Final ID: MP881
Impact of Cerebral Embolic Protection Devices on Stroke Outcomes in TAVR: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Real-World Studies
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Stroke is a devastating complication of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Cerebral embolic protection devices (CEPD) have been introduced to reduce TAVR-related stroke by capturing or deflecting debris during the procedure. While these devices can capture embolic material, their clinical benefit in preventing stroke remains uncertain. We aimed to determine whether the use of CEPD during TAVR reduces the incidence of periprocedural stroke.
Methods We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing TAVR with versus without CEPD. We searched PubMed, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov for RCTs (randomized controlled trials) comparing CEPDs to no protection in TAVR patients from 2011 to May 2025. Nine RCTs involving a total of 11,608 patients (CEPD group n=5,953; control n=5,655) were included. Stroke outcomes were defined according to Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 (VARC-2) criteria and categorized as- all stroke, disabling stroke, or non-disabling stroke. Risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a fixed-effects model. Heterogeneity also was measured.
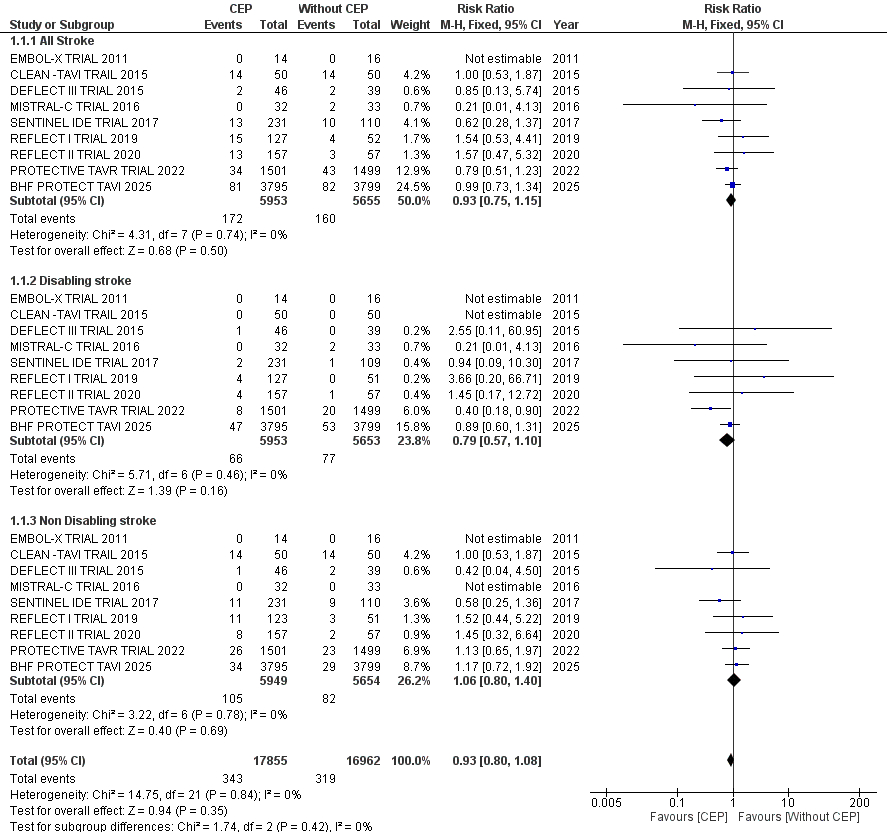
Results Stroke rates were low and did not differ significantly between the CEPD (n=343) and control (n=319) groups. The incidence of all strokes was 1.96% with CEPD vs 1.88% without CEPD (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.75–1.15; p=0.50). Disabling stroke occurred in 0.79% of CEPD patients vs 0.95% of controls (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.57-1.10; p=0.16). Non-disabling stroke occurred in 1.26% of patients in both groups (RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.8 -1.40; p=0.64). There was no significant heterogeneity across trials is (0) for all endpoints. Notably, the largest trial in the analysis (BHF PROTECT-TAVI, n=7,635) showed no difference in stroke rates with CEPD, aligning with the overall results. Subgroup analyses revealed a trend toward fewer disabling strokes with CEPD use, but this trend was not statistically significant.
Conclusion We found no significant stroke risk reduction with the use of CEPDs during TAVR. While a trend toward fewer disabling strokes was observed, it was not statistically significant. Routine use of CEPDs is not supported, and selective use in high-risk patients warrants further large RCTs.
Methods We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing TAVR with versus without CEPD. We searched PubMed, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov for RCTs (randomized controlled trials) comparing CEPDs to no protection in TAVR patients from 2011 to May 2025. Nine RCTs involving a total of 11,608 patients (CEPD group n=5,953; control n=5,655) were included. Stroke outcomes were defined according to Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 (VARC-2) criteria and categorized as- all stroke, disabling stroke, or non-disabling stroke. Risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a fixed-effects model. Heterogeneity also was measured.
Results Stroke rates were low and did not differ significantly between the CEPD (n=343) and control (n=319) groups. The incidence of all strokes was 1.96% with CEPD vs 1.88% without CEPD (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.75–1.15; p=0.50). Disabling stroke occurred in 0.79% of CEPD patients vs 0.95% of controls (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.57-1.10; p=0.16). Non-disabling stroke occurred in 1.26% of patients in both groups (RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.8 -1.40; p=0.64). There was no significant heterogeneity across trials is (0) for all endpoints. Notably, the largest trial in the analysis (BHF PROTECT-TAVI, n=7,635) showed no difference in stroke rates with CEPD, aligning with the overall results. Subgroup analyses revealed a trend toward fewer disabling strokes with CEPD use, but this trend was not statistically significant.
Conclusion We found no significant stroke risk reduction with the use of CEPDs during TAVR. While a trend toward fewer disabling strokes was observed, it was not statistically significant. Routine use of CEPDs is not supported, and selective use in high-risk patients warrants further large RCTs.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparative Outcomes of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation and Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Right Heart Failure: Insights from Nationwide Readmission Database
Kansakar Sajog, Katz Daniel, Shrestha Dhan, Shtembari Jurgen, Sharma Nava, Pant Kailash, Moskovits Norbert, Shetty Vijay, Dahal Khagendra, Mattumpuram Jishanth
Association Between Kidney Function and Severity of White Matter Hyperintensity: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities StudyLittig Lauren, Krothapalli Neeharika, Wong Ka-ho, Kim Yvonne, Smith Harper, De Havenon Adam