Final ID: Su3151
Direct Oral Anticoagulants versus Vitamin K Antagonists for Left Ventricular Thrombus Resolution: An Updated Pooled Analysis of Randomized Studies
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Left ventricular thrombus (LVT) remains a significant complication after anterior MI and among patients with reduced systolic function. VKAs have traditionally been the treatment of choice for LVT although have the disadvantages of having a less predictable pharmacokinetic profile, need for INR monitoring, and slower onset of action as compared to DOACs. Clinically, DOAC have been used for LVT but they remain an off-label use as per the FDA. The purpose of this pooled analysis is to quantify the safety and efficacy of DOACs versus VKAs for LVT resolution.
Methods: A systematic review according to PRISMA guidelines was conducted of MEDLINE to search for randomized controlled trials comparing a DOAC to VKA for any LVT. Search terms included “Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban, Dabigatran” and “LV thrombus OR left ventricular thrombus”. Studies were only included if they were prospective and randomized with a control group using VKA. Clinical characteristics and dichotomous outcomes of LVT resolution at 3 months were aggregated using a random effects model to calculate odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals using the Mantel-Haenszel method. Revman 5.4 was used to aggregate statistics and generate the forest plot.
Results:
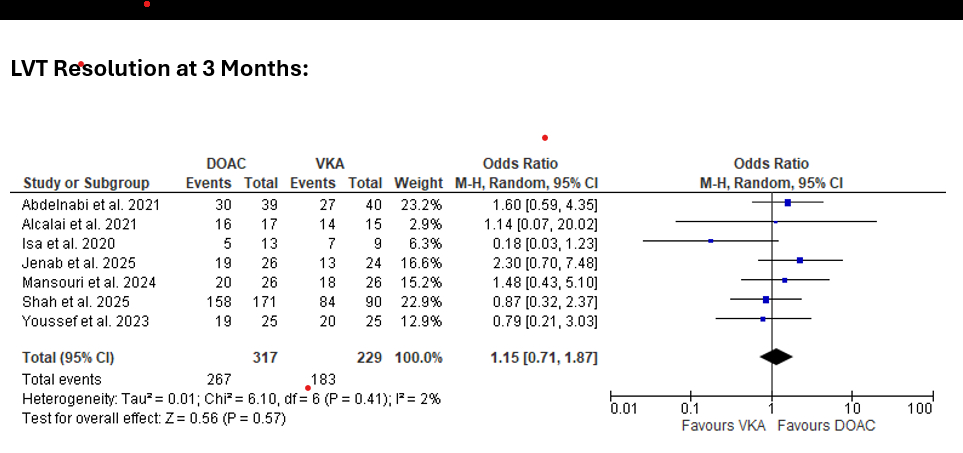
A total of 546 patients from seven randomized controlled trials were included. The average age ranged from 50-60 years. Females were presented about 5-20% in the trials. Most patients represented were within 2 weeks from an anterior STEMI with an average EF of 30%. Four trials utilized rivaroxaban while 3 trials used Apixaban. LVT resolved in 257 of the 317 patients in the DOAC arm versus 183 in the VKA arm representing an odds ratio of 1.15 [0.71, 1.87] P=0.57. Study heterogeneity was not significant (p=0.41).
Conclusions:
In this pooled analysis of seven randomized studies, DOAC’s were non-inferior to VKAs for LVT resolution at 3 months. Further long-term data from an adequately powered RCT are needed to quantify safety outcomes including the risk of systemic embolism and stroke.
Methods: A systematic review according to PRISMA guidelines was conducted of MEDLINE to search for randomized controlled trials comparing a DOAC to VKA for any LVT. Search terms included “Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban, Dabigatran” and “LV thrombus OR left ventricular thrombus”. Studies were only included if they were prospective and randomized with a control group using VKA. Clinical characteristics and dichotomous outcomes of LVT resolution at 3 months were aggregated using a random effects model to calculate odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals using the Mantel-Haenszel method. Revman 5.4 was used to aggregate statistics and generate the forest plot.
Results:
A total of 546 patients from seven randomized controlled trials were included. The average age ranged from 50-60 years. Females were presented about 5-20% in the trials. Most patients represented were within 2 weeks from an anterior STEMI with an average EF of 30%. Four trials utilized rivaroxaban while 3 trials used Apixaban. LVT resolved in 257 of the 317 patients in the DOAC arm versus 183 in the VKA arm representing an odds ratio of 1.15 [0.71, 1.87] P=0.57. Study heterogeneity was not significant (p=0.41).
Conclusions:
In this pooled analysis of seven randomized studies, DOAC’s were non-inferior to VKAs for LVT resolution at 3 months. Further long-term data from an adequately powered RCT are needed to quantify safety outcomes including the risk of systemic embolism and stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Synthetic Small Molecule Efficiently Sequesters Carbon Monoxide from Hemoglobin and Red Blood Cells In Vitro
Correnti Jacob, Ai Yong, Gladwin Mark, Xue Fengtian, Rose Jason, Demartino Anthony
Administration of the Recombinant Activated Protein C Rescues the Cardiac Vulnerability to Ischemic Insults in Aging through Modulating Inflammatory Response during Ischemia and ReperfusionSlotabec Lily, Rouhi Nadiyeh, Seale Blaise, Wang Hao, Filho Fernanda, Adenawoola Michael, Li Ji