Final ID: Mo078
Identifying Genetic Determinants of Phytosterol Levels: A Genome-Wide Association and Meta-Analysis Study Unveils a New Locus Influencing Campesterol Serum Concentrations
Abstract Body: Background: Sitosterolemia, a rare inherited disorder, stems from mutations in the ABCG5/ABCG8 genes, which play a critical role in plant sterol transport. These genetic anomalies result in reduced phytosterol excretion, causing an accumulation in the body that can lead to serious health issues, such as premature coronary artery disease.
Hypothesis: The study aimed to uncover the genetic determinants influencing plant sterol levels within the Middle East/North Africa (MENA) population, focusing on individuals from Qatar. It hypothesized that unique genetic variations might influence these levels, contributing to the development of sitosterolemia.
Aims: To conduct the first genome-wide association study (GWAS) in the MENA region to identify genetic variants affecting plant sterol levels in the Qatari population, and to compare these findings with those from populations of European ancestry.
Methods: The study utilized the Metabolon platform for analyzing serum levels of β-sitosterol and campesterol, combined with genome sequence data from the Qatar Genome Program. A trans-ancestry meta-analysis compared our findings with those from a large European cohort, while conditional analysis helped identify specific single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with these sterols.
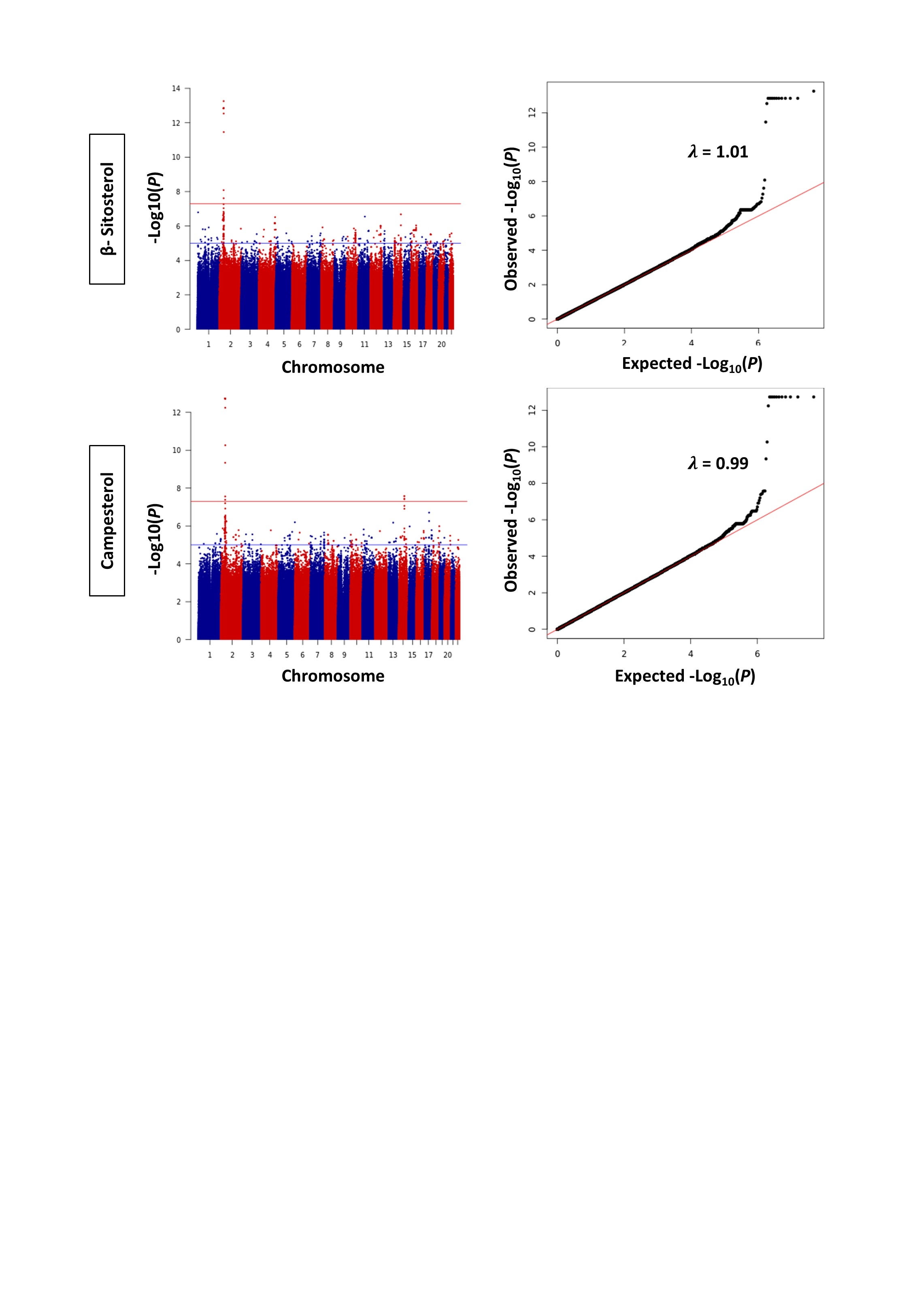
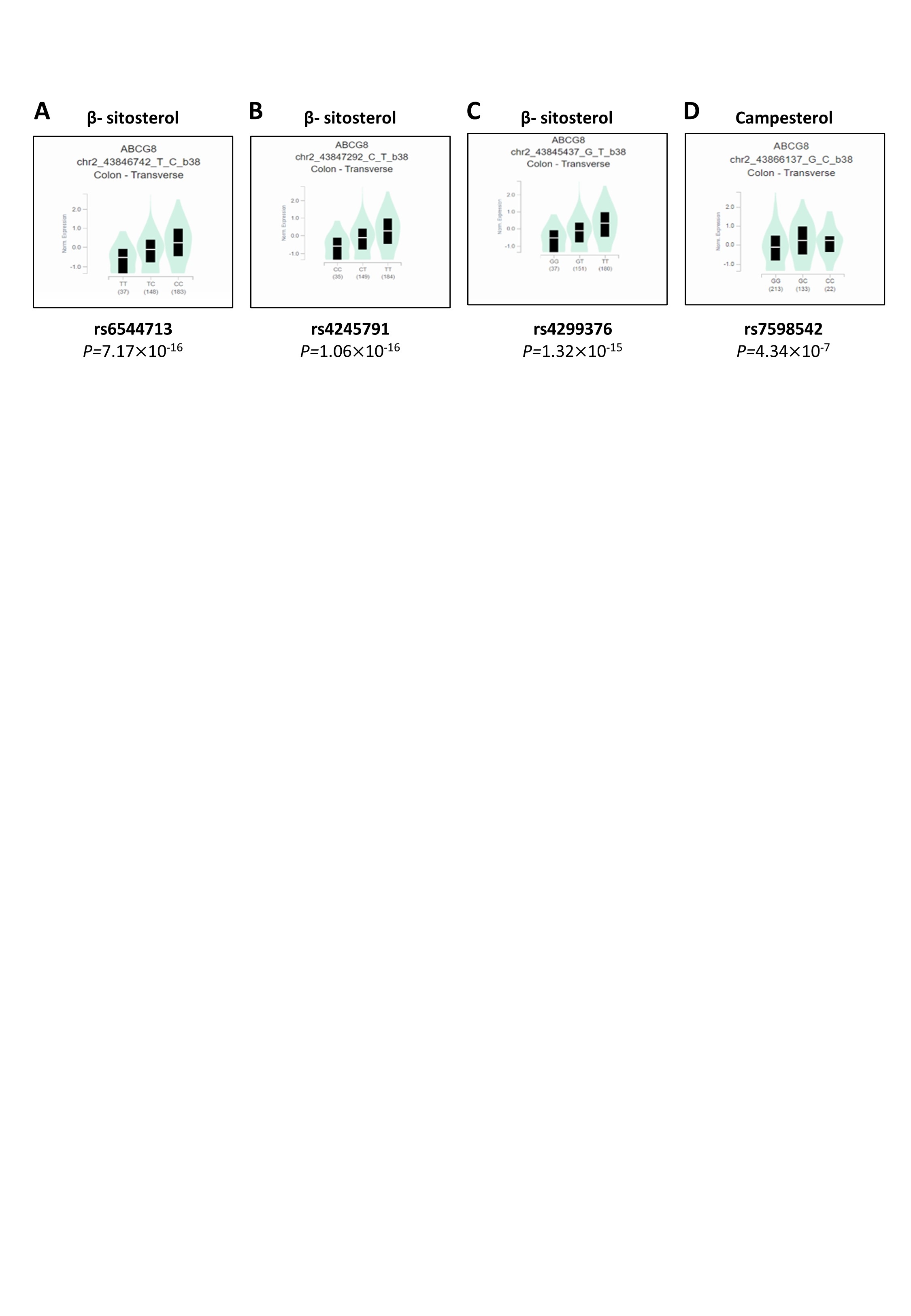
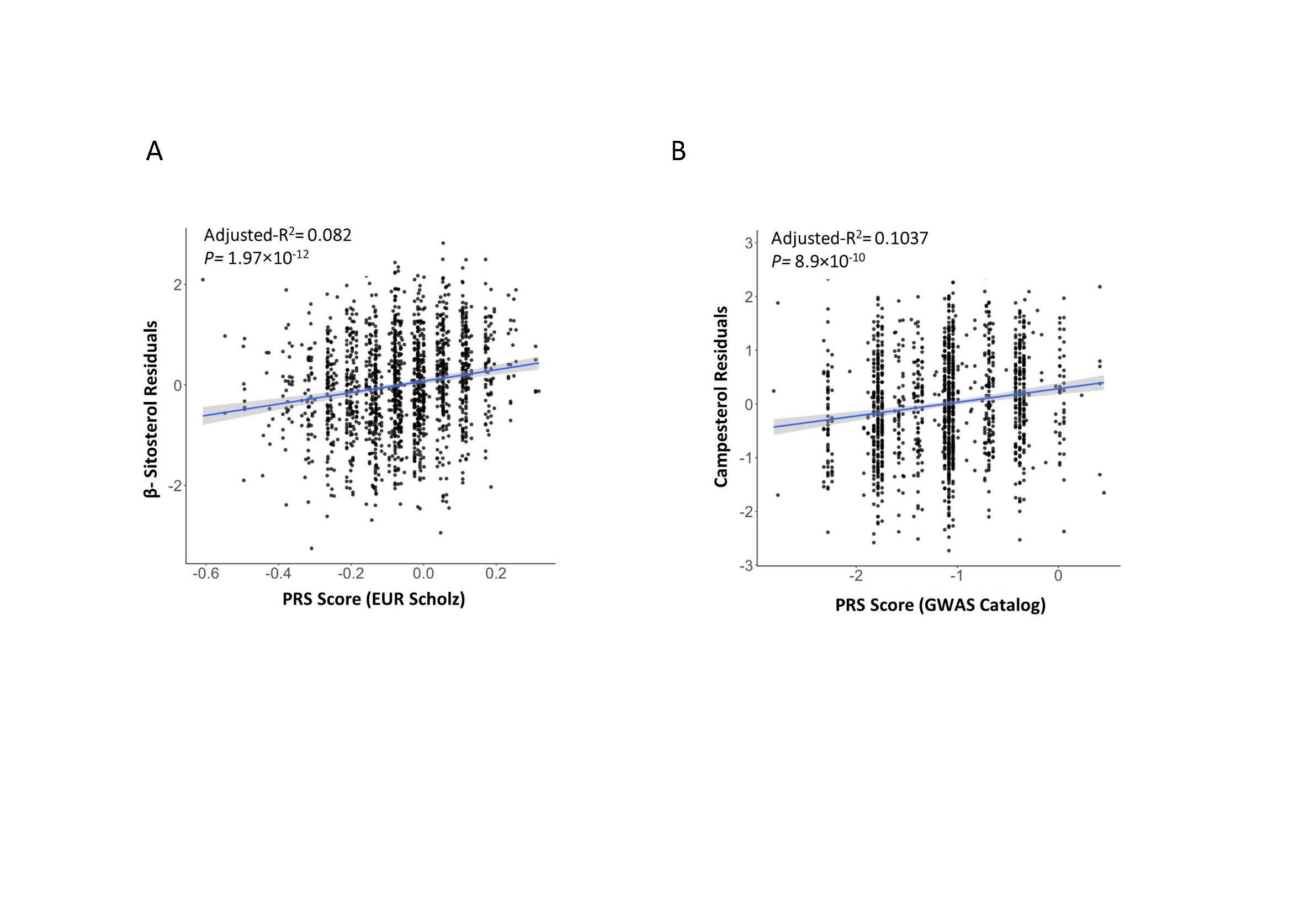
Results: The research identified two independent SNPs related to β-sitosterol ((rs145164937 and rs4299376) and two to campesterol (rs7598542 and rs75901165) in the Qatari population, alongside previously reported variants (P <5.0 ×10-8) .Notably, one variant (rs75901165) was located in the Intraflagellar Transport 43 (IFT43) gene, diverging from the common ABCG5/8 locus. The study also supported the association of variants in the SCARB1 and ABO genes with sitosterolemia and assessed a polygenic risk score's efficacy based on European GWAS data in the Qatari cohort.
Conclusion(s): The findings underscore the significance of conducting population-specific genetic research to understand better and manage conditions like sitosterolemia. This research highlights the importance of personalized treatment approaches for hyperlipidemia and the value of establishing comprehensive multi-omics databases tailored to specific populations.
