Final ID: MP616
Novel Strategies for Inferential Error Management in Reused Clinical Datasets
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction
The use of publicly available datasets and large-scale registries, such as the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) National Databases and the Medicare database, has revolutionized accessibility to large sample data across research centers. However, there are few existing data governance protocols for managing the risk of Type I and Type II across the expanding portfolio of studies requesting from the same registry.
Research Questions
We investigate how repeated and uncoordinated reuse of datasets increases the riskiness of Type I/II errors due to dependent risks, undermining the reliability of research findings. We also examine strategies to manage this risk by differentiating between actively managed and passively managed databases.
Methods
We adopt a decision-theoretic perspective to analyze how reuse of datasets can result in a dependence structure between tests that increases the disutility of the portfolio of Type I/II errors as measured by the actuarial notion of stop loss order.
Results
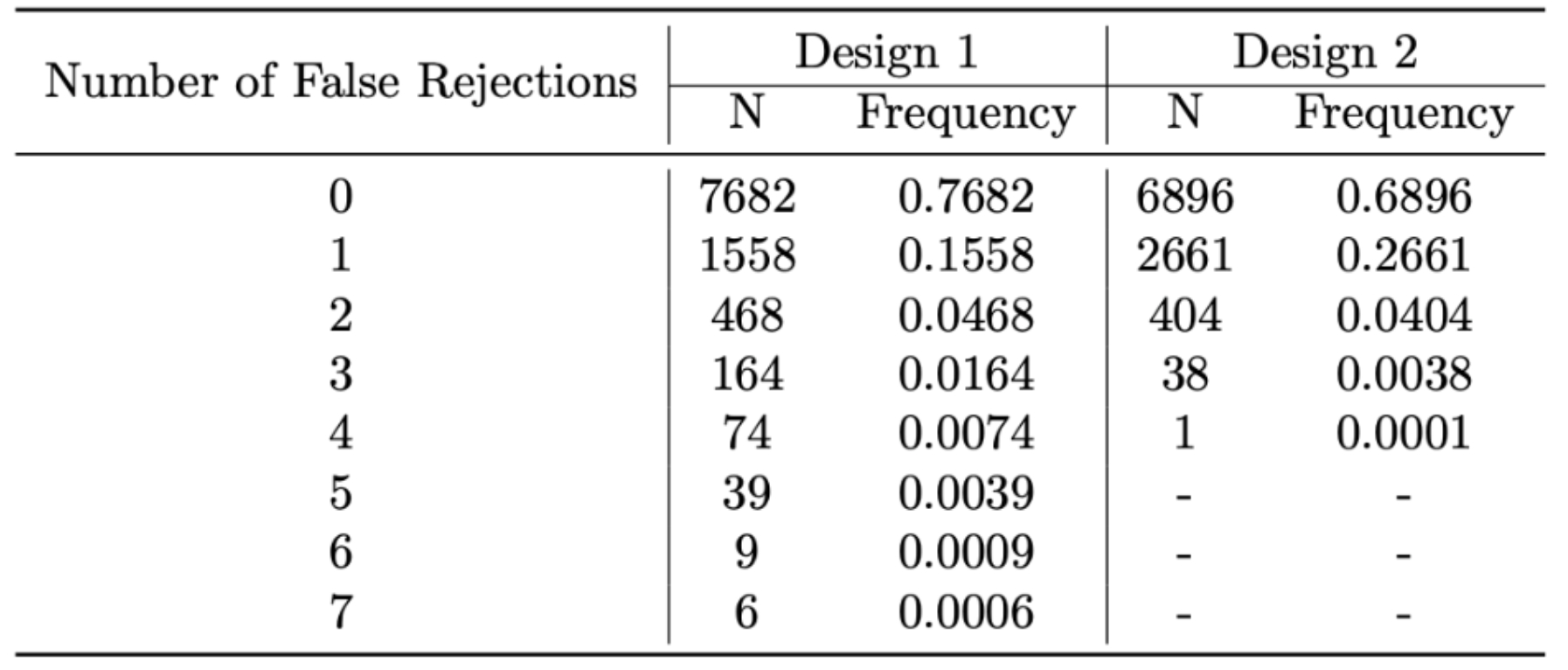
Figure 1 shows the distribution of Type I errors for a two-sample t-test comparing the means of seven treatment groups against a common control group with data reuse of the control (Design 1) vs. without reuse of the control (Design 2) in 10,000 simulations of the global null. While the FWER of Design 1 was lower than that of Design 2, the error distribution of Design 1 is strictly preferable in stop loss order. We further demonstrate how subsampling strategies and portfolio optimization techniques can be deployed in a variety of contexts to mitigate the effects of data reuse.
Conclusion
We are the first to propose a novel quantitative framework for reducing false positives and false negatives across multiple requests of the same database, providing a foundation for database managers to implement error control policies.
Existing measures of error control, such as per-comparison error rates, false discovery rates, and familywise error rates fail to address the complex error structures that arise from multiple, overlapping studies.
As reliance on large clinical datasets grows, especially those with high usage, robust error management strategies are crucial. Active dataset management offers a way to maintain the validity of conclusions from large registries. We advocate for increased funding of small, well-powered studies and the development of guidelines and software for dataset managers to effectively allocate inferential resources.
Introduction
The use of publicly available datasets and large-scale registries, such as the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) National Databases and the Medicare database, has revolutionized accessibility to large sample data across research centers. However, there are few existing data governance protocols for managing the risk of Type I and Type II across the expanding portfolio of studies requesting from the same registry.
Research Questions
We investigate how repeated and uncoordinated reuse of datasets increases the riskiness of Type I/II errors due to dependent risks, undermining the reliability of research findings. We also examine strategies to manage this risk by differentiating between actively managed and passively managed databases.
Methods
We adopt a decision-theoretic perspective to analyze how reuse of datasets can result in a dependence structure between tests that increases the disutility of the portfolio of Type I/II errors as measured by the actuarial notion of stop loss order.
Results
Figure 1 shows the distribution of Type I errors for a two-sample t-test comparing the means of seven treatment groups against a common control group with data reuse of the control (Design 1) vs. without reuse of the control (Design 2) in 10,000 simulations of the global null. While the FWER of Design 1 was lower than that of Design 2, the error distribution of Design 1 is strictly preferable in stop loss order. We further demonstrate how subsampling strategies and portfolio optimization techniques can be deployed in a variety of contexts to mitigate the effects of data reuse.
Conclusion
We are the first to propose a novel quantitative framework for reducing false positives and false negatives across multiple requests of the same database, providing a foundation for database managers to implement error control policies.
Existing measures of error control, such as per-comparison error rates, false discovery rates, and familywise error rates fail to address the complex error structures that arise from multiple, overlapping studies.
As reliance on large clinical datasets grows, especially those with high usage, robust error management strategies are crucial. Active dataset management offers a way to maintain the validity of conclusions from large registries. We advocate for increased funding of small, well-powered studies and the development of guidelines and software for dataset managers to effectively allocate inferential resources.
More abstracts on this topic:
Altering Cardiovascular Mortality in HFpEF with SGLT2i or ARNI — A Head-to-Head Analysis
Hariyanto Jesslyn, Veera Chirag, Lenzi Pinto Manoela, Chatterjee Anoushka, Eltawansy Sherif
Cardiologist Attitude to Lipid Control in Patients with ASCVD without Major Cardiovascular Events: Insights from the 2024 ACS EuroPath SurveyZaman Azfar, De Caterina Raffaele, Schiele Francois, Sionis Alessandro, Catapano Alberico, Laufs Ulrich