Final ID:
Infrared Sensor Evaluation for Noninvasive Screening and Early triage in Acute Coronary Syndromes: The iSENSE-ACS Multicenter Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: With the rising prevalence of non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) relative to ST-elevation, current guidelines show gaps in the early identification of patients with severe coronary artery disease (CAD) who require time-sensitive reperfusion therapies. This study evaluated the diagnostic utility of a wrist-worn, transdermal infrared spectrophotometric biosensor (Infrasensor) in comparison with standard ECG and blood biomarker-based risk assessment for the early diagnosis and triage of NSTE-ACS and severe obstructive CAD, including cases with total coronary occlusion, referred to as occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI).
Methods: In this prospective, multicenter study, 776 subjects were enrolled across 21 sites in two countries and grouped into five analytical cohorts. Evaluations included Infrasensor data, HEART (history, ECG, age, risk factors, and high-sensitivity troponin) and HEAR (without troponin) risk scores, coronary angiography (n = 445), and 30-day clinical follow-up. We implemented machine learning models using a leave-one-cohort-out external validation approach to predict the primary angiographic endpoint of OMI or severe obstructive CAD (defined as>70% stenosis in any coronary artery or >50% stenosis in the left main coronary artery). The secondary model included a final discharge diagnosis of NSTE-ACS, coronary revascularization, or death within 30 days.
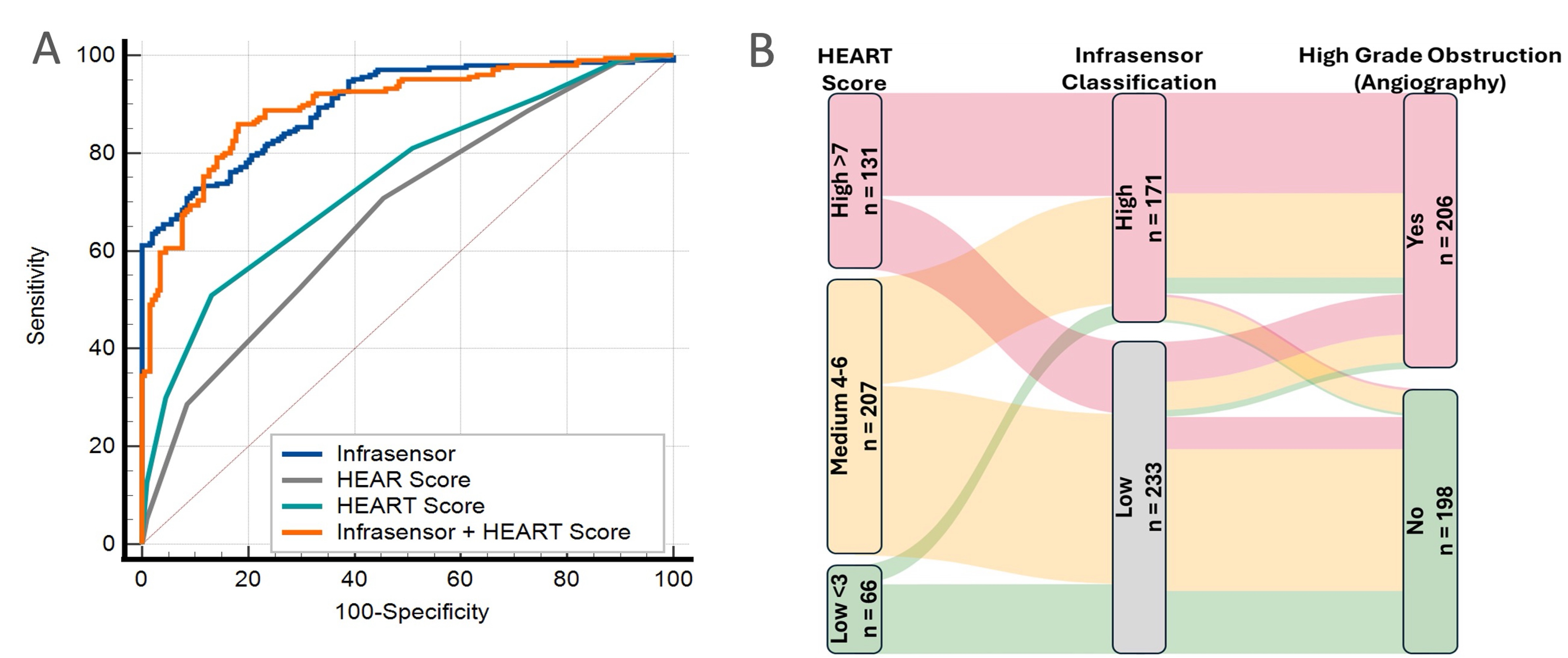
Results: Severe obstructive CAD was identified in 215 (48%), including 92 (20%) diagnosed as OMI. The primary model showed an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.91 (95% confidence interval, CI: 0.88–0.93), outperforming both HEAR (AUC, 0.64; 95% CI: 0.60-0.68) and HEART (AUC, 0.68;95% CI: 0.64-0.72) risk scores, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 1A). A rule-in strategy using the Infrasensor model demonstrated 90% specificity and 88% positive predictive value, with a 68% net reclassification improvement (95% CI: 54%–82%) over the HEART score (Figure 1B). The secondary model yielded an AUC of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.86–0.94) and achieved 94% sensitivity and 86% negative predictive value for ruling out the composite clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: The Infrasensor model significantly outperformed standard guideline-based risk stratification in identifying high-risk CAD and OMI. This wearable, noninvasive technology can safely enhance early triage and decision-making in emergency settings for patients with NSTE-ACS, offering substantial diagnostic improvement over existing methods.
Methods: In this prospective, multicenter study, 776 subjects were enrolled across 21 sites in two countries and grouped into five analytical cohorts. Evaluations included Infrasensor data, HEART (history, ECG, age, risk factors, and high-sensitivity troponin) and HEAR (without troponin) risk scores, coronary angiography (n = 445), and 30-day clinical follow-up. We implemented machine learning models using a leave-one-cohort-out external validation approach to predict the primary angiographic endpoint of OMI or severe obstructive CAD (defined as>70% stenosis in any coronary artery or >50% stenosis in the left main coronary artery). The secondary model included a final discharge diagnosis of NSTE-ACS, coronary revascularization, or death within 30 days.
Results: Severe obstructive CAD was identified in 215 (48%), including 92 (20%) diagnosed as OMI. The primary model showed an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.91 (95% confidence interval, CI: 0.88–0.93), outperforming both HEAR (AUC, 0.64; 95% CI: 0.60-0.68) and HEART (AUC, 0.68;95% CI: 0.64-0.72) risk scores, respectively (P<0.001, Figure 1A). A rule-in strategy using the Infrasensor model demonstrated 90% specificity and 88% positive predictive value, with a 68% net reclassification improvement (95% CI: 54%–82%) over the HEART score (Figure 1B). The secondary model yielded an AUC of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.86–0.94) and achieved 94% sensitivity and 86% negative predictive value for ruling out the composite clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: The Infrasensor model significantly outperformed standard guideline-based risk stratification in identifying high-risk CAD and OMI. This wearable, noninvasive technology can safely enhance early triage and decision-making in emergency settings for patients with NSTE-ACS, offering substantial diagnostic improvement over existing methods.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Myocardial Infarction with Non-obstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA) Complicated by a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
Thai Theresa, Lipinski Jerry, Sola Michael, El Rafei Abdelghani, Desai Aken, Sailer Christine
Abbreviated Ticagrelor-Based Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisHarmouch Wissam, Elbadawi Ayman, Thakker Ravi, Khalid Umair, Khalife Wissam, Kleiman Neal, Rangasetty Umamahesh, Kayani Waleed, Jneid Hani, Al Hemyari Bashar