Hypothesis: The study aimed to uncover the genetic determinants influencing plant sterol levels within the Middle East/North Africa (MENA) population, focusing on individuals from Qatar. It hypothesized that unique genetic variations might influence these levels, contributing to the development of sitosterolemia.
Aims: To conduct the first genome-wide association study (GWAS) in the MENA region to identify genetic variants affecting plant sterol levels in the Qatari population, and to compare these findings with those from populations of European ancestry.
Methods: The study utilized the Metabolon platform for analyzing serum levels of β-sitosterol and campesterol, combined with genome sequence data from the Qatar Genome Program. A trans-ancestry meta-analysis compared our findings with those from a large European cohort, while conditional analysis helped identify specific single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with these sterols.
Results: The research identified two independent SNPs related to β-sitosterol ((rs145164937 and rs4299376) and two to campesterol (rs7598542 and rs75901165) in the Qatari population, alongside previously reported variants (P <5.0 ×10-8) .Notably, one variant (rs75901165) was located in the Intraflagellar Transport 43 (IFT43) gene, diverging from the common ABCG5/8 locus. The study also supported the association of variants in the SCARB1 and ABO genes with sitosterolemia and assessed a polygenic risk score's efficacy based on European GWAS data in the Qatari cohort.
Conclusion(s): The findings underscore the significance of conducting population-specific genetic research to understand better and manage conditions like sitosterolemia. This research highlights the importance of personalized treatment approaches for hyperlipidemia and the value of establishing comprehensive multi-omics databases tailored to specific populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Loss-of-Function Missense Variant in ANGPTL3 Exerts Protective Effects Against Kidney Disease Risk
Zhang David, Ritchie Marylyn, Rader Daniel, Cuchel Marina
Acute Rhythm Change Reveals Atrial-Specific Metabolomic and Lipidomic Alterations in Atrial FibrillationKassar Ahmad, Bockus Lee, Haykal Romanos, Chamoun Nadia, Chahine Yaacoub, Al Yasiri Hala, Hensley Tori, Akoum Nazem