Final ID: Mo060
SPEG mediates increased atrial fibrillation incidence in chronic kidney disease
Abstract Body: INTRODUCTION: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major public health problem. CKD is a risk factor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality due to the increased incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF). AF onset is known to be the consequence of cardiomyocyte intracellular calcium (Ca2+) mishandling where increased ryanodine receptor type 2 (RyR2) activity causes triggered activity. RyR2 activity is regulated by phosphorylation of serine 2367 (S2367) by the ‘striated muscle preferentially expressed protein’ (SPEG). Reduced RyR2 phosphorylation at S2367 increases the risk of AF. We hypothesized that changes in atrial SPEG underly the increased risk of AF in CKD patients.
METHODS: The experimental 5/6 nephrectomy model was used to mimic CKD disease in mice. AF inducibility was determined using intracardiac programmed electric stimulation. Echocardiography was used to analyze cardiac structure. RYR2 phosphorylation and SPEG levels were measured by western blotting. Intracellular Ca2+ dynamics were assessed by confocal microscopy.
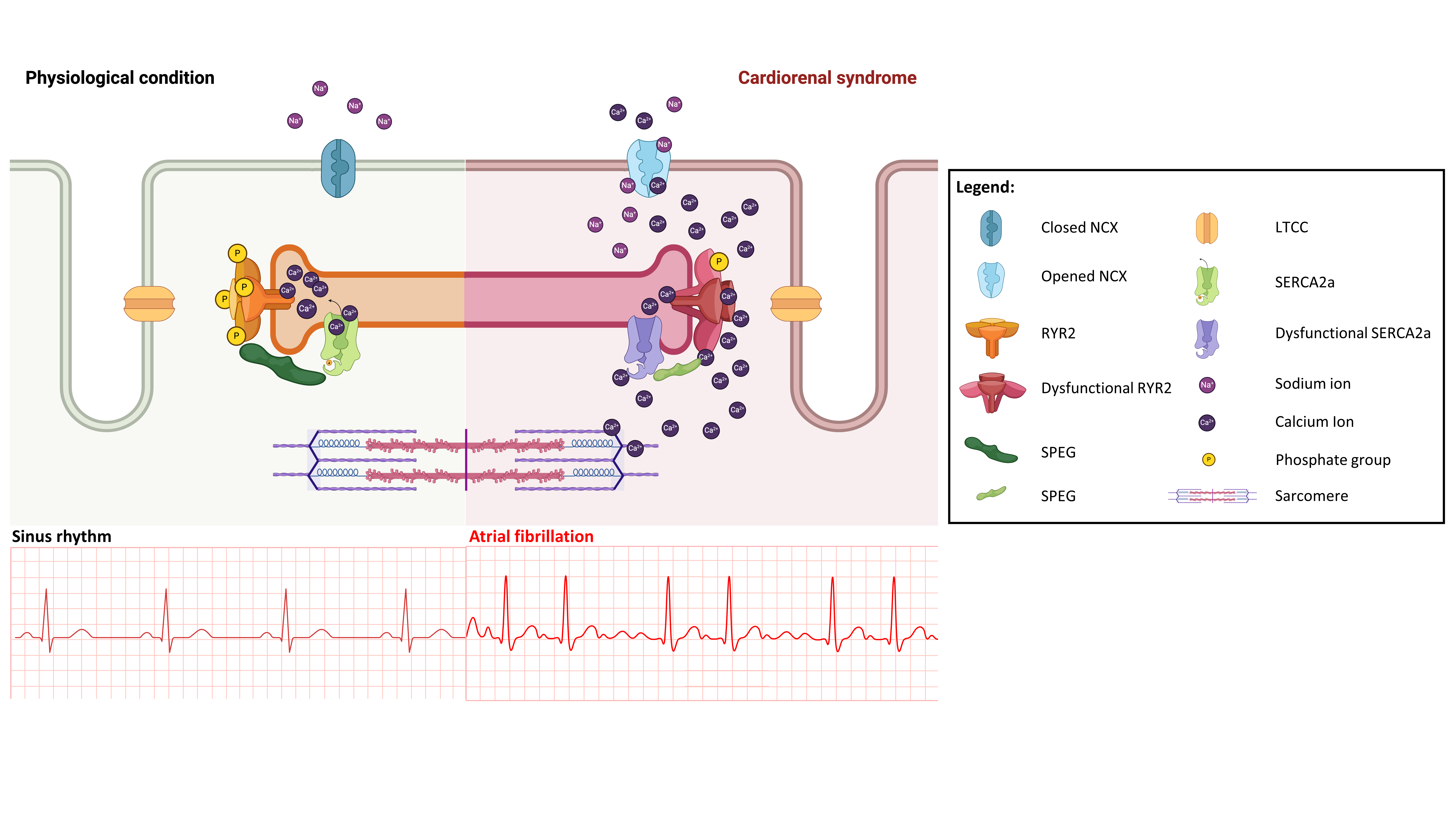
RESULTS: CKD mice showed increased serum phosphate (14.1±1.4 vs 9.3±0.4mg/dL; p<0.01), creatinine (0.4±0.1 vs 0.8±0.3 mg/dL; p<0.001) and urea (30.5±1.1 vs 20.9±0.4 mg/dL; p<0.001). AF incidence was 4-fold higher in CKD respect sham mice (60 vs 14.2%; p<0.05). CKD mice showed longer P waves (14.3±0.4 vs 12.5±0.3; p<0.01) and greater increase of left atrial size than Sham mice (35.0±7.5 vs 13.9±4.6; p<0.05). Ejection fraction was reduced in CKD mice after 6 weeks of CKD progression (57.9±0.6 vs 61.7±0.8%; p<0.001) while no changes were observed in Sham mice. SPEG levels were decreased in atria from CKD mice compared to sham (0.64±0.11 vs 1.19±0.13; p<0.05). RyR2 phosphorylation at S2367 was reduced in CKD mice atria (0.66±0.16 vs 1.25±0.26 in sham; p=0.098). Atrial cardiomyocytes from CKD mice exhibited altered Ca2+ handling, with decreased SERCA activity (p<0.05), increased spark-mediated diastolic Ca2+ leak (p<0.01) and increased NCX activity (p<0.05). Finally, CKD-induced AF onset was prevented in a mice with a mutation that mimics RYR2 phosphorylation at SPEG site (S2367D mice)
