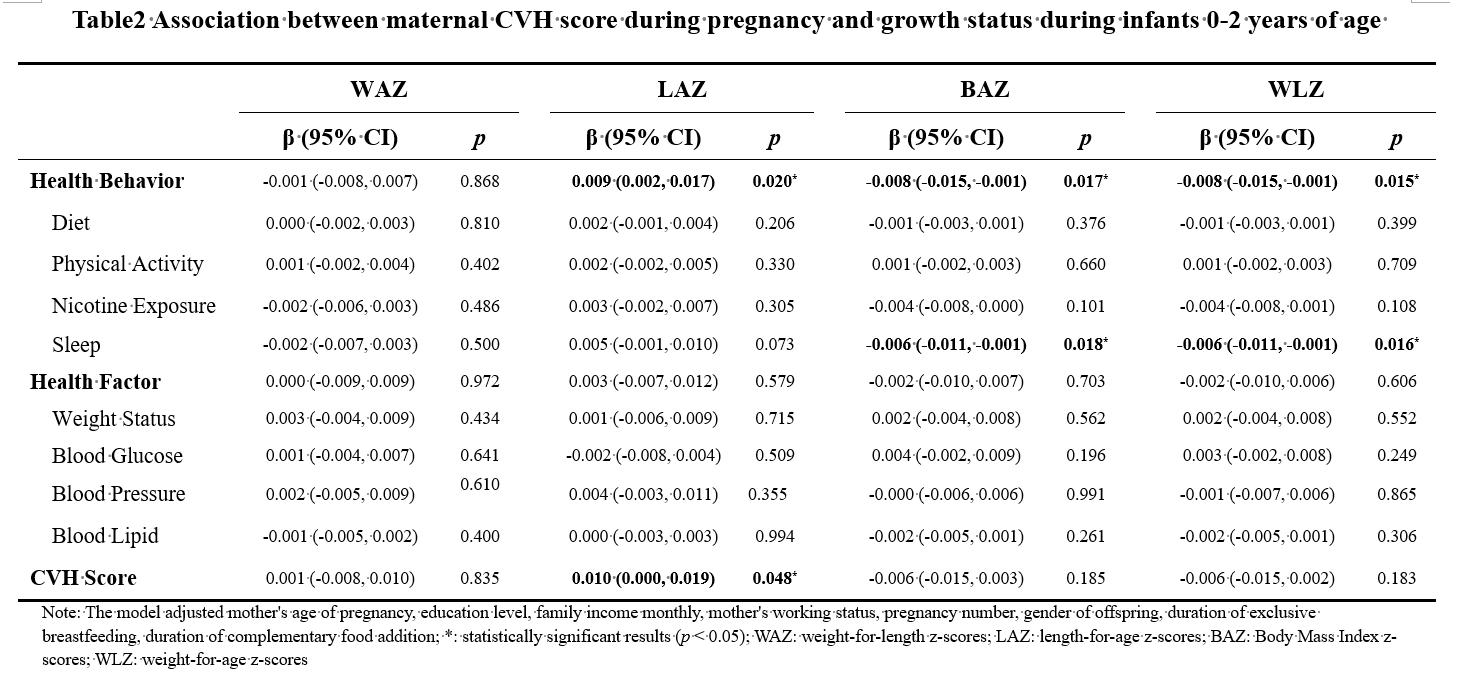
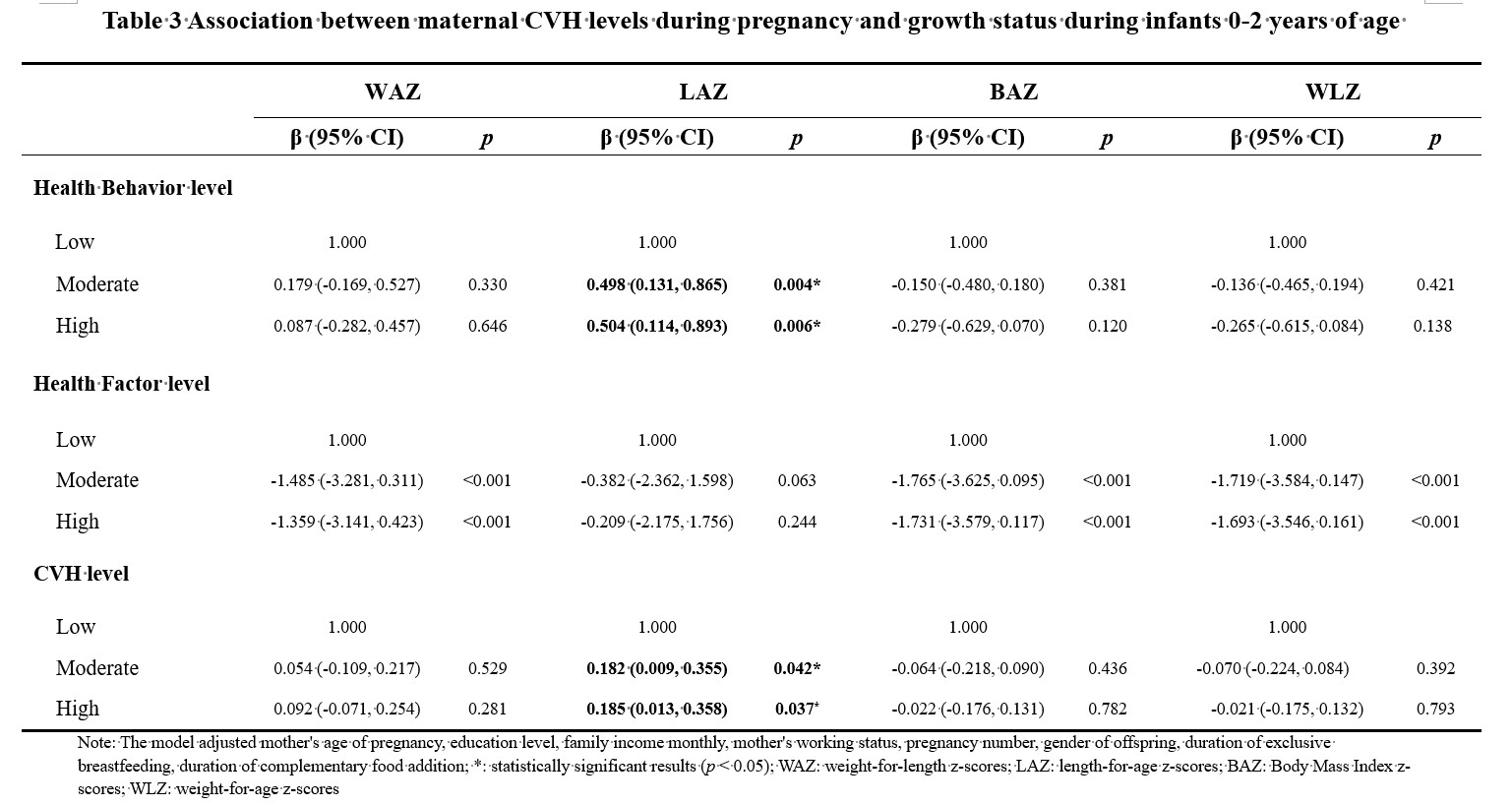
Results: In 691 mother-child pairs, the average of CVH score was 67.02±9.52, with diet scoring the lowest (42.17±32.94). Approximately 3.47%, 85.82%, and 10.71% of mothers scored low (≤50), moderate (50-79), and high (≥80) in CVH levels, respectively. The CVH and health factor scores were positively correlated with family monthly income. Higher prenatal health behaviors and CVH scores were associated with increased LAZ, and health behavior, especially in sleep, was negatively associated with BAZ and WLZ of infants.
Conclusion: This revised CVH score indicated a moderate overall health status for pregnant women, with dietary health warranting further improvement. Priority should be given to modifiable health behaviors during pregnancy, which showed a stronger and more stable association with the infant's physical growth.
Methods: Pregnant women in 20-28 weeks of gestation were recruited in Guangzhou, China, from 2017 to 2018, and their offspring were followed up until 2 years old. Maternal behavioral factors were collected by standardized questionnaires, including diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure, and sleep. Maternal biochemical data were extracted from medical records, including weight, blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipid. Higher scores indicating better health (ranging from 0 to 100), three of the eight metrics were specifically adapted for pregnant women. Pre-pregnancy BMI and pregnancy weight gain were used to evaluate weight status. The Chinese Healthy Diet Index and the standard of the Chinese Guidelines for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus were applied to assess diet and blood glucose. Infants’ length and weight were repeatedly