Final ID: 4393041
Evaluating Precision Therapy Efficacy in Post-MI Cardiac Tissue Regeneration using Noninvasive Optoacoustic Imaging
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) causes adverse remodeling, leading to heart failure. To reverse this damage, we applied and evaluated two anti-inflammatory therapies on neovascularization (NV) and fibrosis in in vivo mouse cardiac tissue using a custom-built optoacoustic tomography, verified with histological analysis by clinical pathologist. This study established a quantitative platform for assessing cardiac regeneration by modulating post-MI inflammation, supporting emerging antifibrotic therapies.
Methods
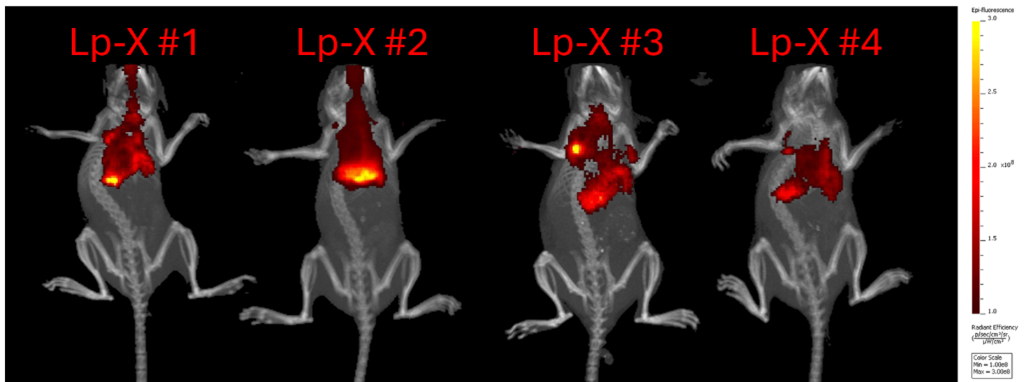
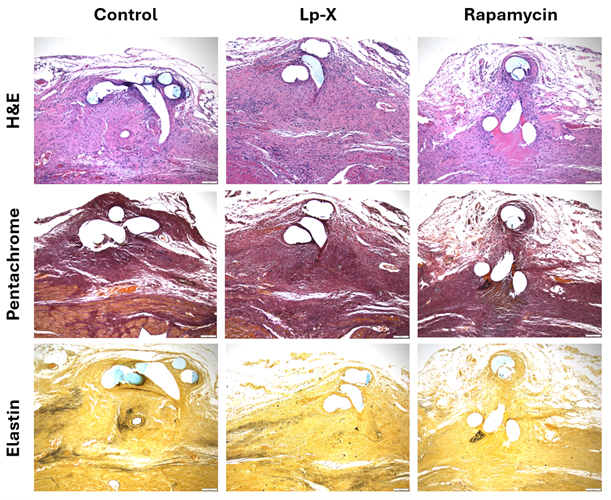
Eighteen-week-old cGAS-null mice (n = 12; 4/group; 5 female, 7 male) were randomized into 3 groups: (a) control (saline), (b) Lp-X nanoparticles, and (c) free drug (rapamycin, an anti-inflammatory). MI was induced by ligating the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery through the 3rd and 4th intercostal space. Weekly tail vein injections (100 μL, 1 mg/mL or saline) began immediately post-surgery for five weeks. At week 2, DiR-labeled Lp-X particles were used for tracking the uptake via IVIS SpectrumCT. Optoacoustic imaging monitored deoxygenated hemoglobin (Hb), oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2), and assess NV at 785 nm over five weeks. At week 5, hearts were excised and stained with H&E, Pentachrome, and Elastic Van Gieson for histological analysis. Fibrosis was quantified by collagen volume fraction (CVF = collagen area/total tissue area ×100%). All procedures followed UTSW protocol 2023-103473.
