Final ID: Tu110
CD36-Mediated Transendothelial Fatty Acid Transport Determines Cardiomyocyte Uptake and is Critical to Limiting a Lipotoxic Ceramide Profile and Supporting Cardiac Function during Pathological Stress.
Abstract Body: The heart primarily relies on long chain fatty acid oxidation (LCFA) to meet ATP demand. CD36, is a transmembrane glycoprotein transferase for LCFA uptake widely expressed in several cell types including endothelial cells (ECs), cardiomyocytes (CMs), skeletal myocytes, adipocytes, and monocyte/macrophages. Notably, genetic deficiency of CD36 in humans is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The role of CD36 in transendothelial LCFA delivery to CMs under physiologic vs pathologic conditions is unknown. We explored consequences of EC-specific CD36 deletion (EC-CD36 KO mice) on the cardiac response to pressure overload.
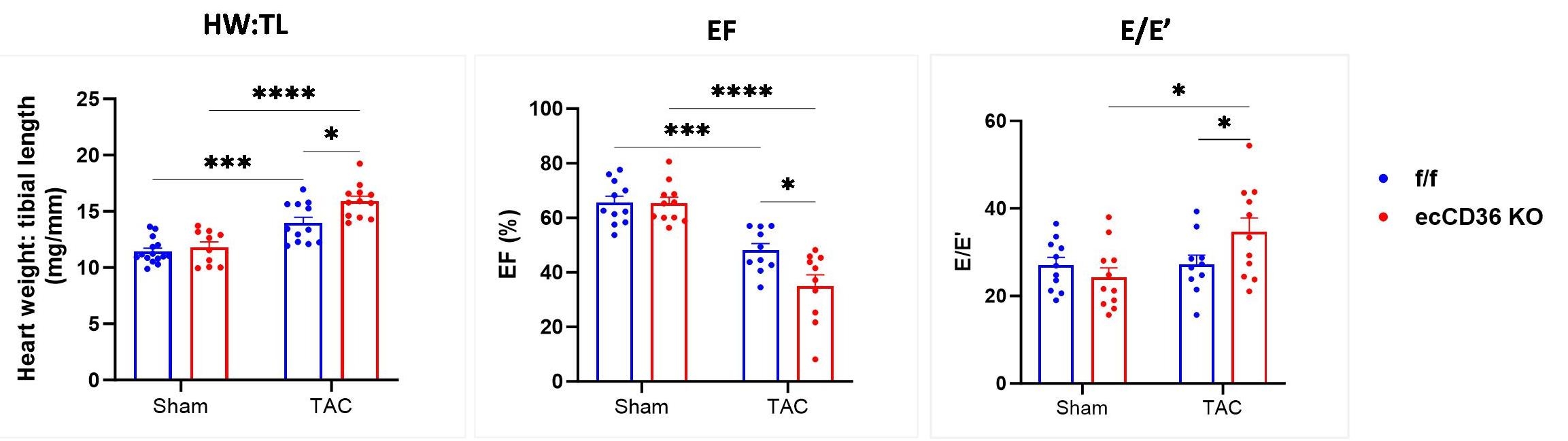
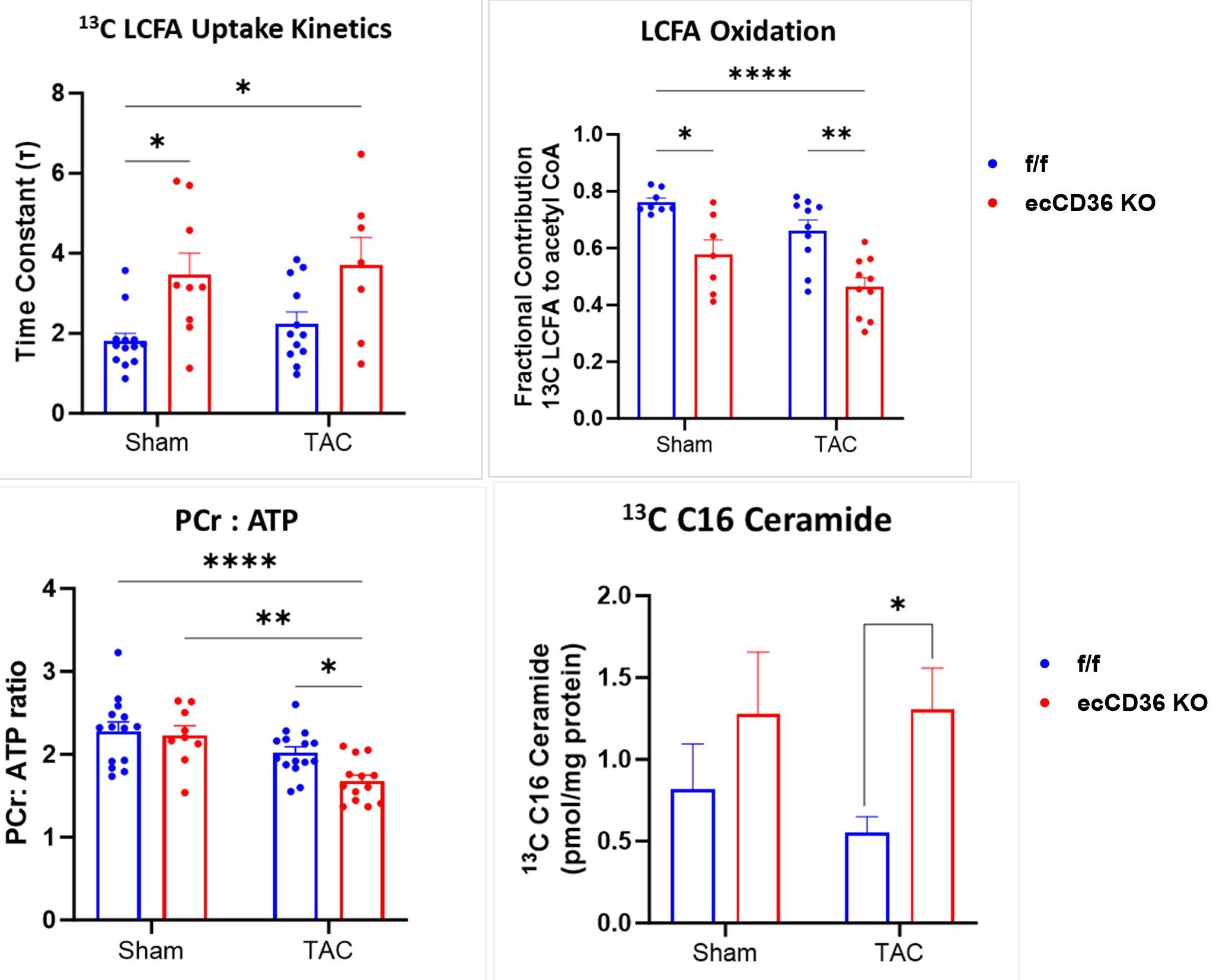
Lack of EC-CD36 increased severity of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and systolic and diastolic dysfunction at 8 weeks of pressure overload via transverse aortic constriction (TAC), with increases in HW:TL ratio, LV mass by echo, reduced EF (p<0.05), and elevated E/E’ in EC-CD36-KO vs. flox/flox littermate controls (f/f) (p<0.5) (Fig 1). Dynamic mode 13C NMR revealed delayed 13C LCFA uptake kinetics (time constant, τ) in CMs of isolated, sham and TAC EC-CD36 KO hearts provided 13C palmitate + 13C oleate (0.02 mM each) + 10 mM glucose + 1 mM lactate (Fig 2). 13C LCFA esterification into triglyceride (TG) was also reduced in EC-CD36-KO vs f/f controls, but without evidence for an additional effect of TAC.
The contribution of 13C LCFA to acetyl CoA entry into oxidation via the TCA cycle, was reduced by lack of EC-CD36 in sham and TAC hearts (p<0.0001) (Fig 2). Consistent with diminished LCFA oxidation, phosphocreatine (PCr) to ATP ratio was also compromised in EC-CD36-KO-TAC hearts (p<0.05). Lack of EC-CD36 during TAC increased 13C LCFA trafficking to lipotoxic C16 ceramide in EC-CD36 KO hearts (Fig 3).
CD36 in ECs is critical to LCFA delivery to CMs during pathological stress on the heart. The imbalance in intramyocellular LCFA dynamics due to restricted transendothelial delivery of LCFA to CMs increased lipotoxic ceramide formation. Thus, EC CD36 is critical to the adaptive cardiac response to pathological stress, and the absence of EC CD36-dependent delivery of LCFA to CMs exacerbates reduced energy potential, adverse cardiac remodeling, and dysfunction during afterload stress.