measured at 1, 3, 6, 8, 12, 18, and 24 months, and weight-for-length z-scores (WAZ), length-for-age z-scores (LAZ), body mass index z-scores (BAZ), and weight-for-age z-scores (WLZ) were calculated. The generalized estimating equation was conducted to explore the association between maternal CVH scores and infants’ growth status.
Results: In 691 mother-child pairs, the average of CVH score was 67.02±9.52, with diet scoring the lowest (42.17±32.94). Approximately 3.47%, 85.82%, and 10.71% of mothers scored low (≤50), moderate (50-79), and high (≥80) in CVH levels, respectively. The CVH and health factor scores were positively correlated with family monthly income. Higher prenatal health behaviors and CVH scores were associated with increased LAZ, and health behavior, especially in sleep, was negatively associated with BAZ and WLZ of infants.
Conclusion: This revised CVH score indicated a moderate overall health status for pregnant women, with dietary health warranting further improvement. Priority should be given to modifiable health behaviors during pregnancy, which showed a stronger and more stable association with the infant's physical growth.
More abstracts on this topic:
Changes in Cardiovascular Health in Midlife Following a Pregnancy Complicated by Preeclampsia and/or Placental Maternal Vascular Malperfusion Lesions
Kozai Andrea, Gandley Robin, Countouris Malamo, Catov Janet
Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior and Risks of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Postmenopausal Cancer Survivors: The Women’s Health Accelerometry CollaborationHyde Eric, Stefanick Marcia, Skiba Meghan, Crane Tracy, Lee I-min, Lacroix Andrea, Bandoli Gretchen, Zou Jingjing, Crespo Noe, Parada Humberto, Evenson Kelly, Lamonte Michael, Nguyen Steve, Howard Annie Green