Final ID: Su2010
From Door to Diagnosis: Prospective Evaluation of OpenAI o3 for Real-Time STEMI/NSTEMI and Culprit Artery Prediction in Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Emergency physicians must interpret ECGs, await high-sensitivity troponins, and achieve timely door-to-balloon interventions in acute myocardial infarction(AMI). Staff shortages, clinician burnout, and overcrowded Emergency Departments(EDs) intensify these challenges. As AI adoption accelerates, rigorous prospective validation in high-stakes domains like cardiology becomes critical. An AI tool that instantly identifies the infarct-related artery could streamline workflows, but prospective validation against angiographic benchmarks is limited.
Research Question: Can OpenAI o3 accurately identify MI subtype, infarct-related artery, and disease extent in angiography-confirmed AMI using multimodal clinical inputs?
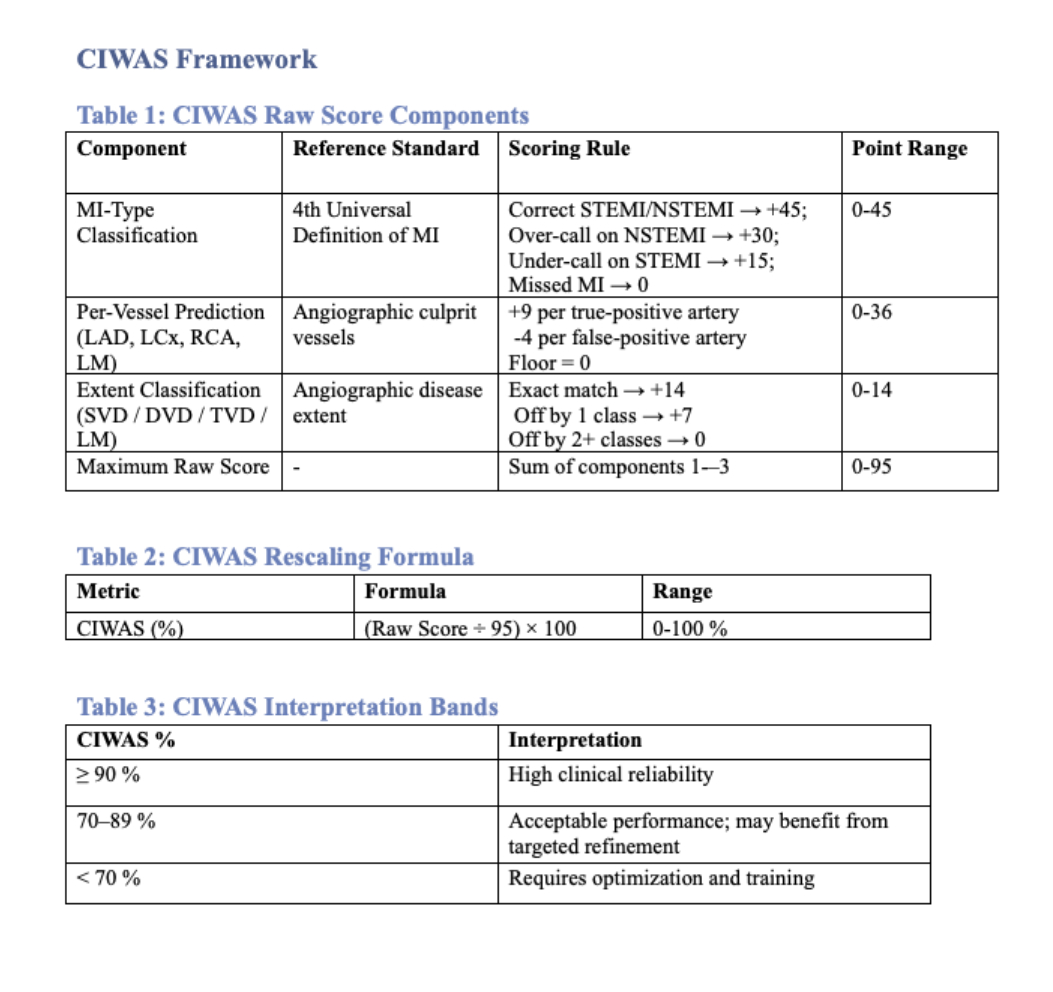
Methods: This single-center, prospective pilot (Sep 2024-Mar 2025) evaluated OpenAI o3 to rapidly predict infarct-related artery involvement and disease extent in 120 patients with angiography-confirmed AMI. De-identified blinded inputs included demographic data, initial ECG, first troponin, and patient symptoms/examination data. o3 delivered binary predictions on the involvement of the LM, LAD, RCA, and LCx arteries, along with STEMI/NSTEMI classification per the 4th Universal Definition of MI. Diagnostic safety was assessed