Final ID: 033
Serum metabolite-based signatures of childhood cardiovascular risk factor burdens associate with subclinical cardiac structure in midlife: Findings from the Bogalusa Heart Study
Abstract Body: Introduction: Childhood cardiovascular risk factors (CVRF) are known to independently contribute to the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life. However, childhood data is often unavailable when assessing adult risk. While CVRFs significantly impact the metabolome, metabolomic signatures of childhood CVRF burdens have not been identified.
Hypothesis: This study aimed to identify metabolomics signatures reflecting cumulative childhood CVRF burden and assess their associations with subclinical cardiac structure in midlife.
Methods: This study included 1,068 participants from the Bogalusa Heart Study (BHS) who underwent untargeted serum metabolomics profiling in midlife and had repeated childhood (aged 4-17 years) measures of clinical CVRFs, including BMI, systolic blood pressure (SBP), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TGs), and glucose. The cumulative childhood burden of CVRFs was estimated as the area under the curve (AUC). Elastic net regression was used to construct metabolomic signatures for each childhood CVRF AUC, with 80% of the data used for training and 20% for testing. Associations were examined between metabolomic signatures of childhood CVRF AUCs and midlife subclinical cardiac structure, including left ventricular (LV) mass index (LVMI), relative wall thickness (RWT), and left ventricular geometry (LVG).
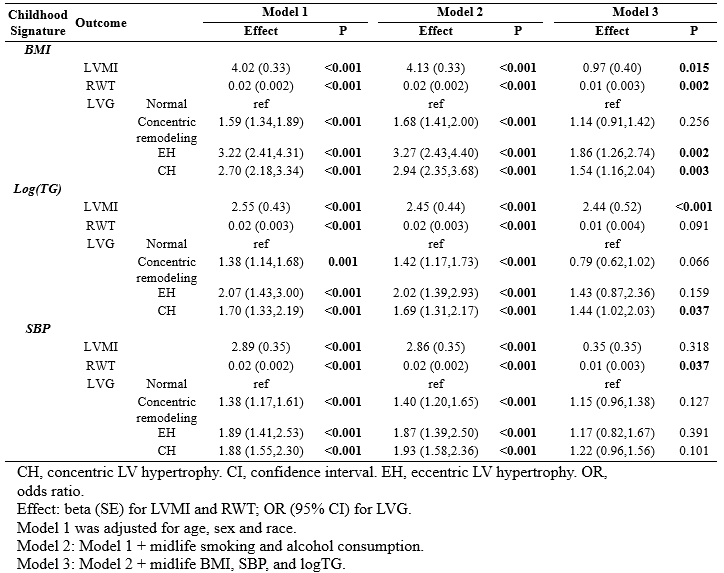
Results: Metabolomic signatures of AUCs for childhood BMI, SBP, LDL-C, TGs, and glucose consisted of 18, 2, 11, 20, and 40 metabolites, explaining 15%, 1%, 12%, 23% and 38% of the variance in the testing dataset, respectively (p<0.001, except SBP AUC signature: p=0.038). Consistent with prior findings in the BHS, AUCs for childhood BMI, SBP, and TGs were associated with midlife LVMI, RWT and LVG, after adjusting for demographic and lifestyle risk factors (data not shown). Increases in the metabolomic signatures for childhood AUCs of BMI, SBP, and TGs were also significantly associated with elevated LVMI, RWT, and higher odds of LVG (all p<0.001, Table). Notably, most associations for childhood BMI AUC remained significant after adjusting for midlife clinical measures, including known mediators of childhood burden's effect on adult LV changes (Table).
Conclusion: Metabolite-based signatures capture childhood CVRF burden and are associated with midlife changes in cardiac structure, independent of adult exposure. These signatures show potential as surrogates when childhood exposure data is unavailable.
Hypothesis: This study aimed to identify metabolomics signatures reflecting cumulative childhood CVRF burden and assess their associations with subclinical cardiac structure in midlife.
Methods: This study included 1,068 participants from the Bogalusa Heart Study (BHS) who underwent untargeted serum metabolomics profiling in midlife and had repeated childhood (aged 4-17 years) measures of clinical CVRFs, including BMI, systolic blood pressure (SBP), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TGs), and glucose. The cumulative childhood burden of CVRFs was estimated as the area under the curve (AUC). Elastic net regression was used to construct metabolomic signatures for each childhood CVRF AUC, with 80% of the data used for training and 20% for testing. Associations were examined between metabolomic signatures of childhood CVRF AUCs and midlife subclinical cardiac structure, including left ventricular (LV) mass index (LVMI), relative wall thickness (RWT), and left ventricular geometry (LVG).
Results: Metabolomic signatures of AUCs for childhood BMI, SBP, LDL-C, TGs, and glucose consisted of 18, 2, 11, 20, and 40 metabolites, explaining 15%, 1%, 12%, 23% and 38% of the variance in the testing dataset, respectively (p<0.001, except SBP AUC signature: p=0.038). Consistent with prior findings in the BHS, AUCs for childhood BMI, SBP, and TGs were associated with midlife LVMI, RWT and LVG, after adjusting for demographic and lifestyle risk factors (data not shown). Increases in the metabolomic signatures for childhood AUCs of BMI, SBP, and TGs were also significantly associated with elevated LVMI, RWT, and higher odds of LVG (all p<0.001, Table). Notably, most associations for childhood BMI AUC remained significant after adjusting for midlife clinical measures, including known mediators of childhood burden's effect on adult LV changes (Table).
Conclusion: Metabolite-based signatures capture childhood CVRF burden and are associated with midlife changes in cardiac structure, independent of adult exposure. These signatures show potential as surrogates when childhood exposure data is unavailable.
More abstracts on this topic:
Estimating Resting Metabolic Rate in Youth with Obesity and Elevated Blood Pressure
Moore Jafar-i, Vizthum Diane, Brady Tammy
Comparative Analysis of Children’s Persistence in a Lifestyle Modification Program and Body Mass Index Z-Score Changes According to the Access to a Family Grant Program at a Pediatric Obesity Management ClinicCyrenne-dussault Marie, St-pierre Julie, Drouin-chartier Jean-philippe