Final ID: MP1256
Performance of Large Language Models in Analyzing Common Hypertension Scenarios in Clinical Practice
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background/Objective: Hypertension is the most prevalent chronic disease in primary care and a leading cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite existing guidelines, therapeutic inertia and suboptimal control persist. Large language models (LLMs) offer a potential valuable addition to augment clinical decision-making, yet their reliability for guideline-driven tasks remains unverified. This study evaluated the accuracy and safety of hypertension management recommendations generated by three LLMs compared to expert responses.
Methods: Fifty-one clinical vignettes representing 17 core hypertension management concepts were constructed by hypertension experts. Each case was submitted to three LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini, MedLM) and a hypertension expert also wrote the “gold standard” answers. Three blinded expert reviewers rated each response on a 4-point accuracy scale, a binary safety (safe/unsafe) scale, and attempted to identify the source (LLM vs. expert) providing the response. Ratings were analyzed using mean scores, percentages of accurate and safe responses, and inter-rater agreement.
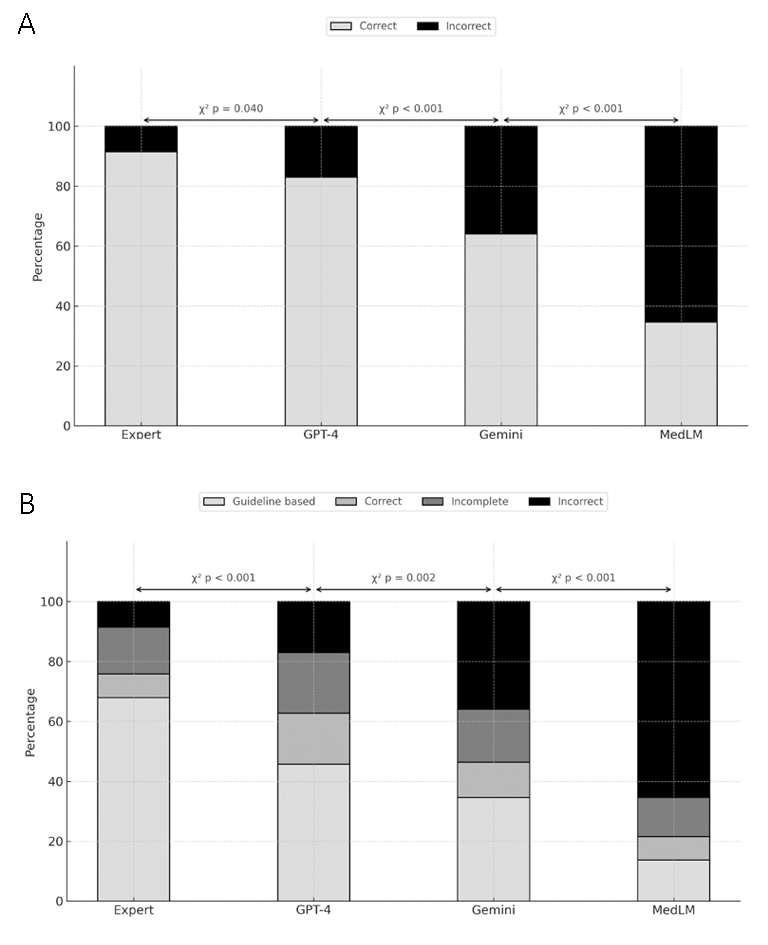
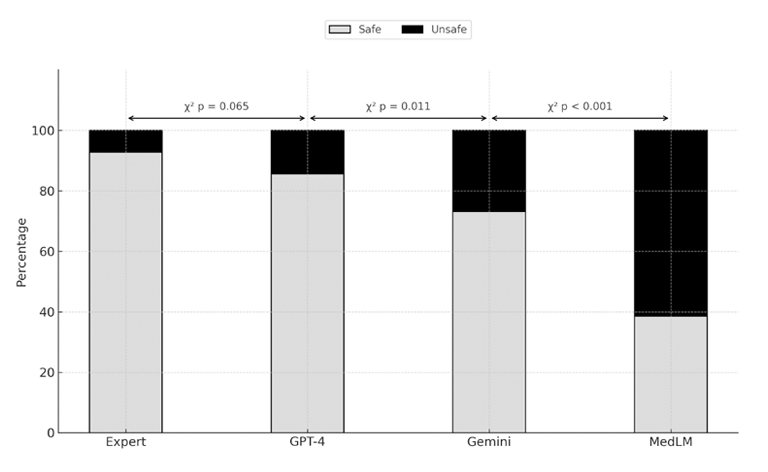
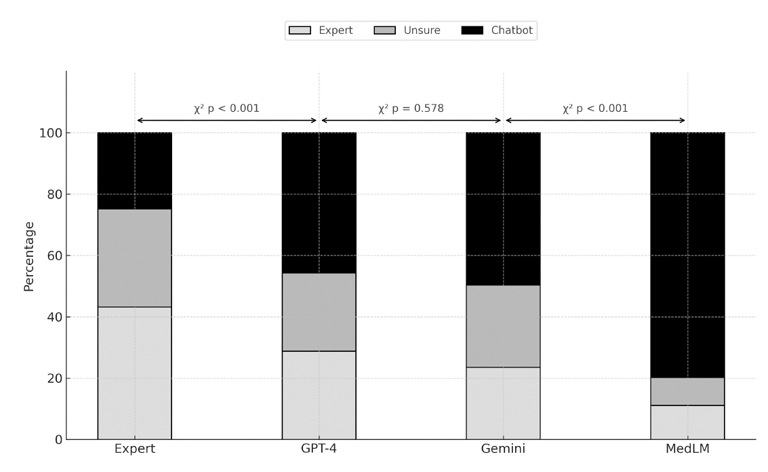
Results: GPT-4 had the highest accuracy (83%) and safety (86%) scores among LLMs but remained inferior to expert responses (92% accuracy, 93% safety). Gemini and MedLM performed significantly worse (accuracy: 64% and 35%; safety: 73% and 39%, respectively). GPT-4 generated the most guideline-concordant responses (46%) among the three LLMs (Gemini 35%, MedLM 14%), but remains lower than experts’ responses (68%). Evaluators misidentified LLM responses as expert-written in 10 to 25% of cases, particularly with GPT-4. Inter-rater reliability for accuracy ratings was highest for expert-generated responses (ICC 0.81), with progressively lower agreement for GPT-4 (0.76), Gemini (0.70), and MedLM (0.68). A similar pattern was observed for safety and source discrimination ratings. The agreement was strongest for safety assessments and weakest for source discrimination.
