Final ID:
Dose-Dependent and Sustained Reduction in Lipoprotein(a) levels after single-dose of Kylo-11, a LPA-targeted Small Interfering RNA, in Healthy Volunteers: A First-in-Human Phase I Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a causal risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, with no approved pharmacological treatments. Kylo-11 is a N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated small interfering RNA that reduces Lp(a) synthesis in the liver. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 study aimed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics characteristics of Kylo-11 in Chinese healthy volunteers (NCT06363851).
Methods: Sixty participants with Lp(a) 75–200 nmol/L were enrolled in Cohorts 1–6 (9–600 mg), while ten participants with Lp(a) >200 nmol/L were enrolled in Cohort 7 (225 mg). Participants received single subcutaneous doses of Kylo-11 or placebo (8:2) and followed up to 48 weeks. Serum Lp(a) was quantified via Roche Diagnostics' assay with a low limit of quantitation of 7 nmol/L.
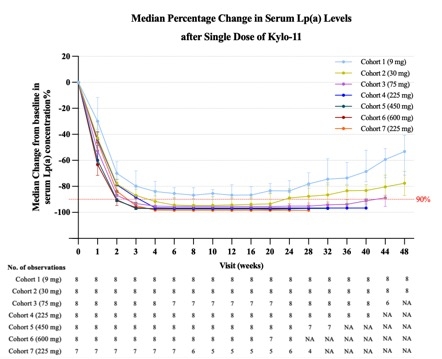
Results: In this ongoing study, mean age was 28.3 years (SD, 7.8) and 35.7% were female. Median (IQR) baseline Lp(a) was 121.1 nmol/L (95.5–151.1 nmol/L) and 219.4 nmol/L (213.1–242.8 nmol/L) for Cohort 1–6 and Cohort 7, respectively. Overall median follow-up was 228.5 days (range, 43–341 days). 55.7% participants experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). Most TEAEs were Grade 1–2 and unrelated to study drug. No serious TEAEs, TEAEs leading to study discontinuation or injection-site reactions occurred. Median percentage changes (IQR) from baseline in serum Lp(a) levels at 24 weeks post dose were –83.5% (–84.9% to –75.6%), –88.9% (–94.9, –81.7), –95.2 (–96.5, –93.5), –96.7 (–97.4, –96.3), –97.2 (–97.8, –96.9), –97.4 (–97.8, –96.5), and –98.4% (–98.5% to –98.3%) in Cohort 1–7, respectively. Lp(a) reduction of participants with baseline Lp(a) of 75–200 nmol/L maintained at 77.6% at Week 48 in 30 mg cohort, 88.8% at Week 44 in 75 mg cohort, and 96.7% at Week 40 in 225 mg cohort, respectively. Serum Lp(a) levels remained below 75 nmol/L in participants receiving≥30 mg of Kylo-11 from 4 weeks post dose during the follow-up.
Conclusions: Kylo-11 was well tolerated in Chinese healthy volunteers. Higher doses produced greater and more sustained reductions in serum Lp(a) levels over 48 weeks of follow-up. These findings support further investigation of Kylo-11 in patients with elevated Lp(a), with potential for administration once every 6 months or annually.
Methods: Sixty participants with Lp(a) 75–200 nmol/L were enrolled in Cohorts 1–6 (9–600 mg), while ten participants with Lp(a) >200 nmol/L were enrolled in Cohort 7 (225 mg). Participants received single subcutaneous doses of Kylo-11 or placebo (8:2) and followed up to 48 weeks. Serum Lp(a) was quantified via Roche Diagnostics' assay with a low limit of quantitation of 7 nmol/L.
Results: In this ongoing study, mean age was 28.3 years (SD, 7.8) and 35.7% were female. Median (IQR) baseline Lp(a) was 121.1 nmol/L (95.5–151.1 nmol/L) and 219.4 nmol/L (213.1–242.8 nmol/L) for Cohort 1–6 and Cohort 7, respectively. Overall median follow-up was 228.5 days (range, 43–341 days). 55.7% participants experienced treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). Most TEAEs were Grade 1–2 and unrelated to study drug. No serious TEAEs, TEAEs leading to study discontinuation or injection-site reactions occurred. Median percentage changes (IQR) from baseline in serum Lp(a) levels at 24 weeks post dose were –83.5% (–84.9% to –75.6%), –88.9% (–94.9, –81.7), –95.2 (–96.5, –93.5), –96.7 (–97.4, –96.3), –97.2 (–97.8, –96.9), –97.4 (–97.8, –96.5), and –98.4% (–98.5% to –98.3%) in Cohort 1–7, respectively. Lp(a) reduction of participants with baseline Lp(a) of 75–200 nmol/L maintained at 77.6% at Week 48 in 30 mg cohort, 88.8% at Week 44 in 75 mg cohort, and 96.7% at Week 40 in 225 mg cohort, respectively. Serum Lp(a) levels remained below 75 nmol/L in participants receiving≥30 mg of Kylo-11 from 4 weeks post dose during the follow-up.
Conclusions: Kylo-11 was well tolerated in Chinese healthy volunteers. Higher doses produced greater and more sustained reductions in serum Lp(a) levels over 48 weeks of follow-up. These findings support further investigation of Kylo-11 in patients with elevated Lp(a), with potential for administration once every 6 months or annually.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Nationwide Italian Network for the Clinical and Genetic Diagnosis of Familial Dyslipidemias: The LIPIGEN registry
Casula Manuela, Galimberti Federica, Olmastroni Elena, Arca Marcello, Averna Maurizio, Catapano Alberico
A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pitavastatin Calcium to Treat Combined Dyslipidemia of Obesity in Adolescents – The Pediatric Heart Network Dyslipidemia of Obesity Intervention in Teens (DO IT!) TrialDe Ferranti Sarah, Cartoski Mark, Brothers Julie, San Giovanni Christine, Zachariah Justin, Pena Sandra, Mahle William, Peterson Amy, Magge Sheela, Raghuveer Geetha, Sharma Binu, Arslanian, Md Silva, Kazlova Valiantsina, Sponseller Craig, Freemon Dandrea, Stylianou Mario, Mccrindle Brian, Mietus-snyder Michele, Urbina Elaine, Ware Adam, Teng Jessica, Trachtenberg Felicia, Russell Mark, Shah Amy