Final ID: MP2441
Post–COVID-19 Pediatric Myocarditis Shows Higher Adjusted Mortality and Greater Response to IVIG With Steroids in Tertiary Care LMIC Setting
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Myocarditis is a rare but potentially life-threatening inflammatory condition of the myocardium, especially in children. Its spectrum ranges from mild symptoms to fulminant heart failure. Often underdiagnosed in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) due to limited diagnostics, the COVID-19 pandemic has altered its incidence, clinical profile, and management patterns.
Research Question:
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical presentation, management strategies, and outcomes of pediatric myocarditis cases across a 12-year period and to compare the differences between pre-COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 eras. We hypothesized that the COVID-19 pandemic significantly influenced myocarditis patterns, including complication rates and treatment outcomes.
Methods:
This was a retrospective analytical study of 130 children (1 month to 18 years) diagnosed with myocarditis at Aga Khan University Hospital, Pakistan (2011–2023). Patients were grouped into pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 onward cohorts. Diagnosis was based on clinical features, elevated cardiac biomarkers, and echocardiographic findings. A multitier approach evaluated clinical presentation, hospital outcomes, and 3-year follow-up.
Results:
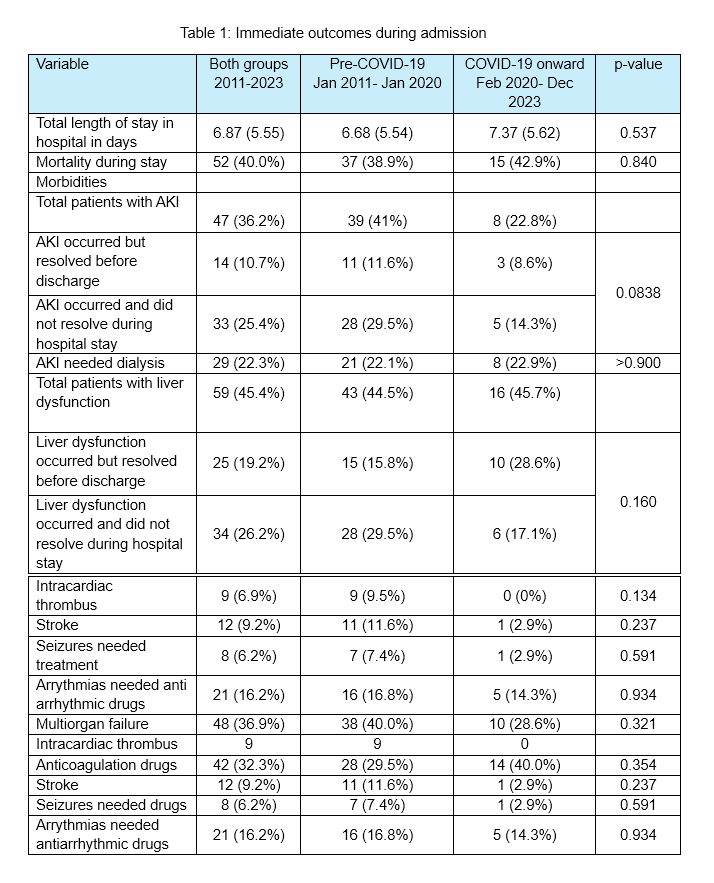
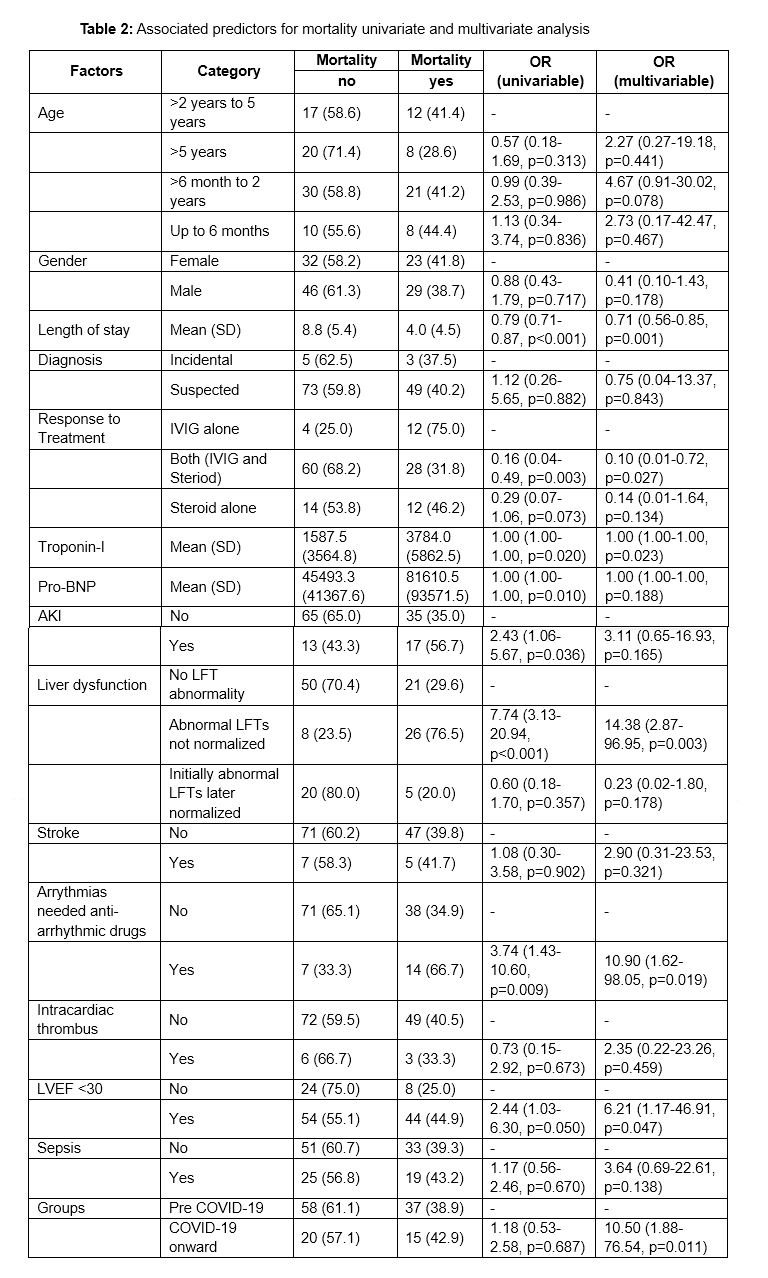
Of 130 cases, 73% were pre-COVID-19. Median age was 3.66 years, with a male predominance. Clinical features were similar across groups. Post-COVID-19 patients more frequently received IVIG with steroids (62.9% vs. 41.1%, p=0.035). Mortality was comparable (38.9% vs. 42.9%). Complications like AKI (41% vs. 22.8%), stroke, and intracardiac thrombus were more prevalent pre-COVID-19. Follow-up data showed that 35% had resolution of LV dysfunction, 30.7% had persistent dysfunction, and 33.3% were lost to follow-up. Mortality was associated with unresolved liver dysfunction (OR 14.38, p=0.003), arrhythmias (OR 10.90, p=0.019), and LVEF <30% (OR 6.21, p=0.047). IVIG plus steroids reduced mortality (OR 0.10, p=0.027) compared to IVIG alone.
Conclusion:
COVID-19 has influenced the diagnostic and therapeutic landscape of pediatric myocarditis, with a shift toward immune-targeted therapies and differing complication profiles. However, adjusted mortality risk was higher post-COVID-19, highlighting unresolved care gaps. Limited access to advanced diagnostics and high loss to follow-up remain key challenges in LMICs. This study emphasizes the need for protocol optimization, improved follow-up systems, and investment in diagnostics to improve long-term outcomes for affected children.
