Final ID: MP142
Artificial Intelligence (AI) empowered Fetal Echocardiography - A Meta-Analysis Exploring its Image Processing and Diagnostic Prowess
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Artificial Intelligence (AI) models have the potential to revolutionize fetal echocardiography, enhancing image processing and diagnostic capabilities. There is promise in AI's potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of congenital heart defect detection in utero. There is significant interest towards Machine learning’s enhanced capabilities in automated segmentation of fetal cardiac structures, reducing inter-observer variability, enhancing image quality and early detection of congenital heart diseases (CHD). Deep learning models have exhibited high sensitivity and specificity in identifying various cardiac anomalies. AI-assisted fetal echocardiography has also demonstrated potential in reducing false-positive rates and minimizing unnecessary interventions, improving fetal survival rates. Traditional fetal echocardiogram has been shown to struggle from limitations such as fetal, maternal and equipment factors, which paves the way for advanced AI models to step-in.
This review was conducted in accordance with the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis” (PRISMA) guidelines. An extensive search was conducted in all the major medical databases for relevant articles concerning machine learning algorithms and its application in fetal echocardiography. This was followed by a detailed systematic review to derive and analyse the relevant qualitative and quantitative data. The statistical analysis was performed in R-Studio. Pooled accuracy was assessed using the metaprop function. The heterogeneity of the papers was assessed using Higgins' I^2 test.
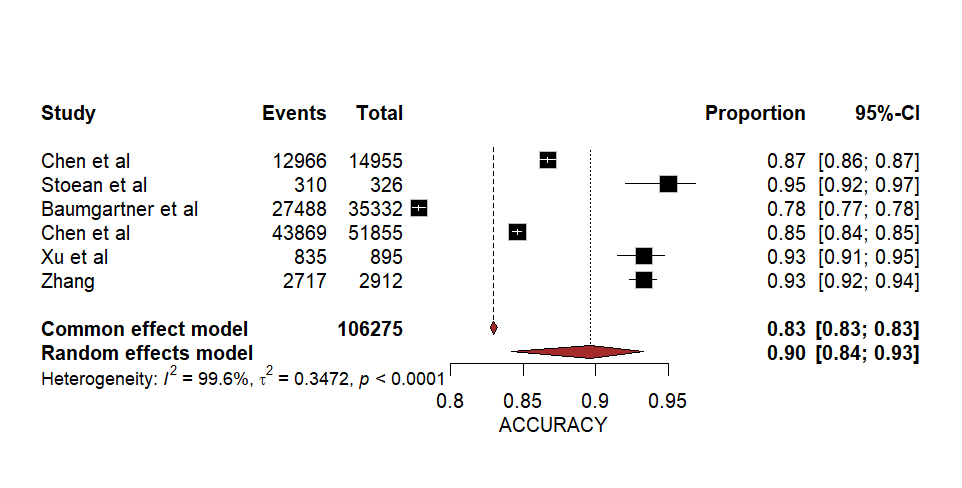
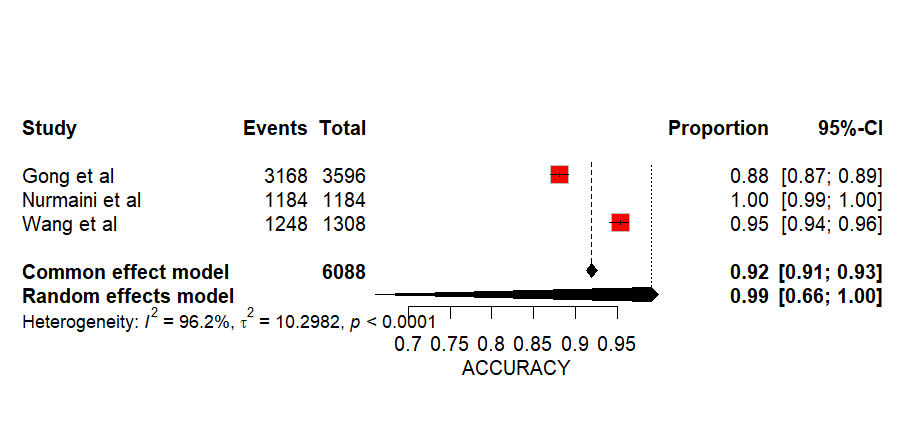
The meta-analysis included a total of 9 papers, amounting to 106275 quantitative elements concerning image processing and 6088 elements on the diagnostic and predictive faculties of the AI algorithms, resulting in a pooled accuracy of 0.90 [0.84;0.93, 95% CI, p<0.0001] and 0.99 [0.66;1.00, 95% CI, p<0.0001] respectively. The highest individual accuracy amounted to 93.32% by Zhang et al for image processing, while an accuracy of 100% by Nurmaini et al was the highest for diagnostic prediction. The random effects model was used to compare and assess the quantitative data. The review also highlighted the individual qualitative characteristics of the AI models.
AI's utility in terms of fortifying fetal echocardiography has been statistically shown to be clinically significant, as evident by its high accuracy. AI's adoption into various clinical aspects has been shown to be promising.
This review was conducted in accordance with the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis” (PRISMA) guidelines. An extensive search was conducted in all the major medical databases for relevant articles concerning machine learning algorithms and its application in fetal echocardiography. This was followed by a detailed systematic review to derive and analyse the relevant qualitative and quantitative data. The statistical analysis was performed in R-Studio. Pooled accuracy was assessed using the metaprop function. The heterogeneity of the papers was assessed using Higgins' I^2 test.
The meta-analysis included a total of 9 papers, amounting to 106275 quantitative elements concerning image processing and 6088 elements on the diagnostic and predictive faculties of the AI algorithms, resulting in a pooled accuracy of 0.90 [0.84;0.93, 95% CI, p<0.0001] and 0.99 [0.66;1.00, 95% CI, p<0.0001] respectively. The highest individual accuracy amounted to 93.32% by Zhang et al for image processing, while an accuracy of 100% by Nurmaini et al was the highest for diagnostic prediction. The random effects model was used to compare and assess the quantitative data. The review also highlighted the individual qualitative characteristics of the AI models.
AI's utility in terms of fortifying fetal echocardiography has been statistically shown to be clinically significant, as evident by its high accuracy. AI's adoption into various clinical aspects has been shown to be promising.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Mitral Inflow Obstruction Induces Left Ventricular Unloading Without Affecting Right Ventricular Hemodynamics in a Fetal Lamb Model
Miyagi Chihiro, Onohara Daisuke, Nakamae Kosuke, Hussaini Syed Faizullah, Watanabe Tatsuya, Yuhara Satoshi, Alaniz Sarah, Louey Samantha, Padala Muralidhar, Jonker Sonnet
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patientsHaimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron