Final ID: MP619
System-level Barriers and Facilitators to EHR Interventions in the Implementation and Interaction of Clinician And Patient-facing Tools Aiming to Optimize Medications for Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction (IICAPTAIN-HF) Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background/Introduction:
Guideline-directed medical therapies (GDMT) for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) result in significant improvements in cardiac function, quality of life, and survival. However, busy clinicians treating stable patients do not often optimize medications. This clinical inertia results in GDMT underuse. The EPIC-HF trial tested effects of patient activation through a brief video and 1-page checklist sent to patients just prior to a clinic visit; the PROMPT-HF trial tested tailored electronic health record (EHR) alerts delivered to clinicians during clinic visits. Both EHR tools increased the appropriate use of GDMT while considering patients’ preferences and overall medical care. Yet, neither EPIC-HF nor PROMPT-HF have been implemented widely.
Research Objective:
The IICAPTAIN trial aims to understand barriers and facilitators within the PRISM framework in implementing automated interventions for GDMT intensification, with the goal of providing a generalizable framework to health systems nationwide.
Methods:
We conducted qualitative interviews with site principal investigators (PIs) and information technology (IT) leads at 5 diverse sites across the US, using a semi-structured interview guide to discuss barriers, facilitators, and adaptations for EPIC-HF and PROMPT-HF implementation at each site. Thematic analysis was used to determine emergent themes.
Results:
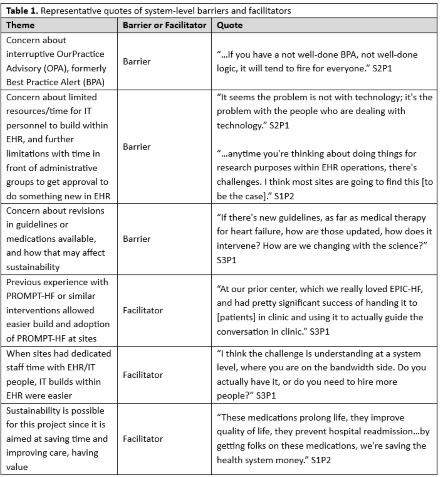
We interviewed 5 site PIs and 5 IT leads. Interviews yielded several themes (Table 1). Key facilitators include previous experience with PROMPT-HF or similar clinician decision support tools, and dedicated staff time with IT analysts. Additionally, respondents endorsed strong sustainability potential if the interventions save time and improve care. Key barriers include concern about interruptive alerts burdening clinicians, limited resources/time for IT teams to build within the EHR, the need for administrative approval, and concern about changing guidelines or medications and how this impacts sustainability.
Conclusions:
To implement GDMT interventions like PROMPT-HF and EPIC-HF, sites should emphasize the low clinician burden of automated processes. Sites should also account for administrative requirements and time limitations with EHR personnel, ensuring time is allocated for IT staff or liaisons to develop builds. Developing relationships with administrative groups and IT personnel can encourage adoption and implementation.
Guideline-directed medical therapies (GDMT) for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) result in significant improvements in cardiac function, quality of life, and survival. However, busy clinicians treating stable patients do not often optimize medications. This clinical inertia results in GDMT underuse. The EPIC-HF trial tested effects of patient activation through a brief video and 1-page checklist sent to patients just prior to a clinic visit; the PROMPT-HF trial tested tailored electronic health record (EHR) alerts delivered to clinicians during clinic visits. Both EHR tools increased the appropriate use of GDMT while considering patients’ preferences and overall medical care. Yet, neither EPIC-HF nor PROMPT-HF have been implemented widely.
Research Objective:
The IICAPTAIN trial aims to understand barriers and facilitators within the PRISM framework in implementing automated interventions for GDMT intensification, with the goal of providing a generalizable framework to health systems nationwide.
Methods:
We conducted qualitative interviews with site principal investigators (PIs) and information technology (IT) leads at 5 diverse sites across the US, using a semi-structured interview guide to discuss barriers, facilitators, and adaptations for EPIC-HF and PROMPT-HF implementation at each site. Thematic analysis was used to determine emergent themes.
Results:
We interviewed 5 site PIs and 5 IT leads. Interviews yielded several themes (Table 1). Key facilitators include previous experience with PROMPT-HF or similar clinician decision support tools, and dedicated staff time with IT analysts. Additionally, respondents endorsed strong sustainability potential if the interventions save time and improve care. Key barriers include concern about interruptive alerts burdening clinicians, limited resources/time for IT teams to build within the EHR, the need for administrative approval, and concern about changing guidelines or medications and how this impacts sustainability.
Conclusions:
To implement GDMT interventions like PROMPT-HF and EPIC-HF, sites should emphasize the low clinician burden of automated processes. Sites should also account for administrative requirements and time limitations with EHR personnel, ensuring time is allocated for IT staff or liaisons to develop builds. Developing relationships with administrative groups and IT personnel can encourage adoption and implementation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiovascular Health Declines During Young Adulthood – An Electronic Health Record Study of >75,000,000 Individuals
Ortiz Robin, Heffron Sean
A novel Notch and WNT signaling mechanism contribute to pediatric DCM: a pathway to new therapeuticsNyarko Obed, Miyamoto Shelley, Stauffer Brian, Sucharov Carmen