Final ID: P2090
Comparison of Medicare Claims Recorded and Surveillance Identified Myocardial Infarction in the Strong Heart Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: The Strong Heart Study (SHS) is a cohort study of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in American Indians. Center for Medicare and Medicaid Service (CMS) data may improve CVD outcome capture.
Hypothesis: Participants with myocardial infarction (MI) events captured in CMS will align with those identified in SHS morbidity and mortality (M&M) surveillance.
Methods: CMS data were available from 2010-2021 for 2,144 SHS participants. A CMS-identified MI event was defined as meeting the Chronic Conditions Data Warehouse (CCW) claims criteria (at least one inpatient claim with an MI ICD-9 or ICD-10 diagnosis code in first or second position) during this timeframe. SHS MI and coronary heart disease (CHD) events were identified by medical chart review, adjudicated by physicians, and classified as definite, possible, or probable (MI only). We defined SHS-identified MI as having a fatal or non-fatal definite MI event during 2010-2021. A summary table compared participants with SHS-identified and CMS-identified MI. Cohen’s kappa coefficient, sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (calculated using SHS as the gold standard) assessed diagnosis agreement.
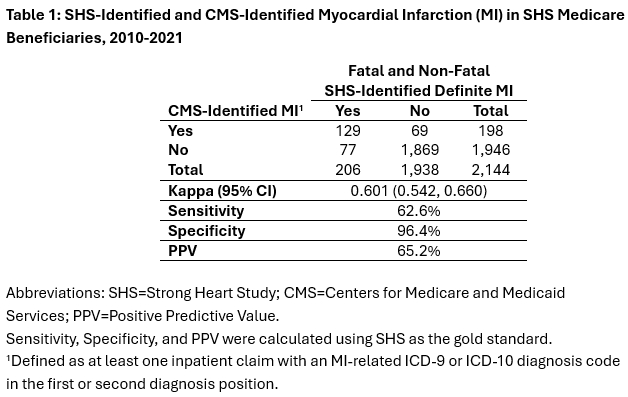
Results: We identified 206 participants with SHS-identified MI and 198 participants with CMS-identified MI. There was moderate agreement between SHS-identified and CMS-identified MI (kappa=0.601, 95% CI: 0.542, 0.660). About 63% of those with SHS-identified MI had a CMS-identified MI and 65% of those with CMS-identified MI had an SHS-identified MI. Among the 69 participants with only an SHS-identified MI, 40.3% had an outpatient MI code or an inpatient MI code in the third position or lower in CMS data. SHS M&M detected possible MI, probable MI, or any type of CHD event, excluding definite MI, in 39.1% of the 77 participants with only a CMS-identified MI.
Conclusions: Moderate agreement was observed between SHS definite MI and CMS MI events. CMS data may complement the identification of MI events in M&M surveillance of prospective cohort studies such as the SHS.
Hypothesis: Participants with myocardial infarction (MI) events captured in CMS will align with those identified in SHS morbidity and mortality (M&M) surveillance.
Methods: CMS data were available from 2010-2021 for 2,144 SHS participants. A CMS-identified MI event was defined as meeting the Chronic Conditions Data Warehouse (CCW) claims criteria (at least one inpatient claim with an MI ICD-9 or ICD-10 diagnosis code in first or second position) during this timeframe. SHS MI and coronary heart disease (CHD) events were identified by medical chart review, adjudicated by physicians, and classified as definite, possible, or probable (MI only). We defined SHS-identified MI as having a fatal or non-fatal definite MI event during 2010-2021. A summary table compared participants with SHS-identified and CMS-identified MI. Cohen’s kappa coefficient, sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (calculated using SHS as the gold standard) assessed diagnosis agreement.
Results: We identified 206 participants with SHS-identified MI and 198 participants with CMS-identified MI. There was moderate agreement between SHS-identified and CMS-identified MI (kappa=0.601, 95% CI: 0.542, 0.660). About 63% of those with SHS-identified MI had a CMS-identified MI and 65% of those with CMS-identified MI had an SHS-identified MI. Among the 69 participants with only an SHS-identified MI, 40.3% had an outpatient MI code or an inpatient MI code in the third position or lower in CMS data. SHS M&M detected possible MI, probable MI, or any type of CHD event, excluding definite MI, in 39.1% of the 77 participants with only a CMS-identified MI.
Conclusions: Moderate agreement was observed between SHS definite MI and CMS MI events. CMS data may complement the identification of MI events in M&M surveillance of prospective cohort studies such as the SHS.
More abstracts on this topic:
3-Minute Heart Health App: A Feasibility Study
Abdulkarim Iya, Metzger Joseph, Stovitz Steven, Van't Hof Jeremy
Digital Patient Navigator Facilitates And Scales Patient Engagement with the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy AssociationSchmidlen Tara, Hayward Laura, Simmons Emilie, Morgan Elena, Montgomery Linda, Hadley Ross, Snir Moran, Salberg Lisa