Final ID: Mo012
Optimizing Mouse Models of Doxorubicin Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Anthracyclines such as doxorubicin (Dox) are effective chemotherapies that treat various cancers, including breast, lymphoma, and leukemia. While effective, their use is limited due to cardiac toxicity, leading to cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
Background:
Several Dox treatment regimens in mice have been reported in the literature, from acute high-dose models to chronic low-dose models. Many of these regimens cause fulminant cardiomyocyte apoptosis and heart failure within days, and they do not accurately recapitulate the human toxicity phenotype.
Objective:
Our goal was to identify a Dox dosing regimen in mice that causes the most consistent subacute/chronic cardiomyopathy, as seen in patients, with the least systemic toxicity.
Methods:
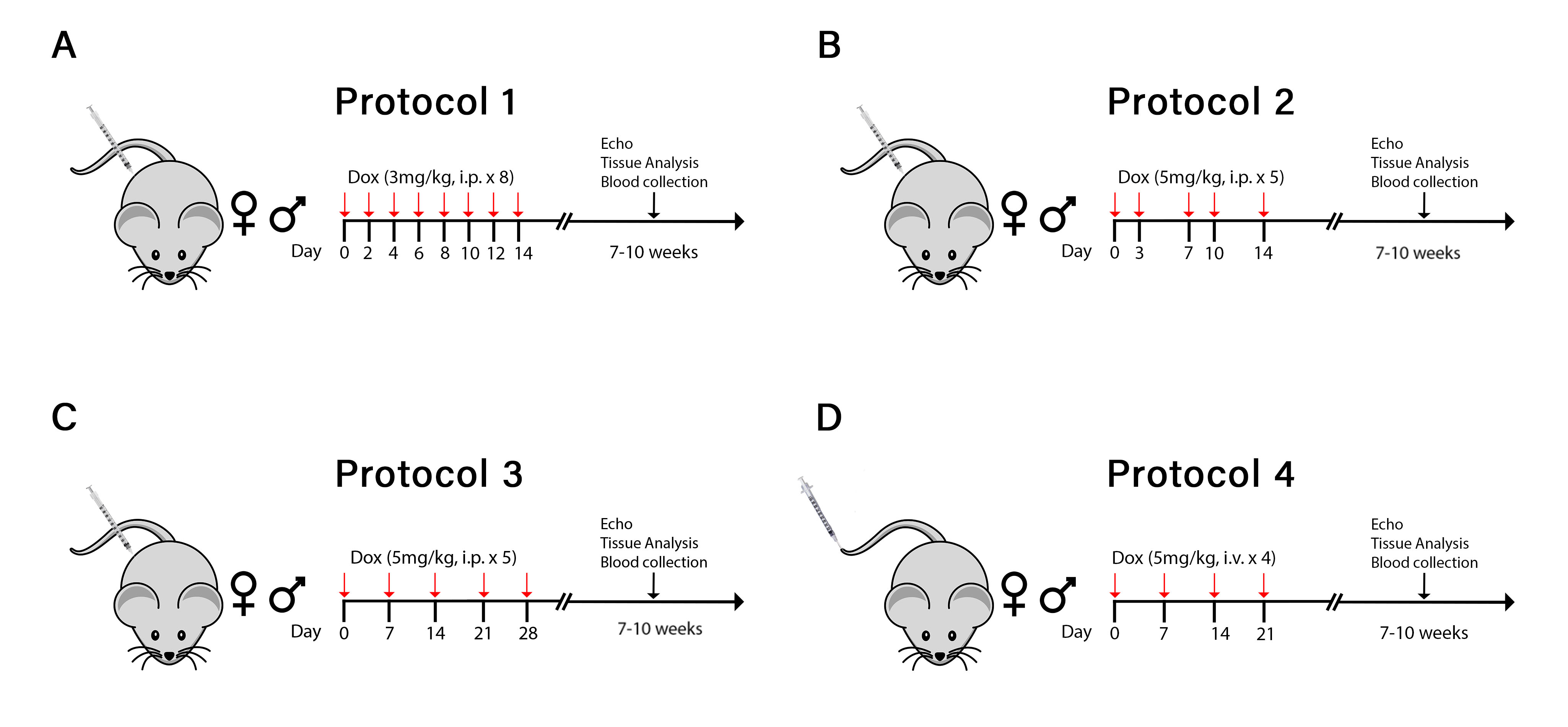
We administered four different Dox dosing regimens to C57BL/6N female and male mice, based on published protocols and our laboratory’s prior studies (Fig. 1):
#1: Dox 3mg/kg intraperitoneally (IP) every other day for two weeks (cumulative dose of 24mg/kg) or saline
#2: Dox 5mg/kg IP twice a week for two and a half weeks (cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) or saline
#3: Dox 5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks (cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) or saline
#4: Dox 5mg/kg intravenously (IV) once a week for four weeks (cumulative dose of 20mg/kg) or saline
Cardiac function was assessed after five to seven weeks by echocardiography, prior to sacrifice. Hearts and blood were isolated for molecular analyses. Regimens were compared using a one-way ANOVA and multiple comparisons analysis.