Conclusion: Among three tested LLMs, GPT-4 demonstrated closer agreement to expert decisions thereby showing greater potential for supporting hypertension management. However, current LLMs’ versions frequently produce inaccurate or unsafe recommendations and remain inferior to expert judgment. Human-in-the-loop supervision remains essential when deploying LLMs for clinical decision-making.
Methods: Fifty-one clinical vignettes representing 17 core hypertension management concepts were constructed by hypertension experts. Each case was submitted to three LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini, MedLM) and a hypertension expert also wrote the “gold standard” answers. Three blinded expert reviewers rated each response on a 4-point accuracy scale, a binary safety (safe/unsafe) scale, and attempted to identify the source (LLM vs. expert) providing the response. Ratings were analyzed using mean scores, percentages of accurate and safe responses, and inter-rater agreement.
Results: GPT-4 had the highest accuracy (83%) and safety (86%) scores among LLMs but remained inferior to expert responses (92% accuracy, 93% safety). Gemini and MedLM performed significantly worse (accuracy: 64% and 35%; safety: 73% and 39%, respectively). GPT-4 generated the most guideline-concordant responses (46%) among the three LLMs (Gemini 35%, MedLM 14%), but remains lower than experts’ responses (68%). Evaluators misidentified LLM responses as expert-written in 10 to 25% of cases, particularly with GPT-4. Inter-rater reliability for accuracy ratings was highest for expert-generated responses (ICC 0.81), with progressively lower agreement for GPT-4 (0.76), Gemini (0.70), and MedLM (0.68). A similar pattern was observed for safety and source discrimination ratings. The agreement was strongest for safety assessments and weakest for source discrimination.
Conclusion: Among three tested LLMs, GPT-4 demonstrated closer agreement to expert decisions thereby showing greater potential for supporting hypertension management. However, current LLMs’ versions frequently produce inaccurate or unsafe recommendations and remain inferior to expert judgment. Human-in-the-loop supervision remains essential when deploying LLMs for clinical decision-making.
More abstracts on this topic:
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiography
Jing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef
A Deep Learning Topic Analysis Approach for Enhancing Risk Assessment in Heart Failure Using Unstructured Clinical NotesAdejumo Philip, Pedroso Aline, Khera Rohan