Myocarditis is a rare but potentially life-threatening inflammatory condition of the myocardium, especially in children. Its spectrum ranges from mild symptoms to fulminant heart failure. Often underdiagnosed in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) due to limited diagnostics, the COVID-19 pandemic has altered its incidence, clinical profile, and management patterns.
Research Question:
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical presentation, management strategies, and outcomes of pediatric myocarditis cases across a 12-year period and to compare the differences between pre-COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 eras. We hypothesized that the COVID-19 pandemic significantly influenced myocarditis patterns, including complication rates and treatment outcomes.
Methods:
This was a retrospective analytical study of 130 children (1 month to 18 years) diagnosed with myocarditis at Aga Khan University Hospital, Pakistan (2011–2023). Patients were grouped into pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 onward cohorts. Diagnosis was based on clinical features, elevated cardiac biomarkers, and echocardiographic findings. A multitier approach evaluated clinical presentation, hospital outcomes, and 3-year follow-up.
Results:
Of 130 cases, 73% were pre-COVID-19. Median age was 3.66 years, with a male predominance. Clinical features were similar across groups. Post-COVID-19 patients more frequently received IVIG with steroids (62.9% vs. 41.1%, p=0.035). Mortality was comparable (38.9% vs. 42.9%). Complications like AKI (41% vs. 22.8%), stroke, and intracardiac thrombus were more prevalent pre-COVID-19. Follow-up data showed that 35% had resolution of LV dysfunction, 30.7% had persistent dysfunction, and 33.3% were lost to follow-up. Mortality was associated with unresolved liver dysfunction (OR 14.38, p=0.003), arrhythmias (OR 10.90, p=0.019), and LVEF <30% (OR 6.21, p=0.047). IVIG plus steroids reduced mortality (OR 0.10, p=0.027) compared to IVIG alone.
Conclusion:
COVID-19 has influenced the diagnostic and therapeutic landscape of pediatric myocarditis, with a shift toward immune-targeted therapies and differing complication profiles. However, adjusted mortality risk was higher post-COVID-19, highlighting unresolved care gaps. Limited access to advanced diagnostics and high loss to follow-up remain key challenges in LMICs. This study emphasizes the need for protocol optimization, improved follow-up systems, and investment in diagnostics to improve long-term outcomes for affected children.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comprehensive Study on Machine Learning Models Combining with Oversampling for One-year Persistent Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
Liang Kaizhi, Pang Yusheng, Su Danyan
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulinDabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey