Final ID: Su2133
Safety and Efficacy of Moderate-Intensity Statin Plus Ezetimibe versus High-Intensity Statin in Older Adult Patients: A Meta-analysis
Guidelines recommend high-intensity statin treatment for achieving target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in high-risk patients. Nonetheless, moderate-intensity statin use has been suggested as an alternative in older adult patients due to concerns about adverse effects. Whether a combination approach of a moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe is superior to high-intensity statins in older adult patients for hypercholesterolemia is unknown.
Objective
We performed a meta-analysis comparing the combination therapy of moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe versus high-intensity statin monotherapy in older adult patients (≥65 years) with hypercholesterolemia.
Methods
PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane CENTRAL databases were searched from inception through May 2025 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe versus high-intensity statin in older adults. Outcomes of interest were reduction in LDL-C levels (LDL-C <70 mg/dL or ≥50% reduction in LDL-C), muscle-related adverse effects, new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM), death, and treatment discontinuation due to drug-related adverse effects. Frequentist random-effects meta-analysis was performed to calculate risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
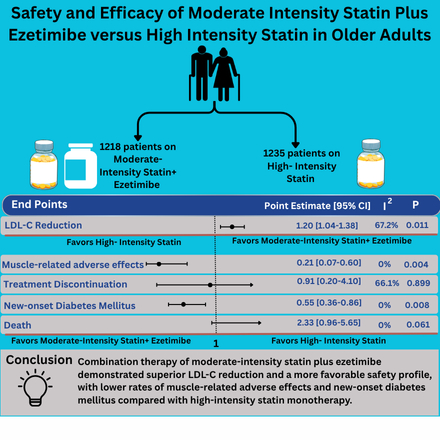
Four RCTs with 2453 patients (moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe: 1218, 49.6%) were included. The rate of reduction in LDL-C levels (RR 1.2; 95% CI 1.04-1.38; p=0.011; I2=67.2%) was higher with the combination therapy of moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe compared with high-intensity statin. Muscle-related adverse effects (RR 0.21; 95% CI 0.07-0.60; p=0.004; I2=0%) and new-onset DM (RR 0.55; 95% CI 0.36-0.86; p=0.008; I2=0%) were lower with moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe compared with high-intensity statin. Death and treatment discontinuation were similar between the groups.
Conclusion
In older adult patients, combination therapy of moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe demonstrated superior LDL-C reduction and a more favorable safety profile, with lower rates of muscle-related adverse effects and new-onset DM compared with high-intensity statin monotherapy. Moderate-intensity statin plus ezetimibe is a viable treatment option for older adult patients with hypercholesterolemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
Fujiwara Takeshi, Swain Subhashisa, Ogden Margaret, Hoshide Satoshi, Kario Kazuomi, Hobbs Richard, Mcmanus Richard, Sheppard James, Koshiaris Constantinos, Cai Ting, Wang Ariel, Lee Joseph, Lay-flurrie Sarah, Banerjee Amitava, Clegg Andrew, Payne Rupert
A transformative LDL cholesterol–lowering in vivo CRISPR gene editing medicine that functionally upregulates LDLR in mice and non-human primatesNewmark Judith, Raghav Jimit, Jaskolka Michael, Diner Benjamin, Soman Vikram, Jinadasa Tushare, Apte Ameya, Wu Meng, Bottega Steve, Thakkar Mansi, Agosto Luis, Wrighton Paul, Majithia Deep, Jambard Shreya, Jansson-fritzberg Linnea, Jones Mark, Fletcher Jillian, Weiss Mckenzie, Kaye Emily, Steward Briana, Bochicchio James, Pietrasiewicz Stephen, Iovino Salvatore, Marco Rubio Eugenio, Trong Phan Huu, Chander Nisha, Kazemian Mohammadreza, Lam Kieu, Reid Steve, Dinsmore Michael, Teslovich Tanya, Xie Jenny, Gupta Anshul, Amin Parth, Burkly Linda, Thompson Morgan, Rizal Salu, Bilodeau Maxime, Dong Ruhong, Zhen Wei