Final ID: We130
Novel Role of RBFox1 in Myocardial Infarction Induced Heart Failure
Abstract Body: Introduction
Alternative mRNA splicing affects a broad spectrum of cardiac genes during pathological manifestation of heart diseases. Earlier studies from our lab have identified a muscle-specific isoform of RBFox1 to be a key RNA splicing regulator in pressure overload induced heart failure through regulating cardiac transcription factor alternative splicing. However, the physiological impact of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction (MI), and the RBFox1 downstream mRNA alternative splicing events during MI induced cardiac remodeling remains unknown.
Goals
To investigate the functional impact of RBFox1 in MI induced cardiac remodeling.
Method and Results
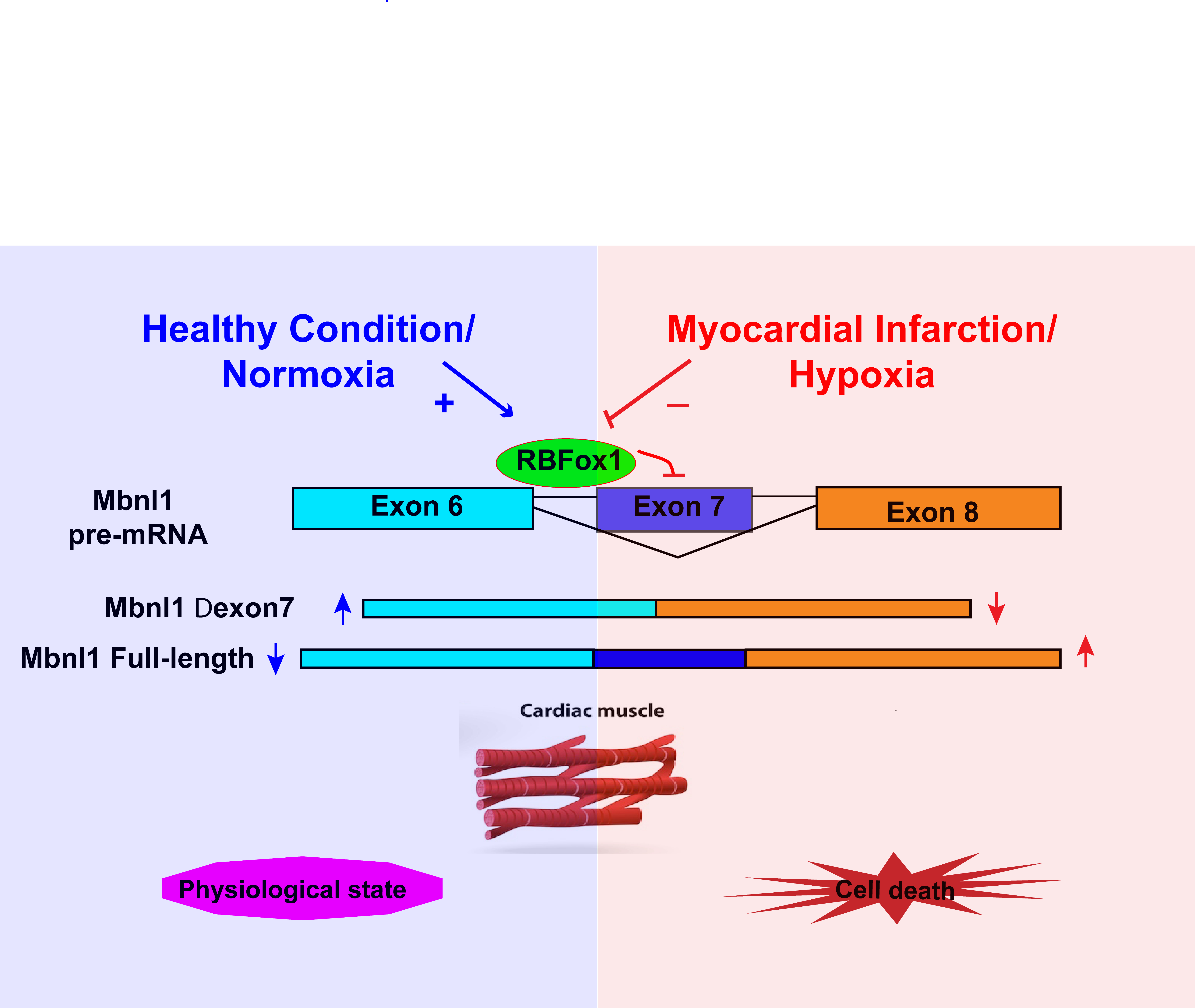
At both mRNA and protein levels, we found RBFox1 to be significantly decreased in Sprague-Dawley Rat hearts post MI. To investigate the functional impact of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction, we utilized AAV9 to achieve cardiac specific expression of RBFox1 in rats. Interestingly, expression of RBFox1 prevented cardiac dysfunction post MI characterized by improved cardiac function based on echocardiography. Expression of RBFox1 further reduced hypertrophy, cell death and fibrotic remodeling at both molecular and histological levels post MI. In vitro, expression of RBFox1 is sufficient to prevent hypoxia induced cardiac cell death based on TUNEL staining and cleaved caspase 3 level, while inactivation of RBFox1 promoted cardiac cell death. To further understand the molecular mechanism underlying RBFox1 mediated cardiac protection, we performed RNA-seq analysis to determine the transcriptome changes in vivo. RNA-seq showed insulin secretion, cAMP signaling and muscle contraction pathways to be top significantly changed pathways in RBFox1 expressed rat hearts post MI. Lastly, we have identified Mbnl1 mRNA alternative splicing to be regulated by RBFox1 through promoting a 36bp exon exclusion at the C-terminal of Mbnl1 protein, potentially affecting the function of Mbnl1.
Conclusion
In summary, we have identified a previously uncharacterized role of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction injury. RBFox1 expression is critical to preserve cardiac function post MI, potentially through regulating downstream targets alternative splicing, including Mbnl1.
