Final ID: MP1290
CT-Based Radiomics Offers Prognostic Insight in Cardiomyopathy Patients Undergoing ICD Implantation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Intramyocardial fat and scar burden have been linked to mortality in cardiomyopathy (CM) patients. However, the prognostic value of advanced imaging features derived from cardiac CT remains underexplored. This study evaluated whether radiomic features from cardiac CT improve prediction of all-cause mortality in CM patients receiving a primary prevention implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
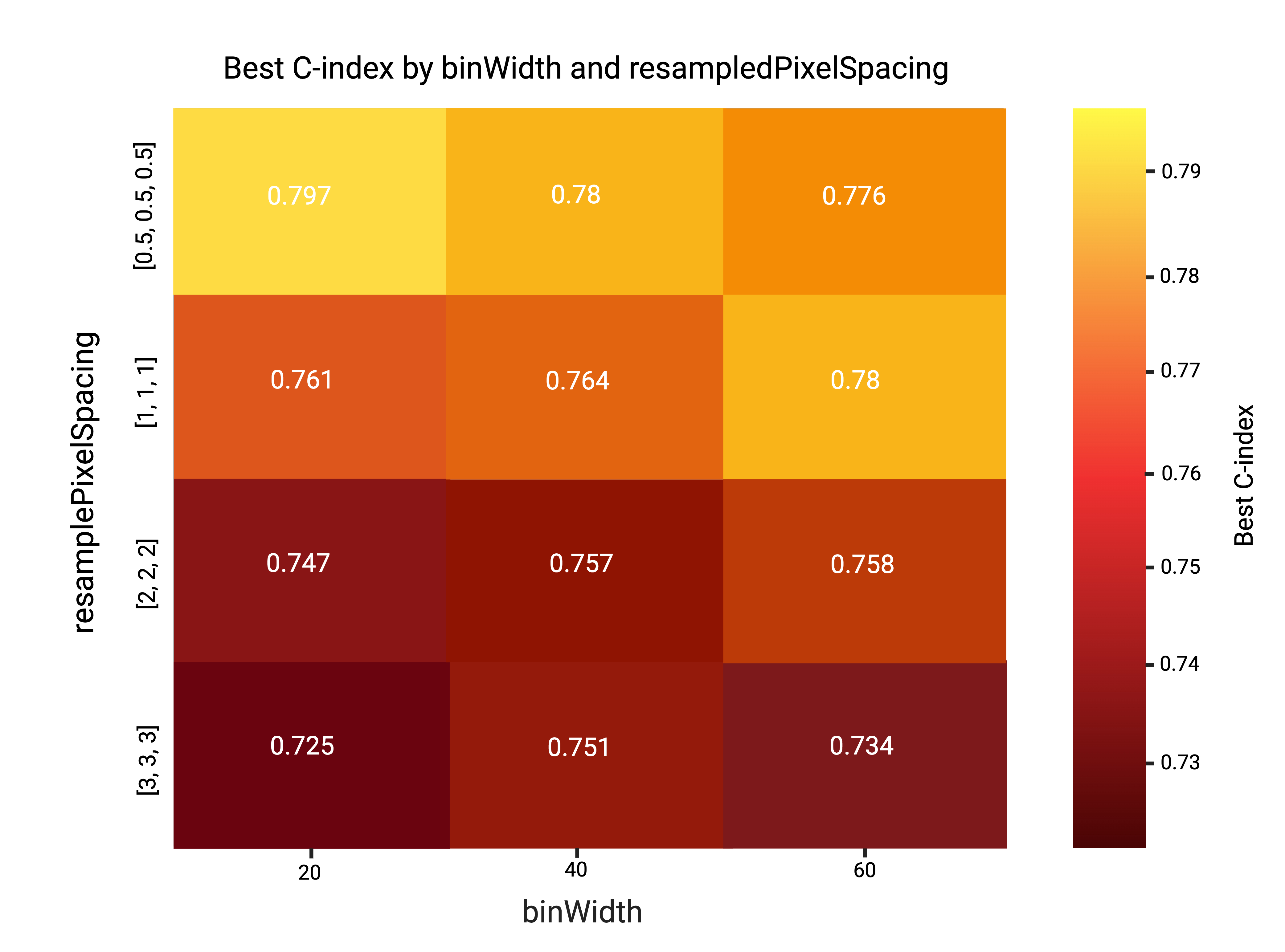
Methods: Patients enrolled in the PROSE-ICD study underwent cardiac CT and were followed for all-cause death. CTs were acquired on 64-slice scanners, and the left ventricle was segmented using 3D Slicer with TotalSegmentator. A total of 92 radiomic features were extracted (PyRadiomics 3.0.1) across four resampling grids (0.5–3 mm) and three bin widths (20–60 HU). The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality; ventricular arrhythmic events (n=6, 11%) were analyzed descriptively due to low counts. A clinical Cox model (age, CM etiology, diabetes) and four radiomics-based survival models were trained using 15×3-fold cross-validation. The best radiomics model (GBS, 0.5 mm grid, 20-HU bin) was combined with clinical variables in a second-stage Cox model. Model discrimination (c-index), calibration, and feature importance were assessed using Python 3.11 (lifelines, scikit-survival).
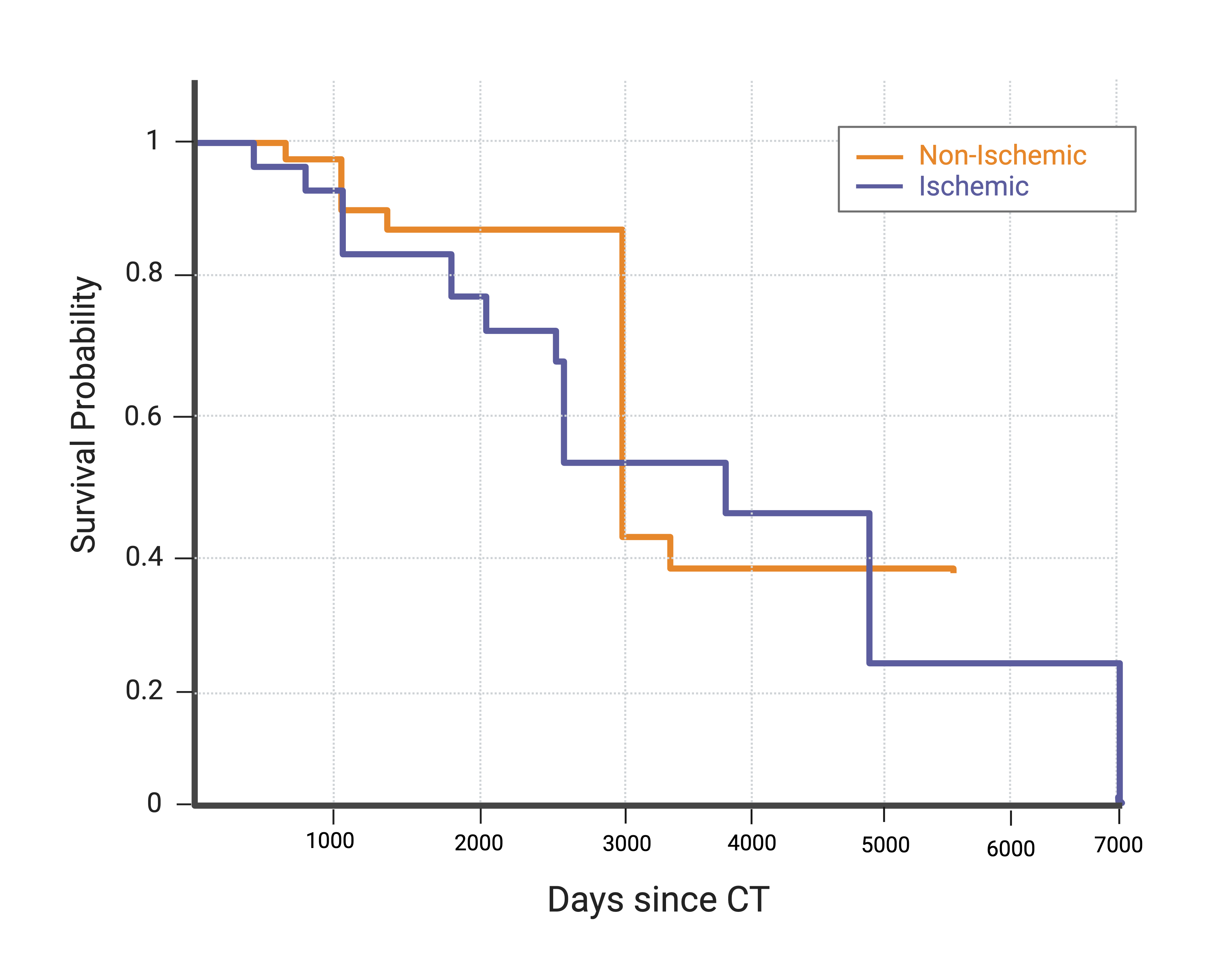
Results: Among 55 patients (mean age 64 ± 9 years; 20% female; 76% White; 65.5% ischemic CM), 13 (24%) died over a median follow-up of 3,284 days (~9 years). Hypertension (89%), hyperlipidemia (95%), and diabetes (47%) were highly prevalent. Mean LVEF was 24 ± 13.7%, and 33% had a history of ventricular arrhythmia. Five-year survival was higher in non-ischemic vs. ischemic CM (89% vs. 74%, p=0.12). Diabetes was the only independent clinical predictor of mortality (HR 5.31, 95% CI 1.14–24.7, p=0.03); age and CM etiology were not significant. The clinical Cox model yielded a c-index of 0.70. The best radiomics model, based on myocardial texture heterogeneity, achieved a c-index of 0.80. Combining radiomics with clinical variables improved discrimination to 0.81 (Δ +0.02, p=0.08) with good five-year calibration (slope = 0.94).
Conclusion: Radiomic features derived from high-resolution cardiac CT substantially enhance prediction of long-term mortality in cardiomyopathy patients receiving primary prevention ICDs, offering a promising non-invasive tool for personalized risk stratification.
Methods: Patients enrolled in the PROSE-ICD study underwent cardiac CT and were followed for all-cause death. CTs were acquired on 64-slice scanners, and the left ventricle was segmented using 3D Slicer with TotalSegmentator. A total of 92 radiomic features were extracted (PyRadiomics 3.0.1) across four resampling grids (0.5–3 mm) and three bin widths (20–60 HU). The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality; ventricular arrhythmic events (n=6, 11%) were analyzed descriptively due to low counts. A clinical Cox model (age, CM etiology, diabetes) and four radiomics-based survival models were trained using 15×3-fold cross-validation. The best radiomics model (GBS, 0.5 mm grid, 20-HU bin) was combined with clinical variables in a second-stage Cox model. Model discrimination (c-index), calibration, and feature importance were assessed using Python 3.11 (lifelines, scikit-survival).
