Final ID: Sa3044
Sex-Specific Differences in Outcomes of Cardiogenic Shock Among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a life-threatening condition characterized by reduced tissue perfusion due to cardiac pump failure. In patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), the incidence and severity of CS are heightened due to accelerated atherosclerosis, microvascular dysfunction, and impaired myocardial recovery. Although sex-based differences in cardiovascular disease are increasingly recognized, their specific impact on outcomes in diabetic patients with CS remains largely understudied. Addressing these disparities is essential for improving outcomes and promoting equity in care.
Hypothesis
This systematic review evaluates whether sex-based differences exist in the presentation, management, and outcomes of CS in patients with type 2 DM. We hypothesize that women experience worse outcomes and receive less aggressive treatment than men.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed was conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Studies published from January 2000 to March 2025 were screened. Inclusion criteria: adults (≥18 years) with type 2 DM and CS, and outcomes reported by sex. Extracted data included study design, population details, interventions, and sex-stratified outcomes. Risk of bias was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Due to heterogeneity, a descriptive synthesis was performed.
Results
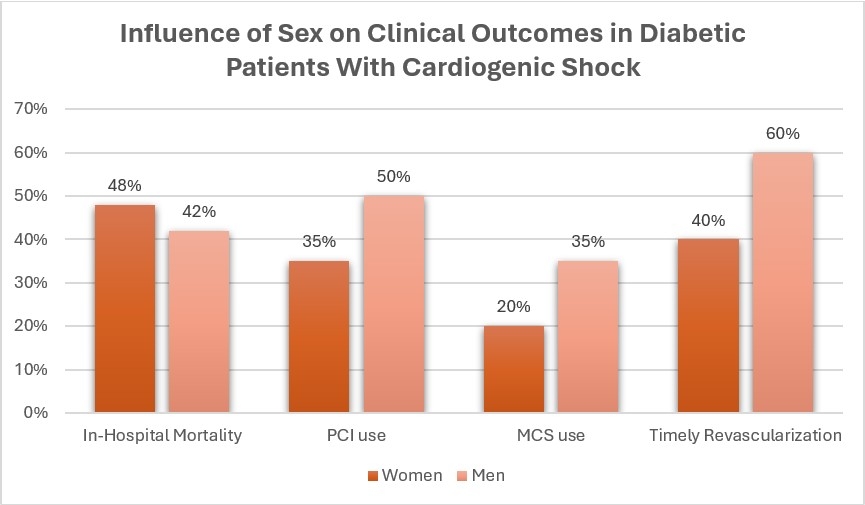
Twelve studies involving 25,000 patients met criteria. Women with CS and DM presented later, experienced longer delays in treatment, and were less likely to receive percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or mechanical circulatory support (MCS). In-hospital mortality among women ranged from 34% to 62%, compared to 28% to 55% in men. Six studies identified female sex as an independent predictor of mortality. Use of advanced hemodynamic monitoring and timely revascularization was lower in women.
Conclusion
Notable sex-specific disparities exist in CS outcomes among diabetic patients. Women face delayed care, reduced access to life-saving interventions, and higher mortality. These gaps reflect a mix of biological, clinical, and systemic factors. Future efforts should include more women in CS research, perform sex-stratified analyses, and develop tailored treatment strategies to reduce disparities.
Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a life-threatening condition characterized by reduced tissue perfusion due to cardiac pump failure. In patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), the incidence and severity of CS are heightened due to accelerated atherosclerosis, microvascular dysfunction, and impaired myocardial recovery. Although sex-based differences in cardiovascular disease are increasingly recognized, their specific impact on outcomes in diabetic patients with CS remains largely understudied. Addressing these disparities is essential for improving outcomes and promoting equity in care.
Hypothesis
This systematic review evaluates whether sex-based differences exist in the presentation, management, and outcomes of CS in patients with type 2 DM. We hypothesize that women experience worse outcomes and receive less aggressive treatment than men.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed was conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Studies published from January 2000 to March 2025 were screened. Inclusion criteria: adults (≥18 years) with type 2 DM and CS, and outcomes reported by sex. Extracted data included study design, population details, interventions, and sex-stratified outcomes. Risk of bias was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Due to heterogeneity, a descriptive synthesis was performed.
Results
Twelve studies involving 25,000 patients met criteria. Women with CS and DM presented later, experienced longer delays in treatment, and were less likely to receive percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or mechanical circulatory support (MCS). In-hospital mortality among women ranged from 34% to 62%, compared to 28% to 55% in men. Six studies identified female sex as an independent predictor of mortality. Use of advanced hemodynamic monitoring and timely revascularization was lower in women.
Conclusion
Notable sex-specific disparities exist in CS outcomes among diabetic patients. Women face delayed care, reduced access to life-saving interventions, and higher mortality. These gaps reflect a mix of biological, clinical, and systemic factors. Future efforts should include more women in CS research, perform sex-stratified analyses, and develop tailored treatment strategies to reduce disparities.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adiponectin and Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio Associate with Cardiometabolic Risk in South Asian Americans: Updates from the MASALA Study
Uttarwar Salil, Shah Nilay, Kanaya Alka, Gadgil Meghana
Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior and Risks of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Postmenopausal Cancer Survivors: The Women’s Health Accelerometry CollaborationHyde Eric, Stefanick Marcia, Skiba Meghan, Crane Tracy, Lee I-min, Lacroix Andrea, Bandoli Gretchen, Zou Jingjing, Crespo Noe, Parada Humberto, Evenson Kelly, Lamonte Michael, Nguyen Steve, Howard Annie Green