Final ID: MP2413
Hemodynamic Determinants of Exercise Oxygen Uptake in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Severely limited exercise tolerance is a hallmark of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity. Stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR) rise coordinately during exertion, thereby increasing oxygen uptake (VO2). However, how obesity modifies the relative contributions of these VO2 component variables remains unclear.
Hypothesis
In patients with HFpEF, the augmentation of VO2 to meet the metabolic demands of exercise—as reflected by relative increases in SV and HR—differs according to the presence or absence of obesity.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 393 patients with HFpEF who underwent invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing (iCPET), comprised of CPET with simultaneous invasive hemodynamic monitoring, at Massachusetts General Hospital. We calculated the changes in direct Fick stroke volume (△SV) and heart rate (△HR) from rest to peak exercise from the iCPET data. The primary analysis examined the association between body-mass index (BMI) and the natural-log–transformed SV-to-HR augmentation ratio [ln(△SV/△HR)]. We also computed the change in O2 pulse (VO2/HR) from rest to peak exercise (△O2 pulse) and evaluated its associations with both BMI and ln(△SV/△HR) to determine whether O2 pulse can serve as a noninvasive surrogate to derive relative SV vs. HR augmentation patterns.
Results
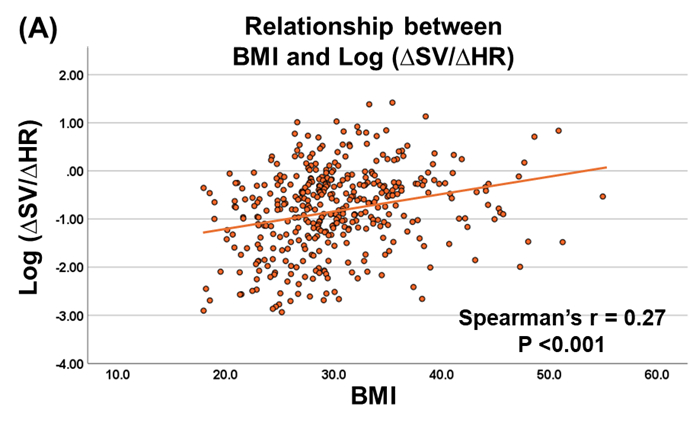
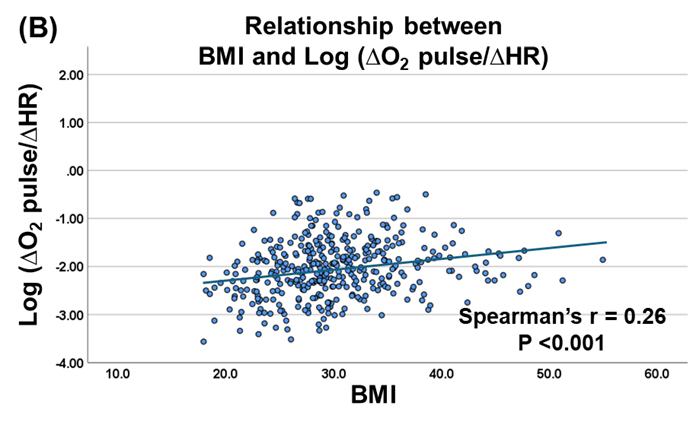
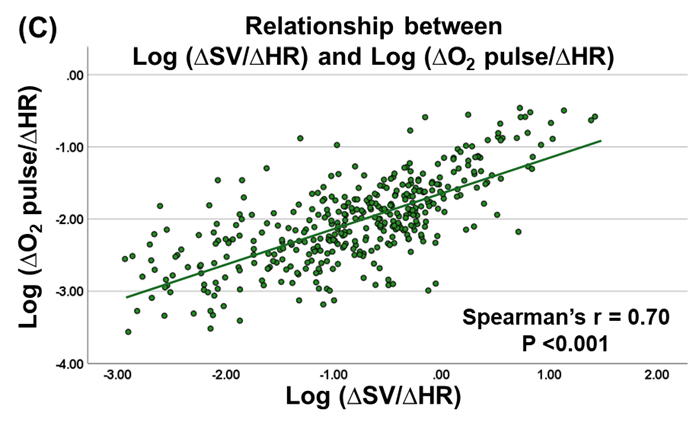
The cohort’s median age was 65 years, and 52.4 % were female. Median BMI was 29.3 kg/m2, with 43.5% classified as obese (BMI ≧ 30 kg/m2). BMI correlated positively with ln(△SV/△HR) (r = 0.27, P <0.001). Median ln(△SV/△HR) was −0.90 (IQR −1.61 to -0.32) in non-obese versus −0.53 (IQR −1.02 to -1.12) in obese patients, indicating a more predominant SV reserve in the obese HFpEF group (P <0.001). Across the cohort, ln(△O2 pulse/△HR) was also positively associated with BMI (r = 0.26, P <0.001) and had moderately strong correlation with ln(△SV/△HR) (r = 0.70, P <0.001).