Results: Among 55 patients (mean age 64 ± 9 years; 20% female; 76% White; 65.5% ischemic CM), 13 (24%) died over a median follow-up of 3,284 days (~9 years). Hypertension (89%), hyperlipidemia (95%), and diabetes (47%) were highly prevalent. Mean LVEF was 24 ± 13.7%, and 33% had a history of ventricular arrhythmia. Five-year survival was higher in non-ischemic vs. ischemic CM (89% vs. 74%, p=0.12). Diabetes was the only independent clinical predictor of mortality (HR 5.31, 95% CI 1.14–24.7, p=0.03); age and CM etiology were not significant. The clinical Cox model yielded a c-index of 0.70. The best radiomics model, based on myocardial texture heterogeneity, achieved a c-index of 0.80. Combining radiomics with clinical variables improved discrimination to 0.81 (Δ +0.02, p=0.08) with good five-year calibration (slope = 0.94).
Conclusion: Radiomic features derived from high-resolution cardiac CT substantially enhance prediction of long-term mortality in cardiomyopathy patients receiving primary prevention ICDs, offering a promising non-invasive tool for personalized risk stratification.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy-Based Model Estimate of the Prevalence of Danon Disease in the United States
Maron Martin, Massera Daniele, Manganaro Susan, Bailey Miranda, Rehbein Fletcher, Taylor Matthew
A-band titin-truncating variant promotes the development of arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy in a novel genetically-engineered porcine modelLee Kwonjae, Del Rio Carlos, Mcnally Elizabeth, Pfenniger Anna, Bhatnagar Ashita, Glinton Kristofor, Burrell Amy, Ober Rebecca, Mcluckie Alicia, Bishop Brian, Rogers Christopher, Geist Gail