Results
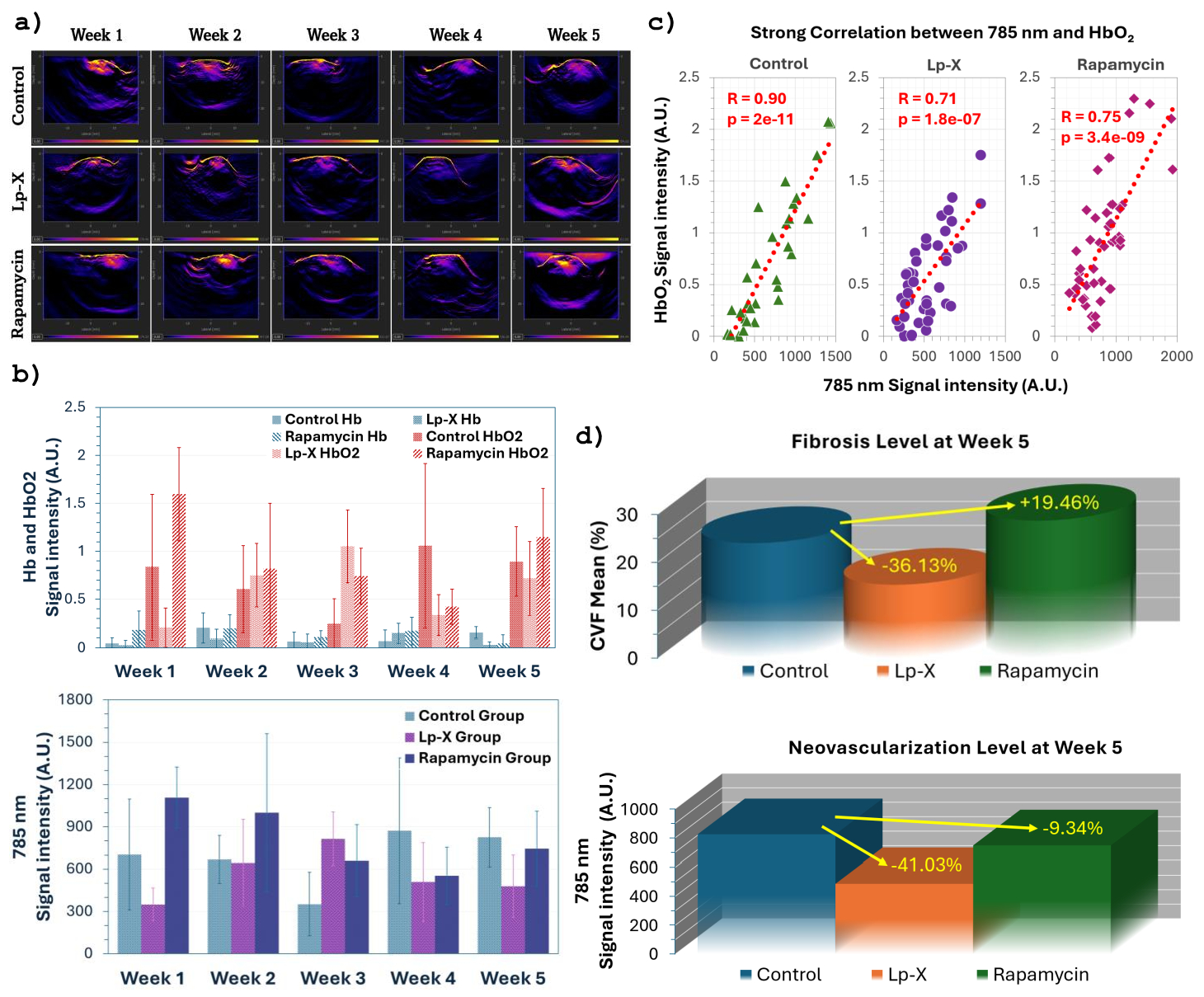
After five weeks of treatment, Lp-X and rapamycin both reduced NV but had opposite effects on fibrosis (Fig.1a, 3). Lp-X reduced fibrosis (36.13%±27.15%) and NV (41.03%±34.32%), while rapamycin increased fibrosis (19.46%±17.32%) and decreased NV (9.34%±47.04%) compared to control (Fig.1d). CT-fluorescence imaging verified targeted drug delivery (Fig.2). Longitudinal quantification of Hb, HbO2, and 785 nm signal intensity is shown with mean ± std (A.U., Fig.1b). A strong positive correlation was observed between HbO2 levels and NV across all groups (Fig.1c), indicating that improved local oxygenation is closely associated with angiogenesis (R = 0.90 control, 0.71 Lp-X, 0.75 rapamycin).