with the Clinically Integrated Weighted Accuracy Score (CIWAS). Sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratios (LR) were reported with log-transformed 95% confidence intervals
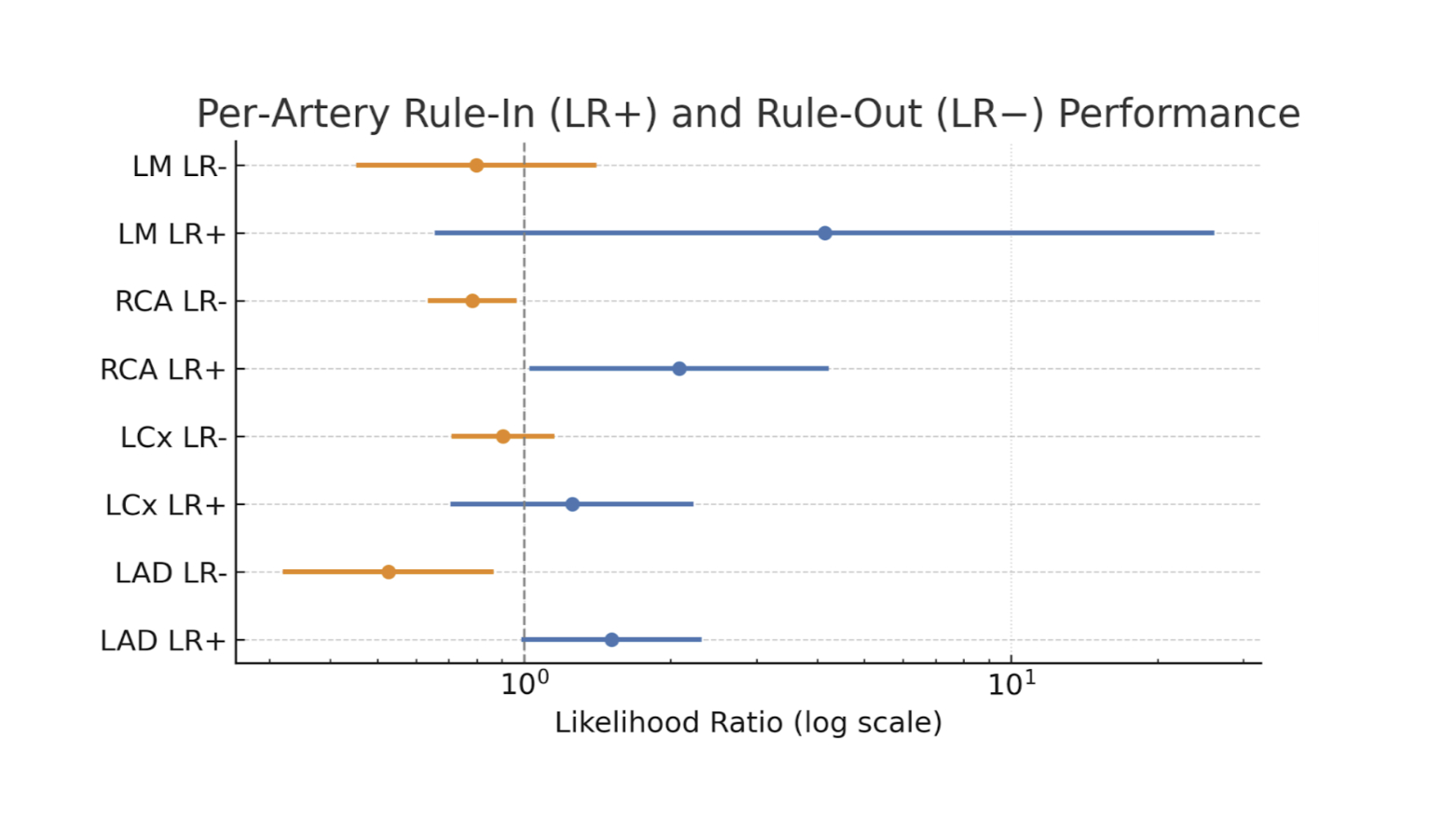
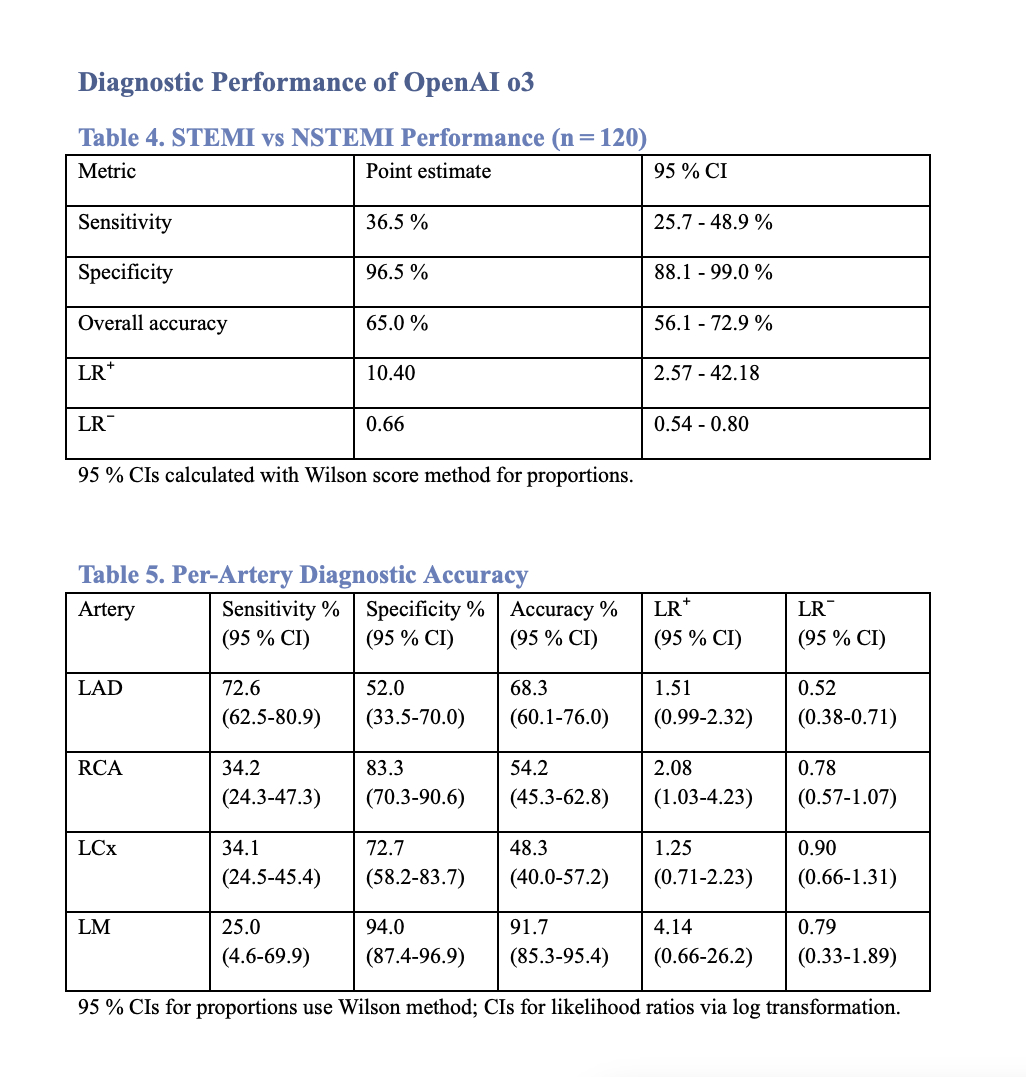
Results: o3 generated outputs within 6 minutes in all cases. Angiographic comparisons showed sensitivity/specificity (LR+/LR-) LAD 73%/52% (1.51 / 0.52), RCA 34%/83% (2.08 / 0.80), LCx 34%/73% (1.25 /0.90), and LM 25%/94% (4.14 / 0.80). For MI subtyping, o3 showed 36%/96% sensitivity/specificity (LR+/LR-: 10.4 / 0.66) with an overall accuracy of 66%.Median CIWAS was 52% (IQR 48.7–55.2). No AI-related adverse events occurred as clinicians did not use outputs.
