Final ID: MP1061
Integrated Assessment of Lipoprotein(a) and ECG Changes to Predict Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Ablation: A Retrospective Study of 2,356 Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels have been associated with cardiovascular risk, but their prognostic value in atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence following radiofrequency ablation remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive role of Lp(a) in post-ablation paroxysmal AF recurrence and explore its association with electrocardiographic (ECG) changes, particularly in lead II. We further assessed whether combining Lp(a) levels with ECG markers could enhance risk stratification after ablation.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 2,356 patients with paroxysmal AF who underwent radiofrequency catheter ablation at Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital between 2000 and 2023. The optimal cut-off value of Lp(a) for predicting post-ablation recurrence was determined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Patients were followed for a median duration of 13.7 months through outpatient visits and Holter monitoring. ECG parameters, including P-wave amplitude, PR interval, and QTc interval in lead II, were compared before ablation and during follow-up. Correlations between Lp(a) levels and ECG changes were also evaluated.
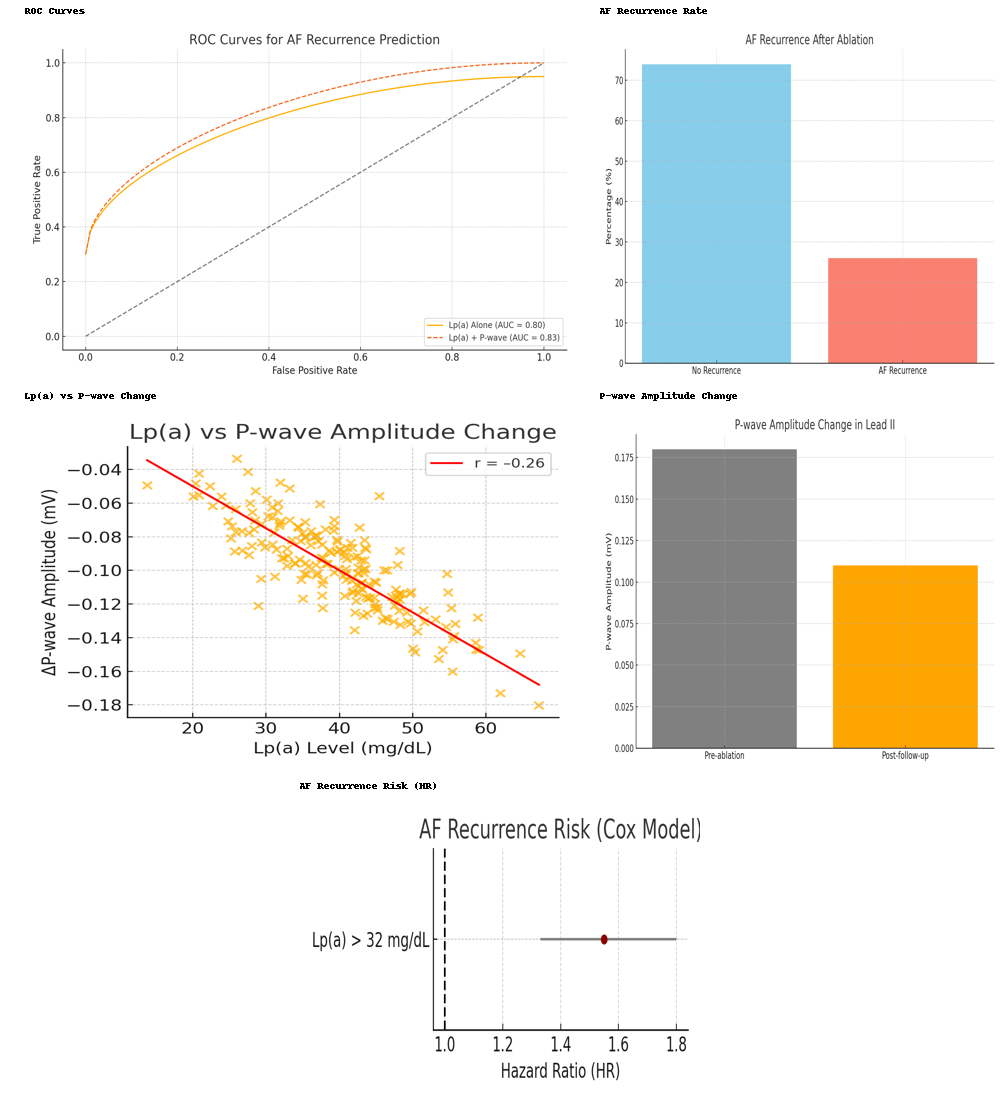
Results: Over a median follow-up of 13.7 months, AF recurrence occurred in 25.4% of patients. ROC analysis identified 32 mg/dL as the optimal Lp(a) threshold for predicting recurrence (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.72; 95% CI, 0.69–0.75; P<0.001), with a sensitivity of 68.2% and specificity of 65.4%. Patients with Lp(a) above this threshold had a significantly higher recurrence risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.55; 95% CI, 1.33–1.80; P<0.001). P-wave amplitude in lead II decreased significantly during follow-up compared to baseline (mean decrease, 0.06 mV; P<0.001), and Lp(a) levels were negatively correlated with this change (r = –0.26; P<0.001). No significant associations were found between Lp(a) and PR or QTc intervals. The combination of Lp(a) and P-wave amplitude change improved predictive performance for recurrence (AUC = 0.78; 95% CI, 0.74–0.81; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Lp(a) is a significant predictor of paroxysmal AF recurrence after catheter ablation and is inversely associated with post-ablation reductions in P-wave amplitude in lead II, potentially reflecting atrial electrical remodeling. Integrating Lp(a) levels with ECG-derived metrics enhances predictive accuracy and may aid in postoperative risk stratification and clinical decision-making.