Final ID: Tu089
p21 Regulates Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Remodeling By Inhibition of Cardiomyocyte Endoreplication
Abstract Body: Background:
We previously discovered that a murine model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy had increased cardiomyocyte endoreplication and replication stress leading to increased DNA damage. Activation of DNA damage response pathways was associated with increased cardiomyocyte expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. However, the role of p21 on pathologic myocardial remodeling in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is poorly understood.
Methods:
We utilized a murine model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that is deficient in cardiac myosin binding protein 3 (Mybpc3-/-). We used murine models deficient in p21 (Cdkn1a-/-) or overexpressed p21 (Cdkn1aSUPER) to determine the role of p21 on hypertrophic remodeling. Heart structure and function were evaluated by echocardiography. Flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry were used to measure cardiomyocyte DNA content and ploidy. Proteomics and biochemical assays were utilized to identify p21 target proteins.
Results:
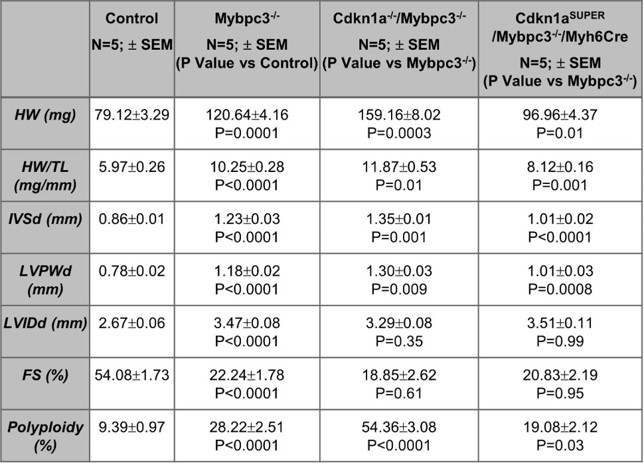
We observed that there was an increased p21 expression in Mybpc3-/- cardiomyocytes during the postnatal day 7 to 25 time interval. Elimination of p21 expression in Mybpc3-/- animals (Cdkn1a-/-/Mybpc3-/-) caused increased myocardial hypertrophy (Table 1). Conversely, selective overexpression of p21 in cardiomyocytes (Cdkn1aSUPER/Mybpc3-/-/Myh6Cre) led to reduced myocardial hypertrophy (Table 1). We discovered that isolated cardiomyocyte nuclei from Mybpc3-/- mice with reduced p21 had increased polyploidy whereas overexpression of cardiomyocyte p21 led to reduced cardiomyocyte polyploidy (Table 1). Using both proteomics and targeted assays we discovered that cardiomyocyte p21 was binding to key cycle regulatory proteins to inhibit cardiomyocyte endoreplication and hypertrophic growth.
Conclusions:
Collectively, our results show that induction of p21 in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy reduces cardiomyocyte growth by inhibiting endoreplication.
We previously discovered that a murine model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy had increased cardiomyocyte endoreplication and replication stress leading to increased DNA damage. Activation of DNA damage response pathways was associated with increased cardiomyocyte expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. However, the role of p21 on pathologic myocardial remodeling in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is poorly understood.
Methods:
We utilized a murine model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that is deficient in cardiac myosin binding protein 3 (Mybpc3-/-). We used murine models deficient in p21 (Cdkn1a-/-) or overexpressed p21 (Cdkn1aSUPER) to determine the role of p21 on hypertrophic remodeling. Heart structure and function were evaluated by echocardiography. Flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry were used to measure cardiomyocyte DNA content and ploidy. Proteomics and biochemical assays were utilized to identify p21 target proteins.
Results:
We observed that there was an increased p21 expression in Mybpc3-/- cardiomyocytes during the postnatal day 7 to 25 time interval. Elimination of p21 expression in Mybpc3-/- animals (Cdkn1a-/-/Mybpc3-/-) caused increased myocardial hypertrophy (Table 1). Conversely, selective overexpression of p21 in cardiomyocytes (Cdkn1aSUPER/Mybpc3-/-/Myh6Cre) led to reduced myocardial hypertrophy (Table 1). We discovered that isolated cardiomyocyte nuclei from Mybpc3-/- mice with reduced p21 had increased polyploidy whereas overexpression of cardiomyocyte p21 led to reduced cardiomyocyte polyploidy (Table 1). Using both proteomics and targeted assays we discovered that cardiomyocyte p21 was binding to key cycle regulatory proteins to inhibit cardiomyocyte endoreplication and hypertrophic growth.
Conclusions:
Collectively, our results show that induction of p21 in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy reduces cardiomyocyte growth by inhibiting endoreplication.
More abstracts on this topic:
A PROtein Signature of PlatelEt Reactivity (PROSPER) Associated with Cardiovascular Events
Hamo Carine, Muller Matthew, Luttrell-williams Elliot, Ruggles Kelly, Barrett Tessa, Berger Jeffrey
AI-enhanced Electrocardiographic Evaluation of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction and Outflow Tract Gradient in Hypertrophic CardiomyopathySangha Veer, Aminorroaya Arya, Dhingra Lovedeep, Pedroso Aline, Oikonomou Evangelos, Khera Rohan