Conclusion: OpenAI o3 identifies infarct-related arteries, distinguishing STEMI from NSTEMI, with high specificity and strong rule-in for left-main infarction. Modest CIWAS scores reflect early-stage performance and the need for further optimization. The single-center design and absence of non-MI controls limit generalizability, but the findings support broader trials to evaluate probabilistic outputs, clinician alignment, and real-world use. Amid rising ED burden and frequent MI misclassification, o3 offers a scalable triage adjunct warranting rigorous validation and domain-specific training.
Research Question: Can OpenAI o3 accurately identify MI subtype, infarct-related artery, and disease extent in angiography-confirmed AMI using multimodal clinical inputs?
Methods: This single-center, prospective pilot (Sep 2024-Mar 2025) evaluated OpenAI o3 to rapidly predict infarct-related artery involvement and disease extent in 120 patients with angiography-confirmed AMI. De-identified blinded inputs included demographic data, initial ECG, first troponin, and patient symptoms/examination data. o3 delivered binary predictions on the involvement of the LM, LAD, RCA, and LCx arteries, along with STEMI/NSTEMI classification per the 4th Universal Definition of MI. Diagnostic safety was assessed with the Clinically Integrated Weighted Accuracy Score (CIWAS). Sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratios (LR) were reported with log-transformed 95% confidence intervals
Results: o3 generated outputs within 6 minutes in all cases. Angiographic comparisons showed sensitivity/specificity (LR+/LR-) LAD 73%/52% (1.51 / 0.52), RCA 34%/83% (2.08 / 0.80), LCx 34%/73% (1.25 /0.90), and LM 25%/94% (4.14 / 0.80). For MI subtyping, o3 showed 36%/96% sensitivity/specificity (LR+/LR-: 10.4 / 0.66) with an overall accuracy of 66%.Median CIWAS was 52% (IQR 48.7–55.2). No AI-related adverse events occurred as clinicians did not use outputs.
Conclusion: OpenAI o3 identifies infarct-related arteries, distinguishing STEMI from NSTEMI, with high specificity and strong rule-in for left-main infarction. Modest CIWAS scores reflect early-stage performance and the need for further optimization. The single-center design and absence of non-MI controls limit generalizability, but the findings support broader trials to evaluate probabilistic outputs, clinician alignment, and real-world use. Amid rising ED burden and frequent MI misclassification, o3 offers a scalable triage adjunct warranting rigorous validation and domain-specific training.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Catheterization Timing with In-Hospital Outcomes in OHCA Patients with NSTEMI: A National Analysis
Ahluwalia Vibhor, Jaiswal Jay, Bhatia Smriti, Dutta Abhishek, Murillo-garcia David, Singer Robert, Dhar Sunil
Absence of standard modifiable risk factors (SMuRF-less) among 5002 Middle Eastern patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: (Interim analysis from the Jo-SMuRF Study)Aldalal'ah Mo'men, Hammoudeh Ayman, Hamza Ibrahem, Alqudah Mohammad, Khasawneh Hasan, Alomari Sawsan, Alomari Ahmad, H. Assaf Sarah, Zaqqa Ayah, Khatatbeh Moawiah