Final ID: Mo3044
High Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children Undergoing Heart Transplantation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction and Objectives: Children with congenital heart disease (CHD) have an increased risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) compared to the general population, with a higher prevalence of ASD in those undergoing surgery early in infancy. However, data regarding the burden of ASD in children with heart failure undergoing ventricular assist device (VAD) or heart transplant (HTx) are scarce.
Methods: A single-center retrospective cohort study including patients who underwent HTx from 2014 to 2024 and were seen in a cardiac developmental outcomes clinic. Primary outcome was diagnosis of ASD as defined by the Childhood Autism Rating Scale 2-ST (CARS2-ST) or Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, 2nd Edition (ADOS-2). CARS2-ST raw score severity was classified as mild/moderate (30-36.5) and severe (≥37). Demographic and clinical data were collected to evaluate factors associated with ASD in this population. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05.
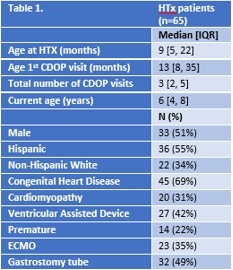
Results: Of the 139 patients who underwent HTx during the study period, 65 (49%) attended the clinic and were included in this study (Table 1). Twenty-seven (42%) were diagnosed with ASD, median age at ASD diagnosis of 46 [interquartile range (IQR) 34, 70] months. All but one patient had ASD diagnosed after HTx. Nineteen (79%) patients had severe CARS-ST scores, while 5 (21%) had mild-moderate scores (3 scores not available). Seventeen patients (63%) had CHD pre-HTx, with 5/17 bridged to HTx on VAD, while 10 (37%) had cardiomyopathy, with 6/10 bridged to HTx on VAD. Within the ASD cohort, 16 (59%) were male, and 4 (15%) were non-Hispanic White. There was no significant association of age at transplant, age at first clinic visit, total number of visits, prematurity, etiology of heart failure (CHD vs cardiomyopathy), presence of VAD, history of ECMO, or gastrostomy tube with ASD diagnosis. However, we observed a greater proportion of Hispanics in the ASD cohort compared to non-ASD (78% vs 39%, p=0.008).
Conclusions: Forty-two percent of children undergoing HTx and enrolled in our outcomes clinic were diagnosed with ASD, representing 19% of all patients who underwent HTx during the study period. This is higher than the prevalence of ASD in the CHD population or the general pediatric population, highlighting the importance of continued neurodevelopmental surveillance and the inclusion of all children undergoing heart transplantation, even those without CHD.
Methods: A single-center retrospective cohort study including patients who underwent HTx from 2014 to 2024 and were seen in a cardiac developmental outcomes clinic. Primary outcome was diagnosis of ASD as defined by the Childhood Autism Rating Scale 2-ST (CARS2-ST) or Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, 2nd Edition (ADOS-2). CARS2-ST raw score severity was classified as mild/moderate (30-36.5) and severe (≥37). Demographic and clinical data were collected to evaluate factors associated with ASD in this population. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05.
Results: Of the 139 patients who underwent HTx during the study period, 65 (49%) attended the clinic and were included in this study (Table 1). Twenty-seven (42%) were diagnosed with ASD, median age at ASD diagnosis of 46 [interquartile range (IQR) 34, 70] months. All but one patient had ASD diagnosed after HTx. Nineteen (79%) patients had severe CARS-ST scores, while 5 (21%) had mild-moderate scores (3 scores not available). Seventeen patients (63%) had CHD pre-HTx, with 5/17 bridged to HTx on VAD, while 10 (37%) had cardiomyopathy, with 6/10 bridged to HTx on VAD. Within the ASD cohort, 16 (59%) were male, and 4 (15%) were non-Hispanic White. There was no significant association of age at transplant, age at first clinic visit, total number of visits, prematurity, etiology of heart failure (CHD vs cardiomyopathy), presence of VAD, history of ECMO, or gastrostomy tube with ASD diagnosis. However, we observed a greater proportion of Hispanics in the ASD cohort compared to non-ASD (78% vs 39%, p=0.008).
Conclusions: Forty-two percent of children undergoing HTx and enrolled in our outcomes clinic were diagnosed with ASD, representing 19% of all patients who underwent HTx during the study period. This is higher than the prevalence of ASD in the CHD population or the general pediatric population, highlighting the importance of continued neurodevelopmental surveillance and the inclusion of all children undergoing heart transplantation, even those without CHD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A CRISPR-Activation CROP-seq Screen Identifies HMGN1 as a Dosage-Sensitive Regulator of Heart Defects in Down Syndrome
Ranade Sanjeev, Mital Rahul, Boileau Ryan, Koback Frances, Padmanabhan Arun, Merriman Alexander, Wallace Langley, Nguyen Annie, Poulis Nikolaus, Gifford Casey, Pollard Katherine, Li Feiya, Srivastava Deepak, Whalen Sean, Angelo Pelonero, Ye Lin, Huang Yu, Brand Abigail, Nishino Tomohiro, Costa Mauro
A Porcine Model of Cardiac Arrest Without Pre-Arrest Fluid Loading, Sternal Molding, or EpinephrineParadis Aidan, Paradis Norman, Gaddy David, Moodie Karen, Mader Timothy, Dufresne Alexandre, Couturier Christine, Dufresne Simon, Davis Daniel, Sims Christopher