Conclusions
In patients with HFpEF, obesity is linked to a hemodynamic shift toward greater reliance on SV reserve and diminished HR contribution during exercise. Moreover, O2 pulse appears to be a practical non-invasive surrogate for SV. These findings have implications for exercise-based phenotyping and individualized interventions that aim to augment exercise capacity in obese HFpEF populations.
Severely limited exercise tolerance is a hallmark of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity. Stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR) rise coordinately during exertion, thereby increasing oxygen uptake (VO2). However, how obesity modifies the relative contributions of these VO2 component variables remains unclear.
Hypothesis
In patients with HFpEF, the augmentation of VO2 to meet the metabolic demands of exercise—as reflected by relative increases in SV and HR—differs according to the presence or absence of obesity.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 393 patients with HFpEF who underwent invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing (iCPET), comprised of CPET with simultaneous invasive hemodynamic monitoring, at Massachusetts General Hospital. We calculated the changes in direct Fick stroke volume (△SV) and heart rate (△HR) from rest to peak exercise from the iCPET data. The primary analysis examined the association between body-mass index (BMI) and the natural-log–transformed SV-to-HR augmentation ratio [ln(△SV/△HR)]. We also computed the change in O2 pulse (VO2/HR) from rest to peak exercise (△O2 pulse) and evaluated its associations with both BMI and ln(△SV/△HR) to determine whether O2 pulse can serve as a noninvasive surrogate to derive relative SV vs. HR augmentation patterns.
Results
The cohort’s median age was 65 years, and 52.4 % were female. Median BMI was 29.3 kg/m2, with 43.5% classified as obese (BMI ≧ 30 kg/m2). BMI correlated positively with ln(△SV/△HR) (r = 0.27, P <0.001). Median ln(△SV/△HR) was −0.90 (IQR −1.61 to -0.32) in non-obese versus −0.53 (IQR −1.02 to -1.12) in obese patients, indicating a more predominant SV reserve in the obese HFpEF group (P <0.001). Across the cohort, ln(△O2 pulse/△HR) was also positively associated with BMI (r = 0.26, P <0.001) and had moderately strong correlation with ln(△SV/△HR) (r = 0.70, P <0.001).
Conclusions
In patients with HFpEF, obesity is linked to a hemodynamic shift toward greater reliance on SV reserve and diminished HR contribution during exercise. Moreover, O2 pulse appears to be a practical non-invasive surrogate for SV. These findings have implications for exercise-based phenotyping and individualized interventions that aim to augment exercise capacity in obese HFpEF populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A RETRO-ENANTIOMER OF ANGIOTENSIN-(1-9) PREVENTS THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION.
Ocaranza Maria Paz, Jimenez Veronica, Yanez Osvaldo, Jalil Jorge, Venegas Camilo, Candia Camila, Hermoso Marcela, Gabrielli Luigi, Morales Javier, Oyarzun Felipe, Torres Cristian, Lillo Pablo
A short version of HFD/L-NAME mouse model enabling time-effective proof of concept studies to evaluate drugs targeting the cardiometabolic and mild hypertension associated HFpEF phenotype.Assaly Rana, Dubroca Caroline, Waget Aurelie, Perrier Kevin, Sulpice Thierry