Final ID: MP437
Comparative Associations of Estrone, Estrone Sulfate, and Estradiol With Cardiovascular Events: Evidence From NHANES 2017–2023
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background:
Emerging research underscores the importance of endogenous estrogens in cardiovascular health across sexes. Estrone sulfate, a stable circulating estrogen reservoir, has been shown to have longer half-life and greater concentrations than estradiol, particularly in postmenopausal women. While estradiol is traditionally considered the dominant cardioprotective hormone, recent findings suggest estrone sulfate may exert direct vascular effects and influence inflammation and lipid metabolism. However, the role of estrone, estrone sulfate, and estradiol in relation to major cardiovascular events—such as heart failure (HF), coronary artery disease (CAD), and myocardial infarction (MI)—remains incompletely understood.
Methods:
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 5,527 participants (2,495 males and 3,032 females) from NHANES with available serum hormone data. Subjects were stratified into quartiles (Q1–Q4) by levels of estrone (ng/dL), estrone sulfate (pg/mL), and estradiol (pg/mL). Multivariate logistic regression was performed to examine the association of each hormone with risk of HF, CAD, or MI, adjusting for age, sex, race, BMI, smoking, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Results:
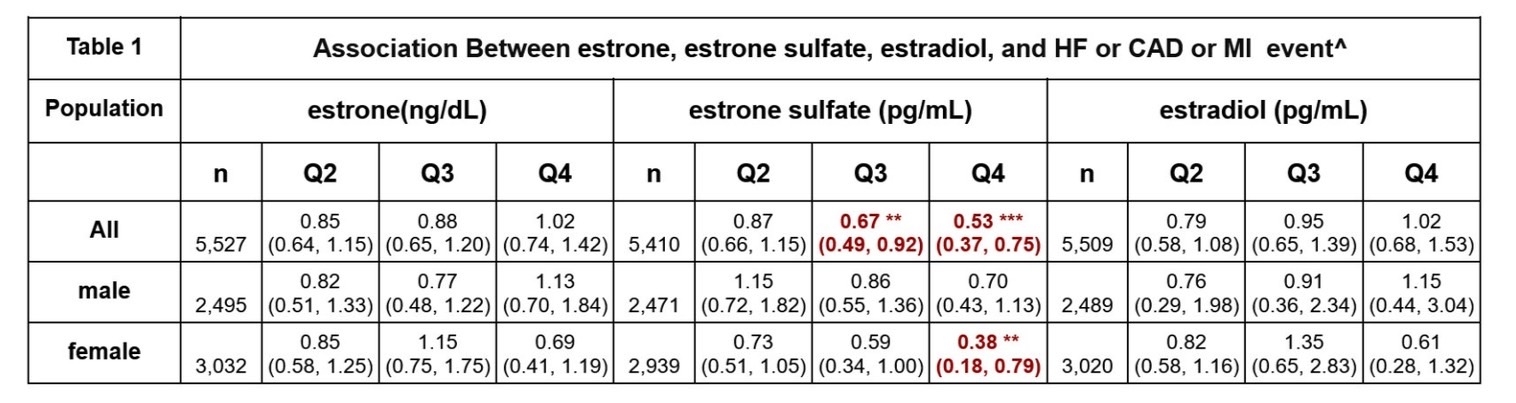
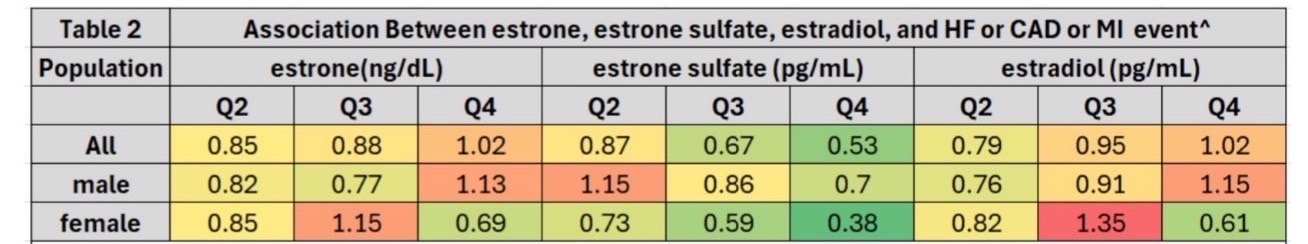
Higher estrone sulfate levels were associated with significantly reduced odds of cardiovascular events. In the overall cohort, Q3 and Q4 estrone sulfate levels were associated with lower risk: OR 0.67 (95% CI: 0.49–0.92) and OR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.37–0.75), respectively. Among females, Q4 estrone sulfate showed an even stronger protective effect (OR 0.38, 95% CI: 0.18–0.79). No consistent associations were found between estrone or estradiol levels and cardiovascular outcomes across groups, though the trends varied by sex.
Conclusions:
Estrone sulfate was independently associated with lower risk of HF, CAD, or MI, especially among women, highlighting its potential cardioprotective role. These findings suggest that estrone sulfate may be a more relevant biomarker than estradiol in cardiovascular risk stratification, warranting further mechanistic studies.
Background:
Emerging research underscores the importance of endogenous estrogens in cardiovascular health across sexes. Estrone sulfate, a stable circulating estrogen reservoir, has been shown to have longer half-life and greater concentrations than estradiol, particularly in postmenopausal women. While estradiol is traditionally considered the dominant cardioprotective hormone, recent findings suggest estrone sulfate may exert direct vascular effects and influence inflammation and lipid metabolism. However, the role of estrone, estrone sulfate, and estradiol in relation to major cardiovascular events—such as heart failure (HF), coronary artery disease (CAD), and myocardial infarction (MI)—remains incompletely understood.
Methods:
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 5,527 participants (2,495 males and 3,032 females) from NHANES with available serum hormone data. Subjects were stratified into quartiles (Q1–Q4) by levels of estrone (ng/dL), estrone sulfate (pg/mL), and estradiol (pg/mL). Multivariate logistic regression was performed to examine the association of each hormone with risk of HF, CAD, or MI, adjusting for age, sex, race, BMI, smoking, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Results:
Higher estrone sulfate levels were associated with significantly reduced odds of cardiovascular events. In the overall cohort, Q3 and Q4 estrone sulfate levels were associated with lower risk: OR 0.67 (95% CI: 0.49–0.92) and OR 0.53 (95% CI: 0.37–0.75), respectively. Among females, Q4 estrone sulfate showed an even stronger protective effect (OR 0.38, 95% CI: 0.18–0.79). No consistent associations were found between estrone or estradiol levels and cardiovascular outcomes across groups, though the trends varied by sex.
Conclusions:
Estrone sulfate was independently associated with lower risk of HF, CAD, or MI, especially among women, highlighting its potential cardioprotective role. These findings suggest that estrone sulfate may be a more relevant biomarker than estradiol in cardiovascular risk stratification, warranting further mechanistic studies.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Promote Heart Failure Though Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP1/Phosphodiesterase 4B Pathway
Cao Ning, Qiu Hui, Li Hongwei
3-Minute Heart Health App: A Feasibility StudyAbdulkarim Iya, Metzger Joseph, Stovitz Steven, Van't Hof Jeremy