Conclusions
Using noninvasive optoacoustic imaging, we quantified the effect of Lp-X nanoparticles and rapamycin on post-MI NV and fibrosis. Both inhibited NV but had opposite effects on fibrosis. This platform offers a robust method to assess cardiac repair and support precision medicine.
Myocardial infarction (MI) causes adverse remodeling, leading to heart failure. To reverse this damage, we applied and evaluated two anti-inflammatory therapies on neovascularization (NV) and fibrosis in in vivo mouse cardiac tissue using a custom-built optoacoustic tomography, verified with histological analysis by clinical pathologist. This study established a quantitative platform for assessing cardiac regeneration by modulating post-MI inflammation, supporting emerging antifibrotic therapies.
Methods
Eighteen-week-old cGAS-null mice (n = 12; 4/group; 5 female, 7 male) were randomized into 3 groups: (a) control (saline), (b) Lp-X nanoparticles, and (c) free drug (rapamycin, an anti-inflammatory). MI was induced by ligating the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery through the 3rd and 4th intercostal space. Weekly tail vein injections (100 μL, 1 mg/mL or saline) began immediately post-surgery for five weeks. At week 2, DiR-labeled Lp-X particles were used for tracking the uptake via IVIS SpectrumCT. Optoacoustic imaging monitored deoxygenated hemoglobin (Hb), oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2), and assess NV at 785 nm over five weeks. At week 5, hearts were excised and stained with H&E, Pentachrome, and Elastic Van Gieson for histological analysis. Fibrosis was quantified by collagen volume fraction (CVF = collagen area/total tissue area ×100%). All procedures followed UTSW protocol 2023-103473.
Results
After five weeks of treatment, Lp-X and rapamycin both reduced NV but had opposite effects on fibrosis (Fig.1a, 3). Lp-X reduced fibrosis (36.13%±27.15%) and NV (41.03%±34.32%), while rapamycin increased fibrosis (19.46%±17.32%) and decreased NV (9.34%±47.04%) compared to control (Fig.1d). CT-fluorescence imaging verified targeted drug delivery (Fig.2). Longitudinal quantification of Hb, HbO2, and 785 nm signal intensity is shown with mean ± std (A.U., Fig.1b). A strong positive correlation was observed between HbO2 levels and NV across all groups (Fig.1c), indicating that improved local oxygenation is closely associated with angiogenesis (R = 0.90 control, 0.71 Lp-X, 0.75 rapamycin).
Conclusions
Using noninvasive optoacoustic imaging, we quantified the effect of Lp-X nanoparticles and rapamycin on post-MI NV and fibrosis. Both inhibited NV but had opposite effects on fibrosis. This platform offers a robust method to assess cardiac repair and support precision medicine.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Role for Lipoprotein(a) in Potentiating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation
Mouawad Sahar, Boffa Michael, Koschinsky Marlys
A20 in the Kidney Epithelium Attenuates Angiotensin II-induced Hypertension by Constraining Renal Tubular NHE3 ExpressionLu Xiaohan, Ren Jiafa, Wen Yi, Griffiths Robert, Yang Ting, Hammer Gianna, Zhuo Jia, Crowley Steven