Results:
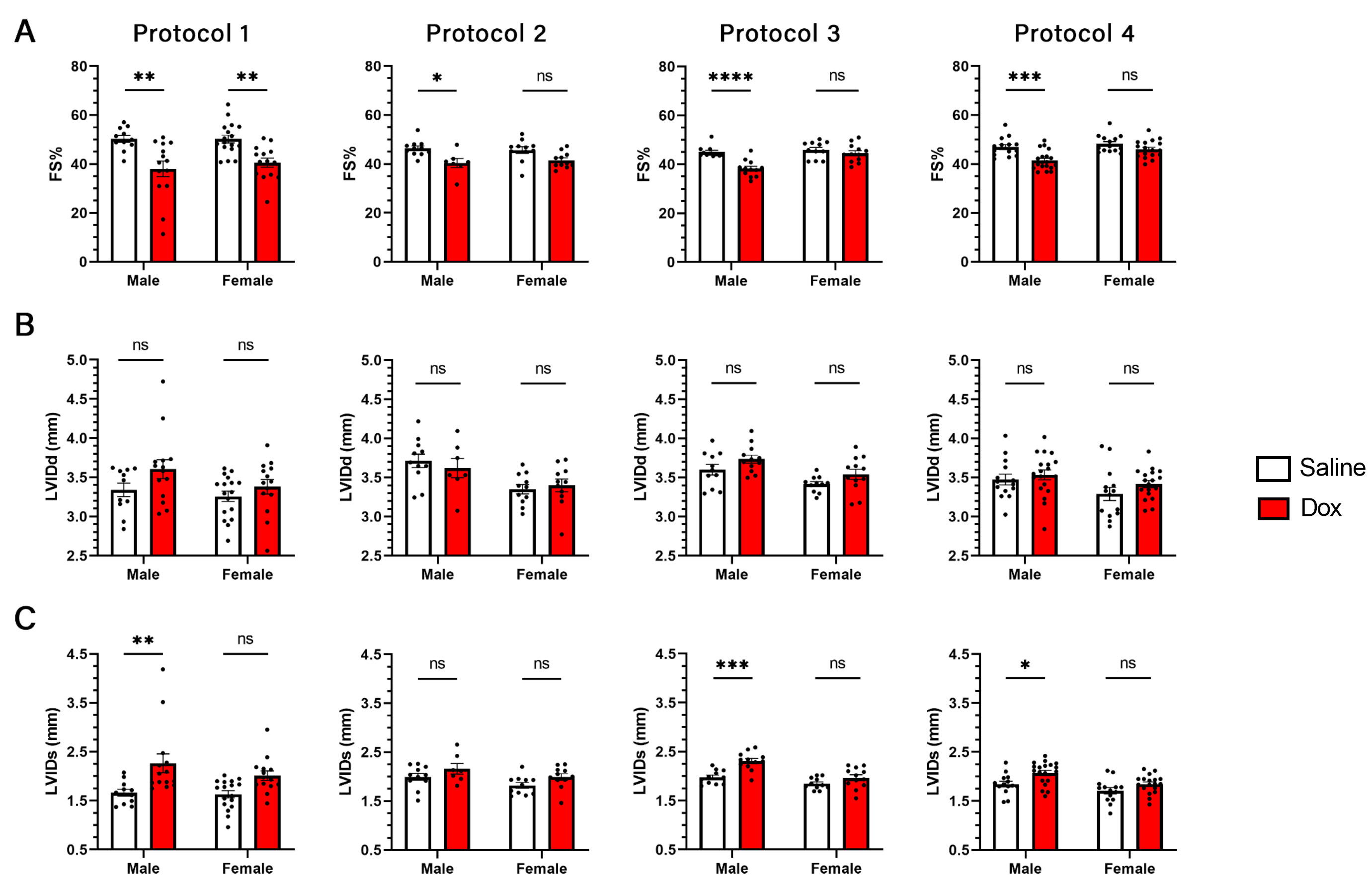
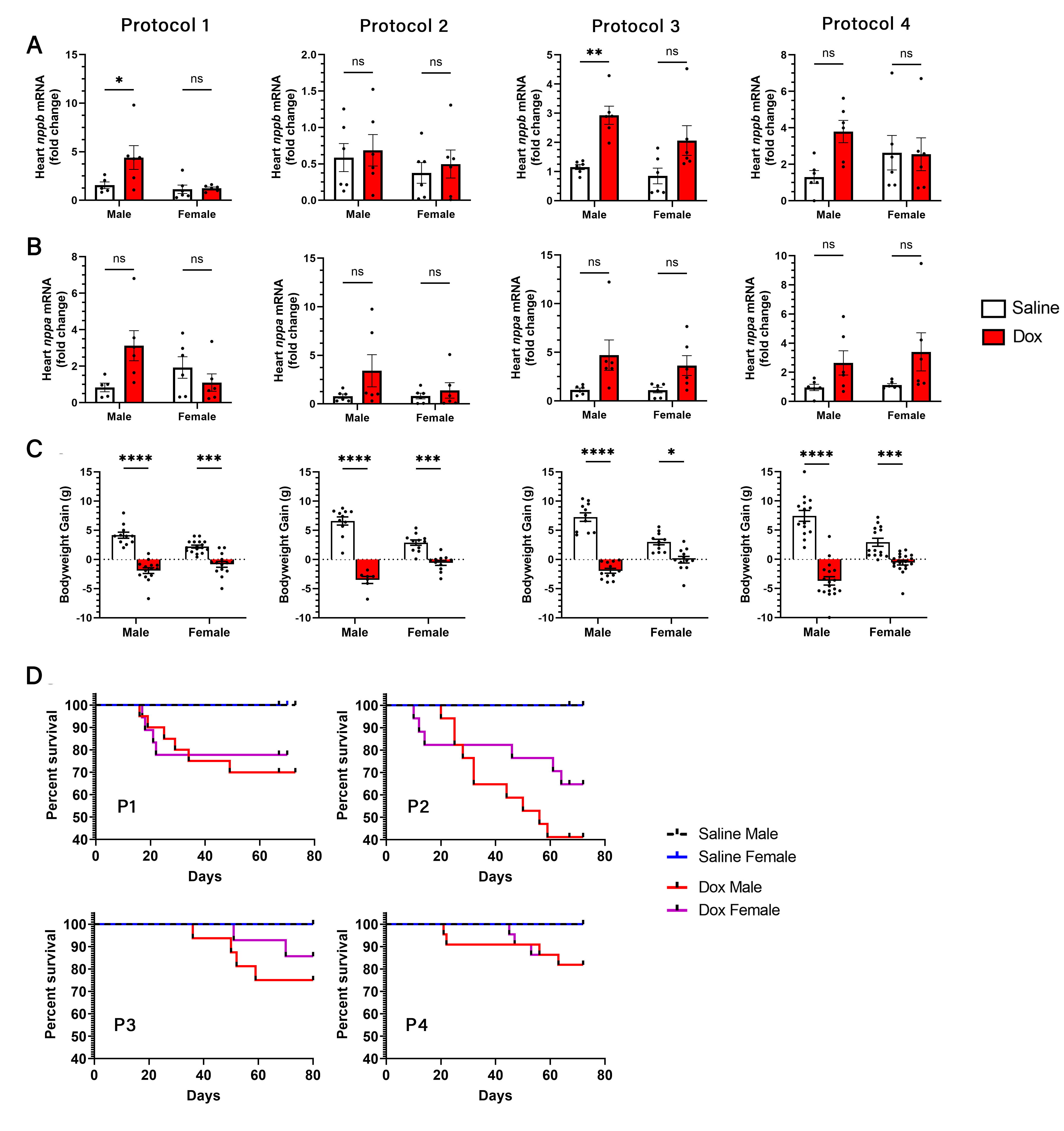
Protocol #3 (Dox 5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks; cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) demonstrated the most consistent difference in fractional shortening between male mice treated with saline compared to those treated with Dox, as assessed by echocardiography (Fig. 2). This protocol resulted in the lowest mortality, as well as the least amount of systemic toxicity (Fig. 3). Protocol #1 (Dox 3mg/kg IP every other day for two weeks; cumulative dose of 24mg/kg) was the only protocol that elicited a decline in fractional shortening in female mice treated with Dox compared to those treated with saline, as assessed by echocardiography.