Alternative mRNA splicing affects a broad spectrum of cardiac genes during pathological manifestation of heart diseases. Earlier studies from our lab have identified a muscle-specific isoform of RBFox1 to be a key RNA splicing regulator in pressure overload induced heart failure through regulating cardiac transcription factor alternative splicing. However, the physiological impact of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction (MI), and the RBFox1 downstream mRNA alternative splicing events during MI induced cardiac remodeling remains unknown.
Goals
To investigate the functional impact of RBFox1 in MI induced cardiac remodeling.
Method and Results
At both mRNA and protein levels, we found RBFox1 to be significantly decreased in Sprague-Dawley Rat hearts post MI. To investigate the functional impact of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction, we utilized AAV9 to achieve cardiac specific expression of RBFox1 in rats. Interestingly, expression of RBFox1 prevented cardiac dysfunction post MI characterized by improved cardiac function based on echocardiography. Expression of RBFox1 further reduced hypertrophy, cell death and fibrotic remodeling at both molecular and histological levels post MI. In vitro, expression of RBFox1 is sufficient to prevent hypoxia induced cardiac cell death based on TUNEL staining and cleaved caspase 3 level, while inactivation of RBFox1 promoted cardiac cell death. To further understand the molecular mechanism underlying RBFox1 mediated cardiac protection, we performed RNA-seq analysis to determine the transcriptome changes in vivo. RNA-seq showed insulin secretion, cAMP signaling and muscle contraction pathways to be top significantly changed pathways in RBFox1 expressed rat hearts post MI. Lastly, we have identified Mbnl1 mRNA alternative splicing to be regulated by RBFox1 through promoting a 36bp exon exclusion at the C-terminal of Mbnl1 protein, potentially affecting the function of Mbnl1.
Conclusion
In summary, we have identified a previously uncharacterized role of RBFox1 in myocardial infarction injury. RBFox1 expression is critical to preserve cardiac function post MI, potentially through regulating downstream targets alternative splicing, including Mbnl1.
More abstracts on this topic:
BMP3 Overexpression Attenuates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Halouani Aymen, Sassi Yassine, Mensah Eric, Athumani Zaujia, Katz Michael, Jankowski Katherine, Mansoori Maryam, Rosen Vicki, Ishikawa Kiyotake, Hadri Lahouaria
Carotid body ablation reduces hypertension following long-term intermittent hypoxia by regulating brainstem glial cell activationIturriaga Rodrigo, Pereyra Katherine, Vicencio Sinay, Bernal Ignacio, Diaz-jara Esteban, Del Rio Rodrigo