Final ID: MP1688
Temporal Sequence of Mitral Valve Disease and Atrial Fibrillation Impacts Cardiovascular Outcomes
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and mitral valve regurgitation (MVR) often co-occur in clinical settings, with the temporal sequence of their diagnoses potentially influencing cardiovascular outcomes. This study aimed to compare major cardiovascular event risks in patients diagnosed first with MVR followed by AF (MVR→AF) versus those with the reverse sequence (AF→MVR).
Methods:
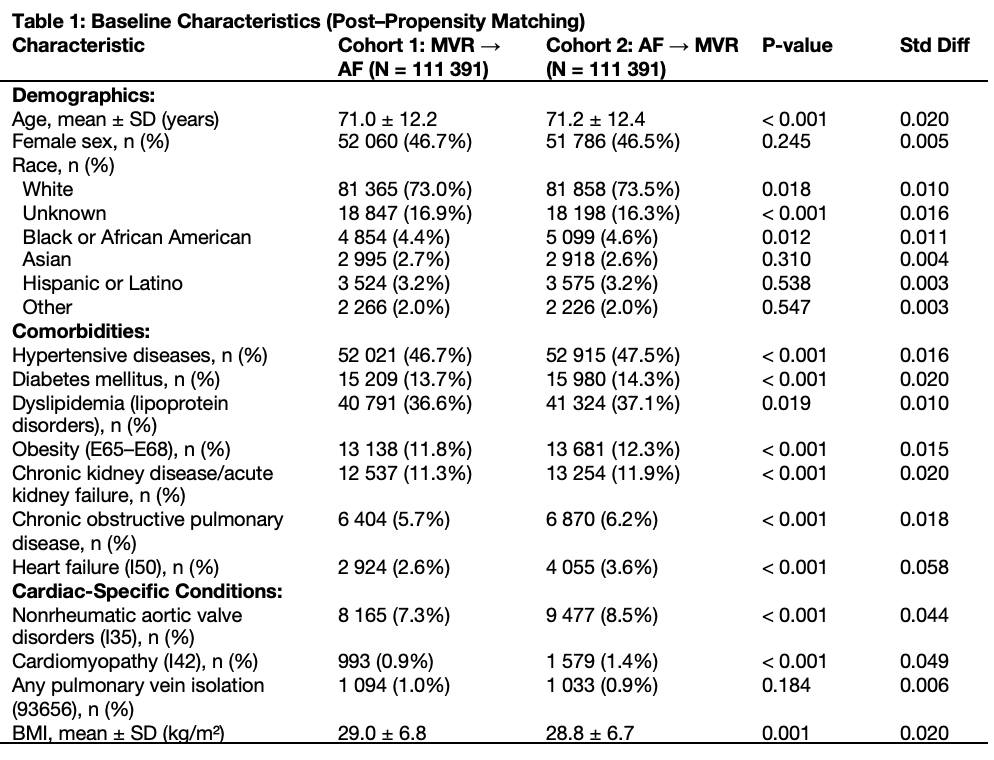
A retrospective comparative outcomes analysis was conducted using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, encompassing data from 135 healthcare organizations. Two cohorts were defined post–propensity score matching using demographic, comorbidities, procedures and treatment: Cohort 1 (MVR→AF; n = 111,391) and Cohort 2 (AF→MVR; n = 111,391). Patients were balanced across demographics and comorbidities to isolate outcome differences. Cardiovascular outcomes were compared via later Cox models to obtain the hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) (table 2).
