Final ID: MP804
Cellular factor loaded dECM patch improving cardiac function of rats after myocardial ischemia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Ischemic heart disease remains a global health challenge characterized by irreversible cardiomyocyte loss and pathological ventricular remodeling. This study introduces a novel therapeutic strategy combining sustained chemokine delivery with structural reinforcement - stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) loaded decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) patch (SDF-dECM patch) designed to address both biological and biomechanical deficiencies in myocardial repair.
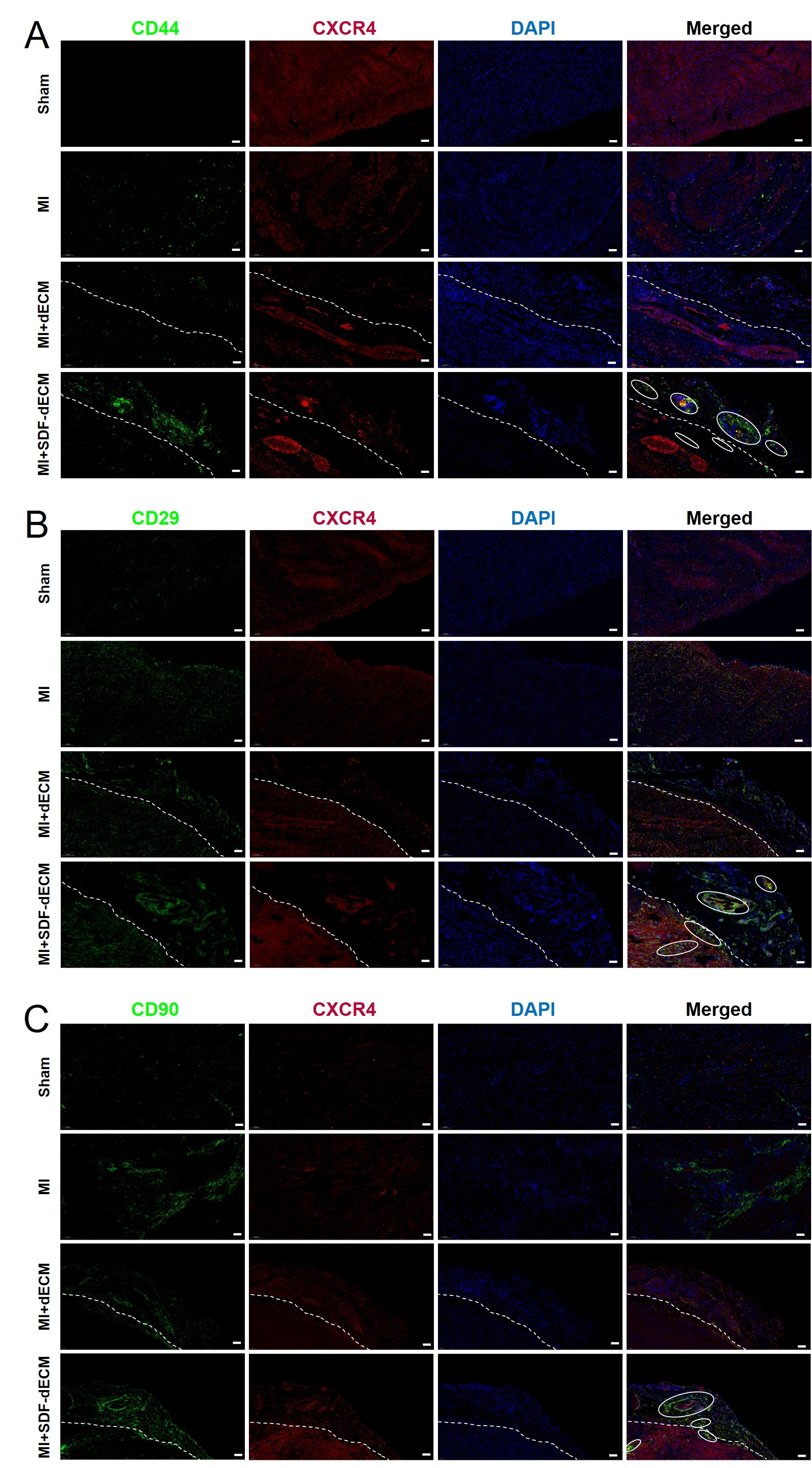
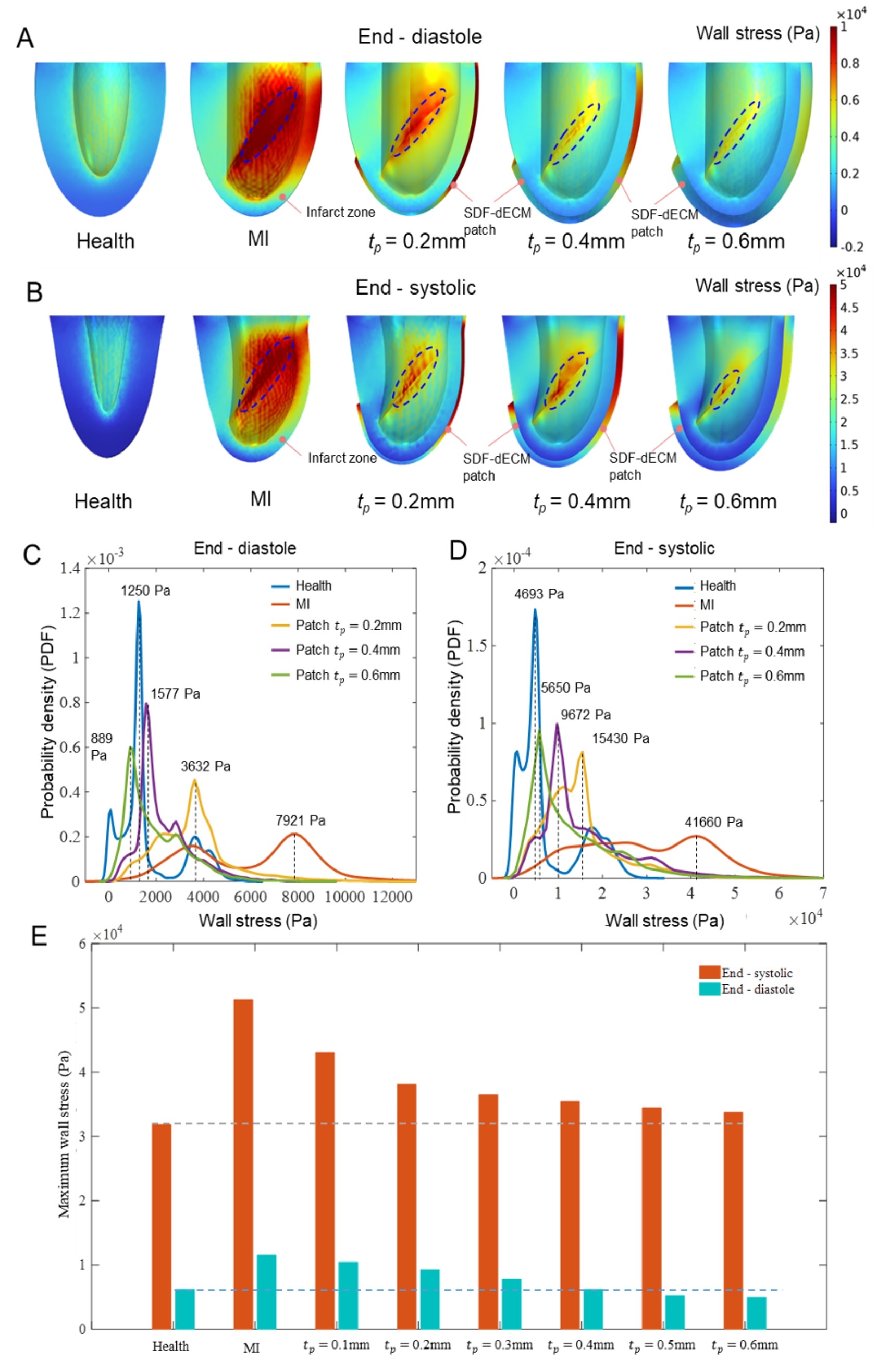
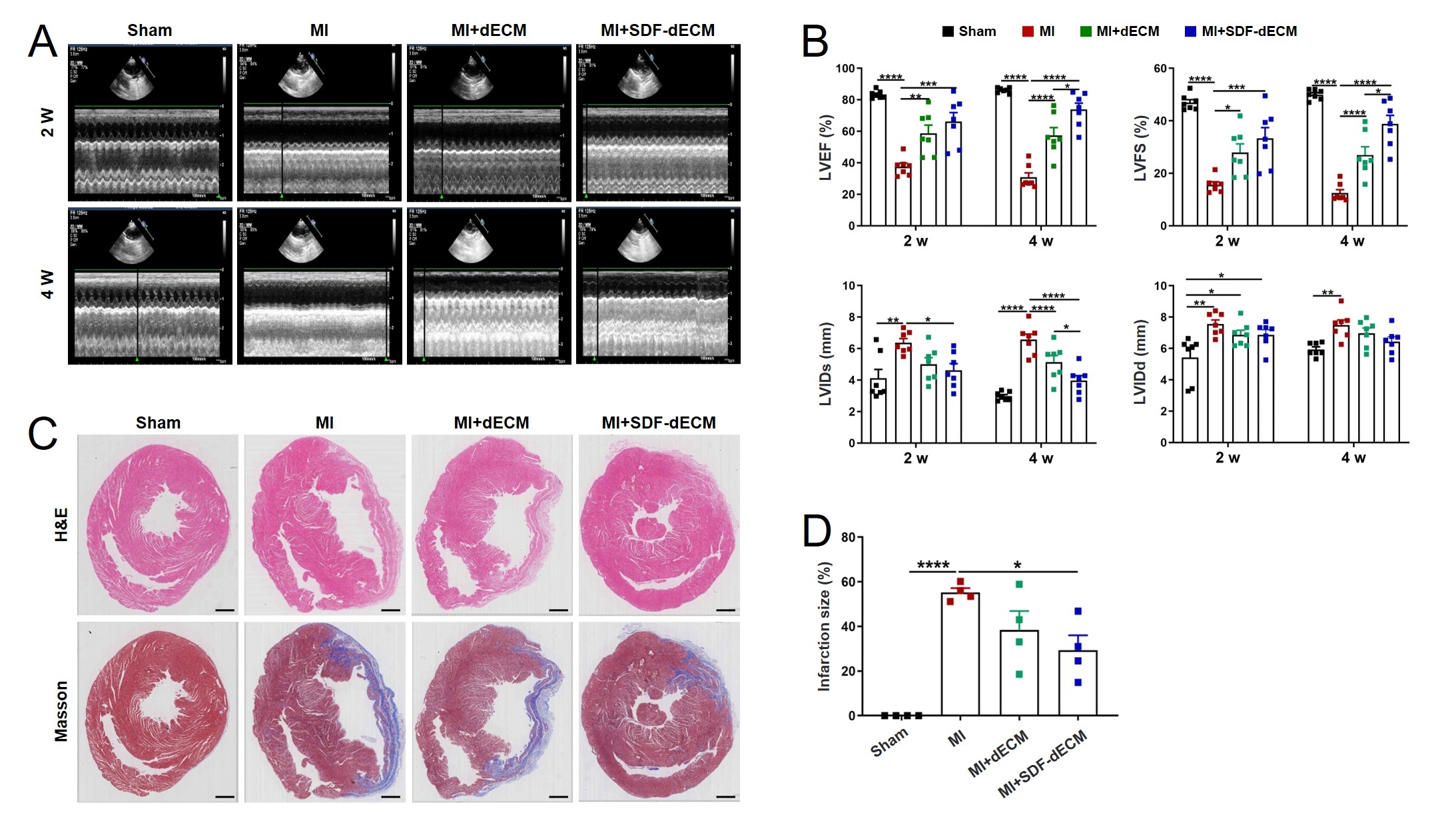
Methods: dECM was prepared from the myocardium of the left ventricle of pig by decellularization and co-cultured with H9c2 cells and BMMSCs to observe its biosafety. Their mechanical properties were tested by uniaxial stretching. SDF-1 was loaded onto dECM to prepare SDF-dECM patch. The period and rule of SDF-1 release on SDF-dECM patch were detected by ELISA. The expression of related proteins were detected by Western blot. The finite element simulation model of SDF-dECM patch implantation after myocardial infarction was established to reveal the effect of SDF-dECM patch on mechanical support and wall stress (WS) of infarcted myocardium through computer simulation. SDF-dECM patch was implanted on the surface of myocardial infarction area in rats, and the expression of related markers and proteins in the homing process of endogenous BMMSCs were observed by immunofluorescence staining. The paracrine mechanism of BMMSCs conditioned medium was detected by ELISA.
