Final ID: Sa2025
Machine Learning-based Mortality Prediction for Pediatric Fulminant Myocarditis Using Cytokine Profiles
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Fulminant myocarditis (FM) is a rare but life-threatening pediatric condition that rapidly progresses to cardiogenic shock and fatal arrhythmias. Prognostic biomarkers in FM are essential for optimizing treatment strategies. Although inflammatory cytokines have been associated with the pathogenesis of FM, their prognostic value remains unclear. This study aimed to identify mortality-associated markers by integrating cytokine profiles and clinical variables through a machine learning approach.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 21 pediatric FM cases from two tertiary centers (2012–2022). At admission, 37 cytokines and 14 clinical parameters were assessed. Partial least squares discriminant analysis was employed to identify prognostic features, with variable importance in projection scores quantifying their contribution. Model performance was evaluated using leave-one-out cross-validation. Statistical significance was determined via the Benjamini–Hochberg method at a false discovery rate of 0.05.
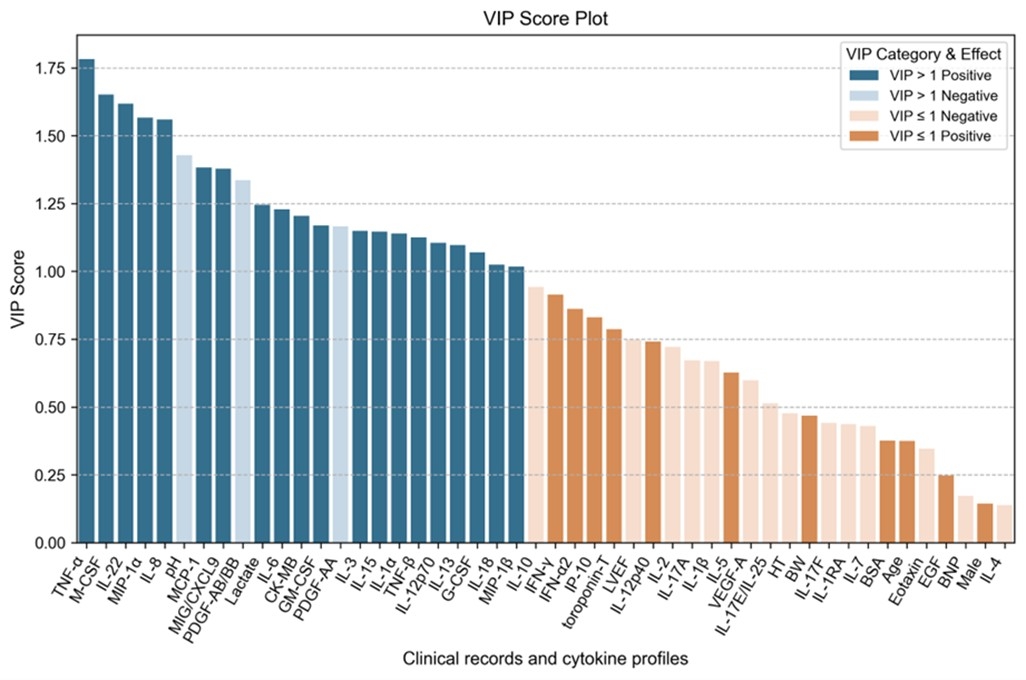
Results: Of the 51 features analyzed, 23 emerged as key predictors, 20 cytokines and 3 clinical parameters, with variable importance in projection scores above 1.0. Six cytokines (TNF-α, M-CSF, MIP-1α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-15) were both statistically significant and highly important. Among them, six cytokines (TNF-α, M-CSF, MIP-1α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-15) were both statistically significant and highly important. TNF-α had the highest VIP score among all predictors. Elevated CK-MB and lactate levels and lower pH were also linked to poor outcomes. The model performed robustly, with an AUC of 0.90, 85.7% accuracy, 92.9% sensitivity, and 71.4% specificity.
Conclusions: TNF-α emerged as a key cytokine linked to mortality in pediatric FM, supporting its role as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 21 pediatric FM cases from two tertiary centers (2012–2022). At admission, 37 cytokines and 14 clinical parameters were assessed. Partial least squares discriminant analysis was employed to identify prognostic features, with variable importance in projection scores quantifying their contribution. Model performance was evaluated using leave-one-out cross-validation. Statistical significance was determined via the Benjamini–Hochberg method at a false discovery rate of 0.05.
Results: Of the 51 features analyzed, 23 emerged as key predictors, 20 cytokines and 3 clinical parameters, with variable importance in projection scores above 1.0. Six cytokines (TNF-α, M-CSF, MIP-1α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-15) were both statistically significant and highly important. Among them, six cytokines (TNF-α, M-CSF, MIP-1α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-15) were both statistically significant and highly important. TNF-α had the highest VIP score among all predictors. Elevated CK-MB and lactate levels and lower pH were also linked to poor outcomes. The model performed robustly, with an AUC of 0.90, 85.7% accuracy, 92.9% sensitivity, and 71.4% specificity.
Conclusions: TNF-α emerged as a key cytokine linked to mortality in pediatric FM, supporting its role as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Cause of a Classic Presentation of NSTEMI: Case of 39-Year-Old Female with Hypothyroidism Induced Myocarditis
Quadri Fayz, Qazi Mariam, Teague Taylor
A Biomarker Based on Aneurysm Wall Enhancement and Blood Gene Expression to Identify Symptomatic Intracranial AneurysmsVeeturi Sricharan, Poppenberg Kerry, Jaikumar Vinay, Pinter Nandor, Levy Elad, Siddiqui Adnan, Tutino Vincent