Final ID: 057
Associations between Body Mass Index, Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Midlife: A Mediation analysis in the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes (HAPO) Study
Abstract Body: INTRODUCTION: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in females globally. Sex-specific CVD risk factors such as adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) are on the rise. Pre-pregnancy obesity is a key modifiable risk factor for both APOs and CVD. However, whether APOs mediate the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and midlife CVD risk factors is unclear.
PURPOSE: Determine the extent to which the associations between pre-pregnancy BMI and CVD risk factors 10-14 years after delivery are mediated by APOs.
METHODS: Participants ≥ 18 years enrolled at 28 weeks’ gestation (range: 24-32 weeks) in the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes (HAPO) study without pre-pregnancy hypertension or diabetes were included in analyses. Counterfactual causal mediation analysis assessed whether gestational diabetes (GDM) and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) mediated associations between self-reported pre-pregnancy BMI and CVD risk factors 10-14 years after delivery. Missing baseline data were computed using multiple imputation by chained equations to create 10 imputed datasets. The results from each imputed dataset were combined using Rubin rules. Covariates included maternal and gestational age, parity, field center, alcohol and smoking status in pregnancy, and fetal sex.
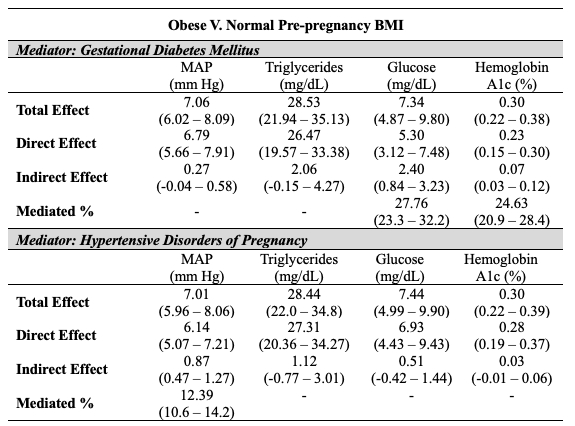
RESULTS: Participants (N = 4,269) were 30.0±5.6 years and 10.6% had a BMI≥30.0 kg/m2. During the HAPO pregnancy, GDM complicated 13.8% and HDP 10.7% of pregnancies. Compared to those with a pre-pregnancy of BMI of 18.5-24.9 kg/m2, those with a BMI ≥30.0 kg/m2 had a greater mean arterial pressure (7.1 mmHg; 95% CI: 6.0 - 8.1), triglyceride (28.5 mg/dL; 95% CI; 21.9 – 35.1), glucose (7.4 mg/dL; 95% CI: 4.9 – 9.8), and hemoglobin A1c (0.3%; 95% CI: 0.2 – 0.4) levels at midlife. Among indivdiuals with a pre-pregnancy BMI≥30.0 kg/m2, GDM mediated a statistically significant portion of associations with fasting glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c whereas HDP mediated the association with mean arterial pressure only (Table).
CONCLUSIONS: In a multinational cohort of pregnant individuals, these findings suggest that APOs do not mediate a majority of the association between obesity and CVD risk factors in mid-life. Prioritizing weight management earlier in the life course before pregnancy may support maternal and future cardiovascular health.
PURPOSE: Determine the extent to which the associations between pre-pregnancy BMI and CVD risk factors 10-14 years after delivery are mediated by APOs.
METHODS: Participants ≥ 18 years enrolled at 28 weeks’ gestation (range: 24-32 weeks) in the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes (HAPO) study without pre-pregnancy hypertension or diabetes were included in analyses. Counterfactual causal mediation analysis assessed whether gestational diabetes (GDM) and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) mediated associations between self-reported pre-pregnancy BMI and CVD risk factors 10-14 years after delivery. Missing baseline data were computed using multiple imputation by chained equations to create 10 imputed datasets. The results from each imputed dataset were combined using Rubin rules. Covariates included maternal and gestational age, parity, field center, alcohol and smoking status in pregnancy, and fetal sex.
RESULTS: Participants (N = 4,269) were 30.0±5.6 years and 10.6% had a BMI≥30.0 kg/m2. During the HAPO pregnancy, GDM complicated 13.8% and HDP 10.7% of pregnancies. Compared to those with a pre-pregnancy of BMI of 18.5-24.9 kg/m2, those with a BMI ≥30.0 kg/m2 had a greater mean arterial pressure (7.1 mmHg; 95% CI: 6.0 - 8.1), triglyceride (28.5 mg/dL; 95% CI; 21.9 – 35.1), glucose (7.4 mg/dL; 95% CI: 4.9 – 9.8), and hemoglobin A1c (0.3%; 95% CI: 0.2 – 0.4) levels at midlife. Among indivdiuals with a pre-pregnancy BMI≥30.0 kg/m2, GDM mediated a statistically significant portion of associations with fasting glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c whereas HDP mediated the association with mean arterial pressure only (Table).
CONCLUSIONS: In a multinational cohort of pregnant individuals, these findings suggest that APOs do not mediate a majority of the association between obesity and CVD risk factors in mid-life. Prioritizing weight management earlier in the life course before pregnancy may support maternal and future cardiovascular health.
More abstracts on this topic:
Alloprevotella rava Alleviates Atherosclerosis through a secondary bile acid
Feng Weiqi, Feng Ruijia, Peng Guiyan, Long Ting, Yang Wenchao, Chang Guangqi, Huang Kan
Association of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes with Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Factors in a Diverse CohortWoo Victoria, Folck Bruce, Tucker Lue-yen, Naderi Sahar