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical data from 2,356 patients with paroxysmal AF who underwent radiofrequency catheter ablation at Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital between 2000 and 2023. The optimal cut-off value of Lp(a) for predicting post-ablation recurrence was determined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Patients were followed for a median duration of 13.7 months through outpatient visits and Holter monitoring. ECG parameters, including P-wave amplitude, PR interval, and QTc interval in lead II, were compared before ablation and during follow-up. Correlations between Lp(a) levels and ECG changes were also evaluated.
Results: Over a median follow-up of 13.7 months, AF recurrence occurred in 25.4% of patients. ROC analysis identified 32 mg/dL as the optimal Lp(a) threshold for predicting recurrence (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.72; 95% CI, 0.69–0.75; P<0.001), with a sensitivity of 68.2% and specificity of 65.4%. Patients with Lp(a) above this threshold had a significantly higher recurrence risk (hazard ratio [HR], 1.55; 95% CI, 1.33–1.80; P<0.001). P-wave amplitude in lead II decreased significantly during follow-up compared to baseline (mean decrease, 0.06 mV; P<0.001), and Lp(a) levels were negatively correlated with this change (r = –0.26; P<0.001). No significant associations were found between Lp(a) and PR or QTc intervals. The combination of Lp(a) and P-wave amplitude change improved predictive performance for recurrence (AUC = 0.78; 95% CI, 0.74–0.81; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Lp(a) is a significant predictor of paroxysmal AF recurrence after catheter ablation and is inversely associated with post-ablation reductions in P-wave amplitude in lead II, potentially reflecting atrial electrical remodeling. Integrating Lp(a) levels with ECG-derived metrics enhances predictive accuracy and may aid in postoperative risk stratification and clinical decision-making.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Idiopathic Ventricular Fibrillation Triggered by Short-Coupled PVCs from the Apical Free Wall of the Right Ventricle
Patel Palak, Patel Gaurav, Oza Jaykumar, Correia Joaquim
Agbaje’s Waist-to-Height Ratio Estimated Fat Mass Pediatric Cutoff Predicts Elevated Blood Pressure Risk in Multi-racial US Children and AdolescentsCorsi Douglas, Agbaje Andrew