Results: The SDF-dECM patch had excellent elastic and mechanical properties, and it also demonstrated sustained chemokine delivery with linear release kinetics, maintaining therapeutic SDF-1 concentrations through 28 days without significant attenuation. Recruited BMMSCs exhibited potent paracrine activity, secreting VEGF and HGF. In vivo implementation of the SDF-dECM patch mobilized endogenous BMMSCs to the myocardial infarction and patch area. The SDF-dECM patch provided good mechanical support for the ventricular wall of the infarction area and effectively reduced the ventricular WS in the infarction area and the stress concentration at the healthy-infarction junction. This bimodal therapeutic strategy ultimately improved ejection fraction relative to untreated controls.
Conclusion: This SDF-dECM patch establishes a regenerative microenvironment through sustained chemokine gradient for endogenous stem cell mobilization, and biomechanical stabilization to prevent adverse remodeling.
Methods: dECM was prepared from the myocardium of the left ventricle of pig by decellularization and co-cultured with H9c2 cells and BMMSCs to observe its biosafety. Their mechanical properties were tested by uniaxial stretching. SDF-1 was loaded onto dECM to prepare SDF-dECM patch. The period and rule of SDF-1 release on SDF-dECM patch were detected by ELISA. The expression of related proteins were detected by Western blot. The finite element simulation model of SDF-dECM patch implantation after myocardial infarction was established to reveal the effect of SDF-dECM patch on mechanical support and wall stress (WS) of infarcted myocardium through computer simulation. SDF-dECM patch was implanted on the surface of myocardial infarction area in rats, and the expression of related markers and proteins in the homing process of endogenous BMMSCs were observed by immunofluorescence staining. The paracrine mechanism of BMMSCs conditioned medium was detected by ELISA.
Results: The SDF-dECM patch had excellent elastic and mechanical properties, and it also demonstrated sustained chemokine delivery with linear release kinetics, maintaining therapeutic SDF-1 concentrations through 28 days without significant attenuation. Recruited BMMSCs exhibited potent paracrine activity, secreting VEGF and HGF. In vivo implementation of the SDF-dECM patch mobilized endogenous BMMSCs to the myocardial infarction and patch area. The SDF-dECM patch provided good mechanical support for the ventricular wall of the infarction area and effectively reduced the ventricular WS in the infarction area and the stress concentration at the healthy-infarction junction. This bimodal therapeutic strategy ultimately improved ejection fraction relative to untreated controls.
Conclusion: This SDF-dECM patch establishes a regenerative microenvironment through sustained chemokine gradient for endogenous stem cell mobilization, and biomechanical stabilization to prevent adverse remodeling.
More abstracts on this topic:
A diagnostic challenge overcome with persistent clinical suspicion in a case of cardiac AL amyloidosis
Zimmerman Allison, Kuriakose Philip, Godfrey Amanda, Ananthasubramaniam Karthikeyan, Cowger Jennifer, Al-darzi Waleed
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathyAl Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika