Final ID: Su1027
Cardiovascular and Renal Effects of Physical Training in Male Rats Under Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Treatment
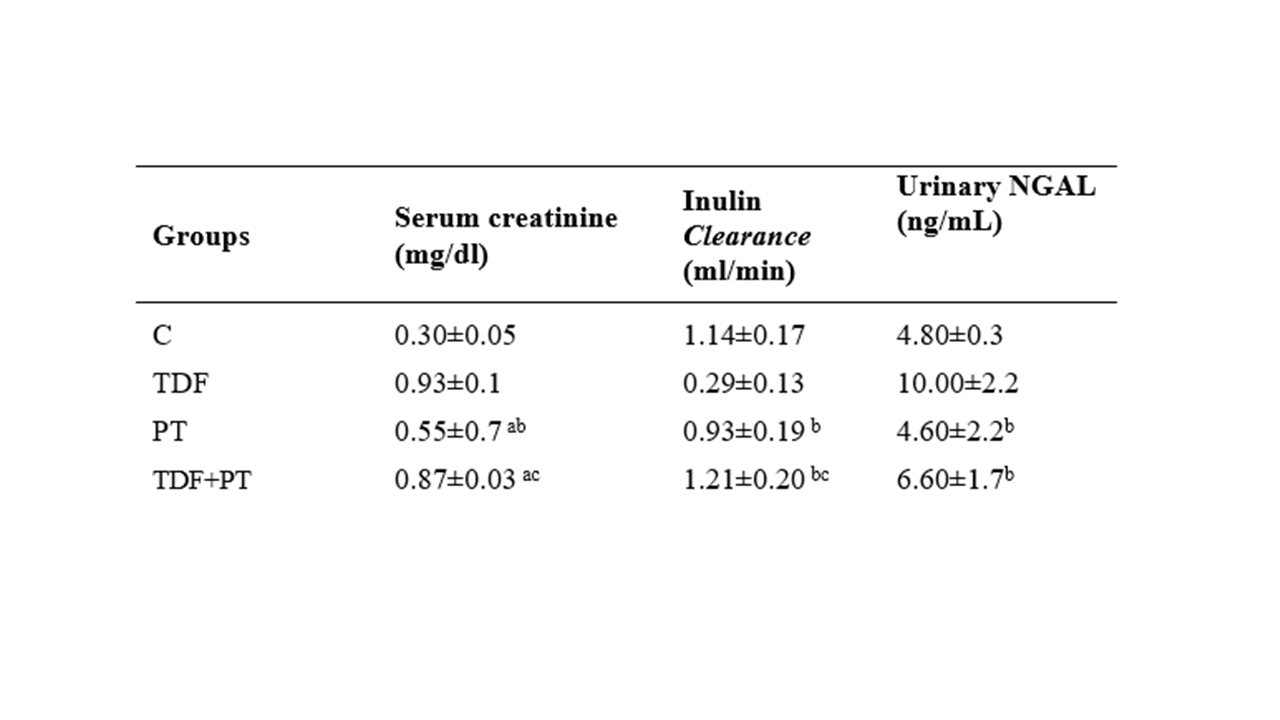
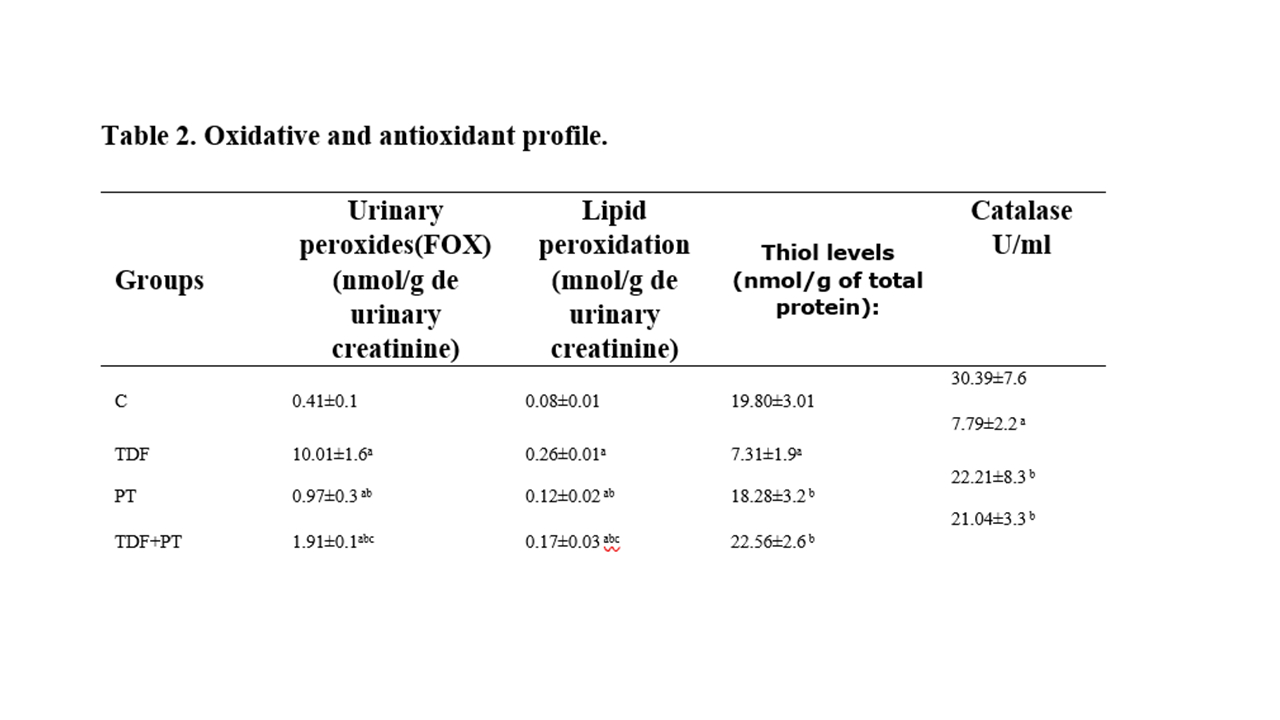
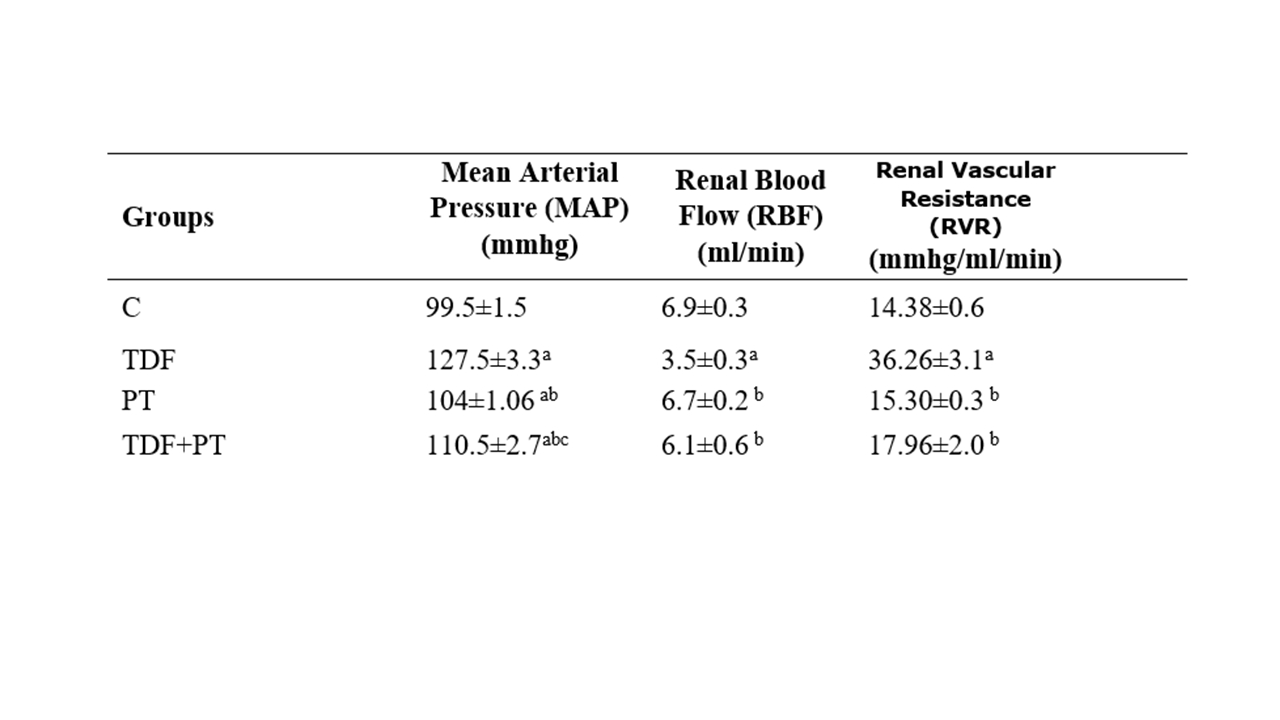
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF), a crucial antiretroviral for HIV/AIDS and hepatitis B, causes nephrotoxicity and cardiovascular dysfunction (including blood pressure alterations) through oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in renal tubules, leading to acute kidney injury in 10-30% of patients. Although these adverse effects are well-documented, protective strategies remain underexplored. Physical exercise can be a promising approach, with renoprotective and vascular benefits. Materials and Methods: Ethics approval: 2100/2024. Adult Wistar rats(n=28) were divided into four groups (n=7/group): Control (C): vehicle treatment; TDF: TDF (600 mg/kg, gavage, 5 days); Physical Training (PT): swimming training (60 minutes, 