Final ID: P3128
Statins and Insulin Resistance in a Pediatric Preventive Cardiology Practice
Abstract Body: Introduction: Statins are prescribed to lower LDL-C in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and other dyslipidemias that accelerate atherosclerosis. Associations between statin use and type 2 diabetes mellitus are reported in adults; there are scant studies in the pediatric literature.
Objective: To determine if statin use is associated with higher HbA1C and HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance) in children prescribed statins compared to non-statin users in a large pediatric preventive cardiology practice.
Methods: Clinical data for patients prescribed statins were analyzed from 2003 through 2024, comparing HbA1C and HOMA-IR, and other characteristics at baseline, early follow-up (6 months) and late follow-up (3 years) post-statin initiation to statin non-users. Linear regression models were used to analyze baseline differences in HbA1C and HOMA-IR in the statin vs. non-statin groups, adjusted for age, sex, and BMI. A linear mixed effect model was used to analyze the longitudinal outcomes of HbA1C and HOMA-IR in the statin vs. non-statin groups.
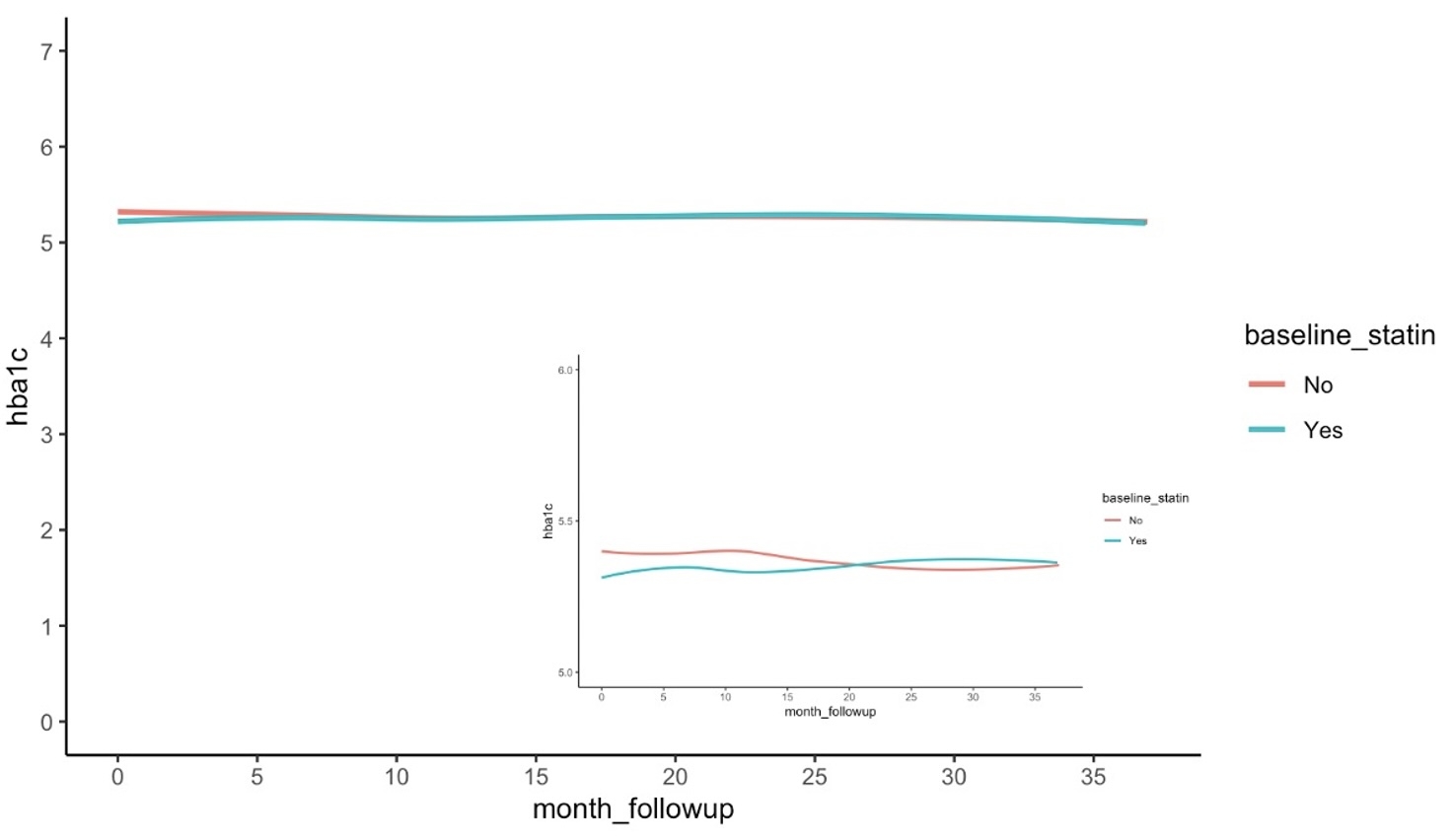
Results: In 757 patients with available data (406 prescribed statins), 51.5% were female with a mean age of 13.8 years at baseline. HbA1C and HOMA-IR were lower at baseline in the statin group vs. non-statin group (5.22% vs. 5.32% and 2.56 vs. 3.78 respectively, p <0.001). At 6 months post-statin initiation, HOMA-IR increased by 0.2 units more per month in the statin group than the non-statin group (p=0.03); the HbA1C rose by 0.01% more per month in the statin vs. non-statin group, approaching statistical significance (p=0.05). At 3 years post-statin initiation, the rate of change in HOMA-IR did not differ between the groups (p=0.78). However, at 3 years, the HbA1C rose by 0.0053% more per month in the statin group vs. non-statin group (p<0.001).