Lack of EC-CD36 increased severity of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and systolic and diastolic dysfunction at 8 weeks of pressure overload via transverse aortic constriction (TAC), with increases in HW:TL ratio, LV mass by echo, reduced EF (p<0.05), and elevated E/E’ in EC-CD36-KO vs. flox/flox littermate controls (f/f) (p<0.5) (Fig 1). Dynamic mode 13C NMR revealed delayed 13C LCFA uptake kinetics (time constant, τ) in CMs of isolated, sham and TAC EC-CD36 KO hearts provided 13C palmitate + 13C oleate (0.02 mM each) + 10 mM glucose + 1 mM lactate (Fig 2). 13C LCFA esterification into triglyceride (TG) was also reduced in EC-CD36-KO vs f/f controls, but without evidence for an additional effect of TAC.
The contribution of 13C LCFA to acetyl CoA entry into oxidation via the TCA cycle, was reduced by lack of EC-CD36 in sham and TAC hearts (p<0.0001) (Fig 2). Consistent with diminished LCFA oxidation, phosphocreatine (PCr) to ATP ratio was also compromised in EC-CD36-KO-TAC hearts (p<0.05). Lack of EC-CD36 during TAC increased 13C LCFA trafficking to lipotoxic C16 ceramide in EC-CD36 KO hearts (Fig 3).
CD36 in ECs is critical to LCFA delivery to CMs during pathological stress on the heart. The imbalance in intramyocellular LCFA dynamics due to restricted transendothelial delivery of LCFA to CMs increased lipotoxic ceramide formation. Thus, EC CD36 is critical to the adaptive cardiac response to pathological stress, and the absence of EC CD36-dependent delivery of LCFA to CMs exacerbates reduced energy potential, adverse cardiac remodeling, and dysfunction during afterload stress.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel Notch and WNT signaling mechanism contribute to pediatric DCM: a pathway to new therapeutics
AAV-mediated Gene Delivery of PERM1 Prevents the Development of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in a Mouse Model of Pressure Overload
Nyarko Obed, Miyamoto Shelley, Stauffer Brian, Sucharov Carmen
AAV-mediated Gene Delivery of PERM1 Prevents the Development of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in a Mouse Model of Pressure Overload
Sreedevi Karthi, Doku Abigail Oforiwaa, Thomas Rebekah, Salama Sarah, Zaitsev Alexey, Warren Junco