Final ID: We015
Modeling Cardiac Arrhythmogenicity of hiPSC-CMs and Cardiac Fibroblasts Nanopatterned Coculture and Machine Learning
Abstract Body: Background: Sudden cardiac death is one of the most threatening heart conditions in the U.S. Most individuals have an underlying structural cardiac disease associated with cardiac fibrosis and ventricular arrhythmia. The relationship between fibrosis and arrhythmias is found to be related to cardiovascular cell couplings, especially cardiomyocytes (CMs) and cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). While animal models have been applied to model cardiac arrhythmias, the disparities between animal models and humans limit the accuracy of pro-arrhythmic predictions. The use of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs)-derived CMs has permitted highly modular testing conditions, specifically the ratio of CFs to CMs in an engineered coculture system. Moreover, machine learning (ML) has become an emerging tool in cardiology, such as cardiac toxicity and function evaluation and classification, with its unique advantages of high accuracy and efficiency with less human bias and intuition.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that cardiac fibrosis-associated arrhythmia will be modeled by nanopatterned coculture of hiPSC-CMs and CFs at varied ratios, and the arrhythmic samples will be accurately and efficiently classified by ML algorithms.
Approach: The hiPSC-CMs were cocultured and nanopatterned with CFs at ratios of 0 to 30% for 7 days. Upon the electrical pacing at 1Hz, the action potential was recorded by live-cell optical mapping with FluoVolt. The recorded membrane potential and electrical propagation were analyzed by Matlab-based Electomap software.
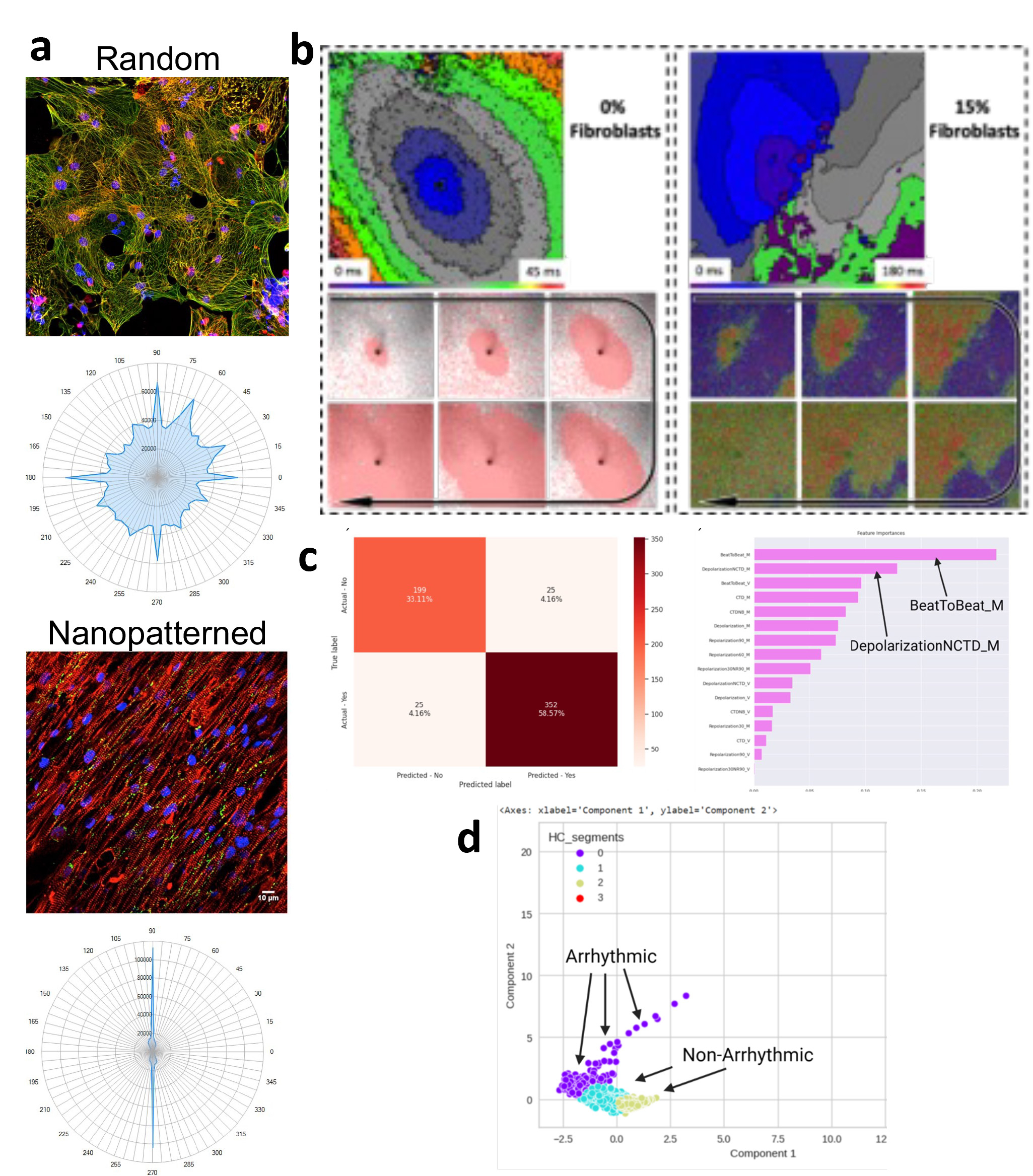
Results: The cocultured hiPSC-CMs and CFs were aligned with aligned sarcomeres and uni-directional contraction (Fig. 1a). The cardiac arrhythmia was observed in 15% CFs with spiral wave (Fig. 1b) in comparison to the hiPSC-CMs with 0% CF. Beat-to-beat and depolarization durations were found significant with top ranks in Feature Importance to facilitate the distinction between arrhythmic and non-arrhythmic samples by the unsupervised K-means Clustering (Figs. 1c and d).