Conclusion: In this large clinical pediatric cohort spanning over 20 years, there was a higher rate of rise of HOMA-IR early on (6 months) in those prescribed statins vs. statin non-users; after 3 years, the rate of rise of HbA1C was higher in the statin group, but HOMA-IR did not differ. Differences in HbA1C and HOMA-IR between the statin and non-statin groups, while statistically significant, were small and not likely clinically meaningful; values were more strongly driven by BMI category. Further research is needed; in the interim, clinical monitoring of HbA1C in children prescribed statins may be warranted.
Objective: To determine if statin use is associated with higher HbA1C and HOMA-IR (homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance) in children prescribed statins compared to non-statin users in a large pediatric preventive cardiology practice.
Methods: Clinical data for patients prescribed statins were analyzed from 2003 through 2024, comparing HbA1C and HOMA-IR, and other characteristics at baseline, early follow-up (6 months) and late follow-up (3 years) post-statin initiation to statin non-users. Linear regression models were used to analyze baseline differences in HbA1C and HOMA-IR in the statin vs. non-statin groups, adjusted for age, sex, and BMI. A linear mixed effect model was used to analyze the longitudinal outcomes of HbA1C and HOMA-IR in the statin vs. non-statin groups.
Results: In 757 patients with available data (406 prescribed statins), 51.5% were female with a mean age of 13.8 years at baseline. HbA1C and HOMA-IR were lower at baseline in the statin group vs. non-statin group (5.22% vs. 5.32% and 2.56 vs. 3.78 respectively, p <0.001). At 6 months post-statin initiation, HOMA-IR increased by 0.2 units more per month in the statin group than the non-statin group (p=0.03); the HbA1C rose by 0.01% more per month in the statin vs. non-statin group, approaching statistical significance (p=0.05). At 3 years post-statin initiation, the rate of change in HOMA-IR did not differ between the groups (p=0.78). However, at 3 years, the HbA1C rose by 0.0053% more per month in the statin group vs. non-statin group (p<0.001).
Conclusion: In this large clinical pediatric cohort spanning over 20 years, there was a higher rate of rise of HOMA-IR early on (6 months) in those prescribed statins vs. statin non-users; after 3 years, the rate of rise of HbA1C was higher in the statin group, but HOMA-IR did not differ. Differences in HbA1C and HOMA-IR between the statin and non-statin groups, while statistically significant, were small and not likely clinically meaningful; values were more strongly driven by BMI category. Further research is needed; in the interim, clinical monitoring of HbA1C in children prescribed statins may be warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Approach to Manage Hypercholesterolemia: The Veterans Affairs Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement (VALOR-QI) Program
Djousse Luc, Leesch Tharen, Pena David, Gaziano Michael, Ward Rachel, Wellman Helen, Yel Nedim, Santos Abigail, Delgrande Jen, Fink Abigail, Colson Kristin, Pan Eddie
Association of County-Level Labor Force Participation During Childhood and Cardiovascular Health in Young AdulthoodArdehali Mariam, Shah Nilay, Gauen Abigail, Kershaw Kiarri, Zheng Veronica, Bolakale-rufai Ikeoluwapo, Goldman Noreen, Notterman Daniel, Lloyd-jones Donald, Allen Norrina