Results:
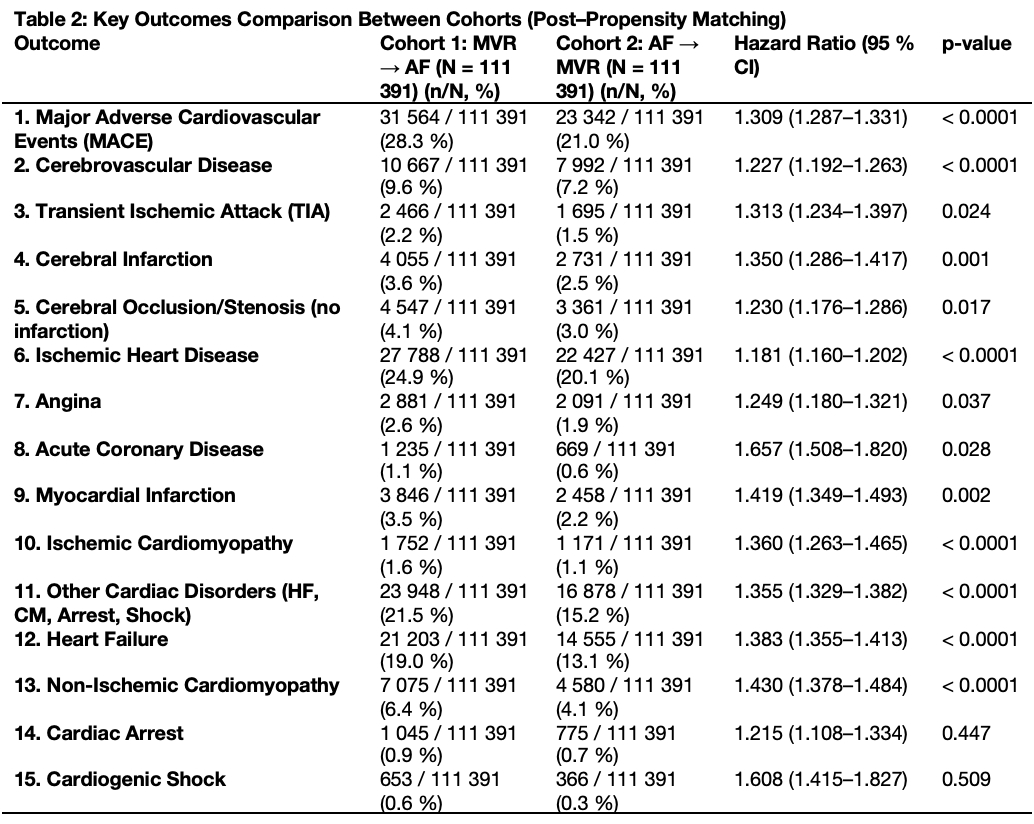
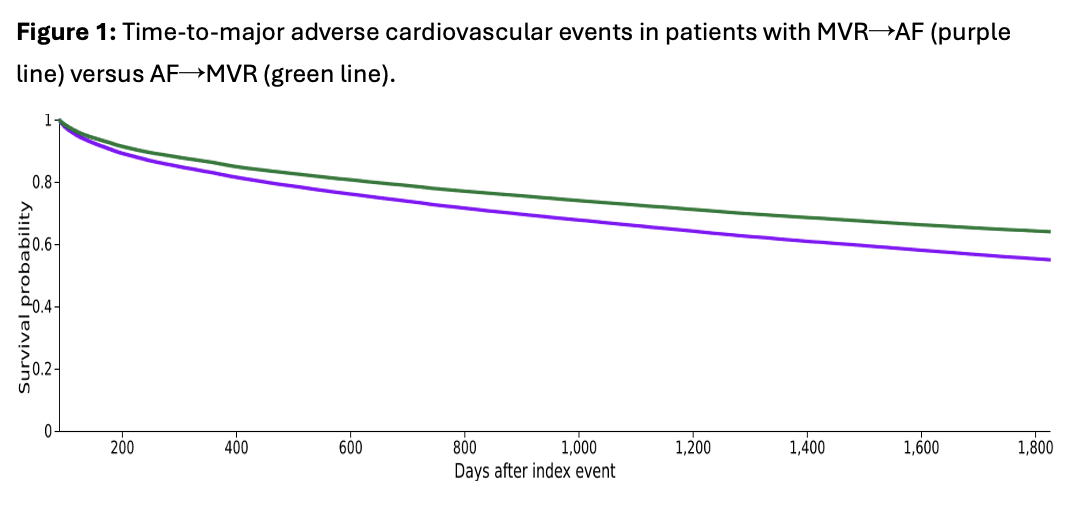
Despite similar baseline characteristics, the MVR→AF group exhibited significantly higher incidence rates of all evaluated cardiovascular outcomes. Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) occurred in 28.3% of MVR→AF patients compared to 21.0% in the AF→MVR cohort (HR 1.30; 95% CI: 1.28–1.33; p < 0.0001) (Figure 1). This trend persisted across subcategories including ischemic heart disease (HR 1.18), heart failure (HR 1.38), myocardial infarction (HR 1.41), and cerebrovascular outcomes such as cerebral infarction (HR 1.35) and TIA (HR 1.31). The most notable disparity was observed in acute coronary disease (HR 1.65; p = 0.028). Cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest, while elevated in the MVR→AF group, did not reach statistical significance (table 2).