5 days/week, with 5% body weight attached to the tail) until the 28th day; PT+TDF: TDF treatment and physical training as described. Methods: Regarding hemodynamic parameters, the animals receiving TDF showed an increase in mean arterial pressure, whereas those that swam exhibited reduction in arterial pressure, decreased renal vascular resistance, and enhanced renal blood flow. Renal function was evaluated by inulin clearance (Clin), Neutrophil gelatinase-associated-lipocalin (NGAL) and serum creatinine were also evaluated. The oxidative profile was evaluated by urinary peroxides (FOX), lipid peroxides (TBARS) and Thiois and catalase. Results Regarding hemodynamic parameters showed that the animals receiving TDF presented an increase in mean arterial pressure, whereas those that swam exhibited improved reduction in arterial pressure, decreased renal vascular resistance, and enhanced renal blood flow. The PT+TDF showed an increased inulin clearance compared with the non trainned rats. The oxidative profile showed a significant improvement as evidenced by PT+TDF enhanced thiol and catalase levels and also an improvement in FOX, compared to the TDF. Conclusions: TDF treatment impaired blood pressure, renal blood flow, renal function and increased oxidative stress. Moderate physical training showed renoprotective effects, improving tubular function and reducing oxidative damage and hemodinamic profile.
More abstracts on this topic:
A soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator improves survival in a rat model of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and chronic kidney disease induced by aorto-caval fistula and 5/6 nephrectomy
Kala Petr, Miklovic Matus, Molnar Matej, Mikula Jan, Skaroupkova Petra, Gawrys Olga, Ostadal Petr, Melenovsky Vojtech, Cervenka Ludek
A Finding of Unique Peak Exercise Level in Respiratory Exchange Ratio during Bicycle Ergometric Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Healthy SubjectsNakayama Atsuko, Sakuma Hiroki, Iwata Tomoharu, Kashino Kunio, Isobe Mitsuaki, Tomoike Hitonobu