CONCLUSION: This study shows for the first time that SPEG levels are decreased in atria from CKD mice what induces increased RyR2 activity leading to increased AF incidence. By conserving RYR2 phosphorylation at Ser2367, CKD-induced AF was prevented. Thus, we propose SPEG as a possible therapeutic target to reduce the increased incidence of AF in CKD patients.
METHODS: The experimental 5/6 nephrectomy model was used to mimic CKD disease in mice. AF inducibility was determined using intracardiac programmed electric stimulation. Echocardiography was used to analyze cardiac structure. RYR2 phosphorylation and SPEG levels were measured by western blotting. Intracellular Ca2+ dynamics were assessed by confocal microscopy.
RESULTS: CKD mice showed increased serum phosphate (14.1±1.4 vs 9.3±0.4mg/dL; p<0.01), creatinine (0.4±0.1 vs 0.8±0.3 mg/dL; p<0.001) and urea (30.5±1.1 vs 20.9±0.4 mg/dL; p<0.001). AF incidence was 4-fold higher in CKD respect sham mice (60 vs 14.2%; p<0.05). CKD mice showed longer P waves (14.3±0.4 vs 12.5±0.3; p<0.01) and greater increase of left atrial size than Sham mice (35.0±7.5 vs 13.9±4.6; p<0.05). Ejection fraction was reduced in CKD mice after 6 weeks of CKD progression (57.9±0.6 vs 61.7±0.8%; p<0.001) while no changes were observed in Sham mice. SPEG levels were decreased in atria from CKD mice compared to sham (0.64±0.11 vs 1.19±0.13; p<0.05). RyR2 phosphorylation at S2367 was reduced in CKD mice atria (0.66±0.16 vs 1.25±0.26 in sham; p=0.098). Atrial cardiomyocytes from CKD mice exhibited altered Ca2+ handling, with decreased SERCA activity (p<0.05), increased spark-mediated diastolic Ca2+ leak (p<0.01) and increased NCX activity (p<0.05). Finally, CKD-induced AF onset was prevented in a mice with a mutation that mimics RYR2 phosphorylation at SPEG site (S2367D mice)
CONCLUSION: This study shows for the first time that SPEG levels are decreased in atria from CKD mice what induces increased RyR2 activity leading to increased AF incidence. By conserving RYR2 phosphorylation at Ser2367, CKD-induced AF was prevented. Thus, we propose SPEG as a possible therapeutic target to reduce the increased incidence of AF in CKD patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation
Ooka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki
Cardiac dysfunction in a preclinical model of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney DiseaseCarter Leah, Reyes Sanchez Ernesto, Vasquez Limeta Alejandra, Fiedler Matthew, Altamirano Francisco