Conclusion:
Going forward, protocol #3 (5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks) will be implemented as the standard dosing regimen in our laboratory. Ensuring consistency in cardiac phenotypes will allow us to better understand the effects of modulating cardioprotective pathways on the development of Dox cardiac toxicity.
Anthracyclines such as doxorubicin (Dox) are effective chemotherapies that treat various cancers, including breast, lymphoma, and leukemia. While effective, their use is limited due to cardiac toxicity, leading to cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
Background:
Several Dox treatment regimens in mice have been reported in the literature, from acute high-dose models to chronic low-dose models. Many of these regimens cause fulminant cardiomyocyte apoptosis and heart failure within days, and they do not accurately recapitulate the human toxicity phenotype.
Objective:
Our goal was to identify a Dox dosing regimen in mice that causes the most consistent subacute/chronic cardiomyopathy, as seen in patients, with the least systemic toxicity.
Methods:
We administered four different Dox dosing regimens to C57BL/6N female and male mice, based on published protocols and our laboratory’s prior studies (Fig. 1):
#1: Dox 3mg/kg intraperitoneally (IP) every other day for two weeks (cumulative dose of 24mg/kg) or saline
#2: Dox 5mg/kg IP twice a week for two and a half weeks (cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) or saline
#3: Dox 5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks (cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) or saline
#4: Dox 5mg/kg intravenously (IV) once a week for four weeks (cumulative dose of 20mg/kg) or saline
Cardiac function was assessed after five to seven weeks by echocardiography, prior to sacrifice. Hearts and blood were isolated for molecular analyses. Regimens were compared using a one-way ANOVA and multiple comparisons analysis.
Results:
Protocol #3 (Dox 5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks; cumulative dose of 25mg/kg) demonstrated the most consistent difference in fractional shortening between male mice treated with saline compared to those treated with Dox, as assessed by echocardiography (Fig. 2). This protocol resulted in the lowest mortality, as well as the least amount of systemic toxicity (Fig. 3). Protocol #1 (Dox 3mg/kg IP every other day for two weeks; cumulative dose of 24mg/kg) was the only protocol that elicited a decline in fractional shortening in female mice treated with Dox compared to those treated with saline, as assessed by echocardiography.
Conclusion:
Going forward, protocol #3 (5mg/kg IP once a week for five weeks) will be implemented as the standard dosing regimen in our laboratory. Ensuring consistency in cardiac phenotypes will allow us to better understand the effects of modulating cardioprotective pathways on the development of Dox cardiac toxicity.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Highly Selective and Orally Available HDAC6 Inhibitor, EKZ-102, Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction and Exercise Intolerance in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Elbatreek Mahmoud, Goodchild Traci, Lefer David, Evans Lauren, Richardson Thomas, James Rebecca, Schroeder Frederick, Wang Jianhong, Luterman Jim, Gilbert Tonya, Fisher Richard
Cardiomyocytes HIPK2 Regulates Myocardial Inflammation And Heart Function Through Purinergic SignalingSultan Tousif, Krishnamurthy Prasanna, Lal Hind, Umbarkar Prachi, Sethi Rohan, Toro Cora Angelica, Chen Yunxi, He Jin, Dubey Praveen, Zhang Qinkun, Xie Min