Conclusion:
Patients with MVR preceding AF diagnosis are at significantly higher risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to those with AF diagnosed prior to MVR. These findings underscore the need for heightened surveillance and potential early intervention strategies in the MVR→AF population to mitigate downstream cardiovascular morbidity.
- Atasi, Mohammad Montaser ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Noujaim, Charbel ( Tulane Univeristy , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Mekhael, Mario ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Campbell, Charles ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Abi-rached, Joe ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Tsakiris, Eli ( Tulane University School of Medicin , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Lim, Chanho ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Hassan, Abboud ( Tulane School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Ksayer, Radia ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Liu, Yingshuo ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Rao, Swati ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Hubbard, Shea ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Kreidieh, Omar ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Pandey, Amitabh ( Tulane Univestiy School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Feng, Han ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Marrouche, Nassir ( Tulane University School of Medicin , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Toraih, Eman ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Younes, Hadi ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Abou Khalil, Michel ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Massad, Christian ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Bsoul, Mayana ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Menassa, Yara ( Tulane School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Bidaoui, Ghassan ( Tulane University , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Predicting Successful Surgical And Catheter-Based Mitral and Tricuspid Valve Repair
Sunday, 11/09/2025 , 09:15AM - 10:30AM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Garcia Huitron Eric Ivan, Zhang Xiaoying, Babcock Lance, Grande-allen Kathryn, Prakash Siddharth
Aortic Valve Neocuspidization Using Autologous Insertion Of Pulmonary SinusTm: A Proof Of ConceptFaateh Muhammad, Raees Muhammad Aanish, Ahmed Hosam, Almiqlash Bushray, Villalobos Lizardi Jose, Ricci Marco, Ashfaq Awais
More abstracts from these authors:
Abou Khalil Michel, Nahle Tarek, Abi-rached Joe, Abou Zeid Karl, Lim Chanho, Ksayer Radia, Hassan Abboud, Liu Yingshuo, Assaf Ala', Noujaim Charbel, Mekhael Mario, Massad Christian, Rao Swati, Kreidieh Omar, Pandey Amitabh, Marrouche Nassir, Jia Yishi, Feng Han, Menassa Yara, Bidaoui Ghassan, Younes Hadi, Atasi Mohammad Montaser, Bsoul Mayana
Pulsed Field Ablation Is Not Functionally Benign: Left Atrial Impact Mirrors Radiofrequency AblationMassad Christian, Hassan Abboud, Liu Yingshuo, Jia Yishi, Abi-rached Joe, Abou Zeid Karl, Noujaim Charbel, Dagher Lilas, Mekhael Mario, Rao Swati, Kreidieh Omar, Atasi Mohammad Montaser, Pandey Amitabh, Marrouche Nassir, Abou Khalil Michel, Bidaoui Ghassan, Younes Hadi, Bsoul Mayana, Menassa Yara, Feng Han, Lim Chanho