Conclusions: We have successfully established a nanopatterned coculturing system of hiPSC-CMs and CFs for modeling cardiac fibrosis-induced arrhythmia, which was further analyzed and classified by ML algorithms. This system reveals great potential for better understanding the relationship between cardiac fibrosis-associated arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death and also drug evaluation for anti-cardiac arrhythmia.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that cardiac fibrosis-associated arrhythmia will be modeled by nanopatterned coculture of hiPSC-CMs and CFs at varied ratios, and the arrhythmic samples will be accurately and efficiently classified by ML algorithms.
Approach: The hiPSC-CMs were cocultured and nanopatterned with CFs at ratios of 0 to 30% for 7 days. Upon the electrical pacing at 1Hz, the action potential was recorded by live-cell optical mapping with FluoVolt. The recorded membrane potential and electrical propagation were analyzed by Matlab-based Electomap software.
Results: The cocultured hiPSC-CMs and CFs were aligned with aligned sarcomeres and uni-directional contraction (Fig. 1a). The cardiac arrhythmia was observed in 15% CFs with spiral wave (Fig. 1b) in comparison to the hiPSC-CMs with 0% CF. Beat-to-beat and depolarization durations were found significant with top ranks in Feature Importance to facilitate the distinction between arrhythmic and non-arrhythmic samples by the unsupervised K-means Clustering (Figs. 1c and d).
Conclusions: We have successfully established a nanopatterned coculturing system of hiPSC-CMs and CFs for modeling cardiac fibrosis-induced arrhythmia, which was further analyzed and classified by ML algorithms. This system reveals great potential for better understanding the relationship between cardiac fibrosis-associated arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death and also drug evaluation for anti-cardiac arrhythmia.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bismuth Nanoparticle-Infused Bioresorbable Graft Enables Multimodal Computed Tomography and Photoacoustic Imaging-Based Monitoring and Promotes Vascular Regeneration
Barcena Allan John, Fowlkes Natalie, Bouchard Richard, Huang Steven, Melancon Marites, Bernardino Marvin, Mishra Archana, Bolinas Dominic Karl, Marco Kitz Paul, Fernandez Kim Claudette, San Valentin Erin Marie, Court Karem, Godin Biana
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseLi Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney