Final ID: MP2110
Caught Between a Clot and a Bleed: Using Transcranial Doppler Microemboli Monitoring to Determine Anticoagulation Management in a Stroke Patient with Mitral Valve Thrombus and Intracranial Hemorrhage
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Description of Case:
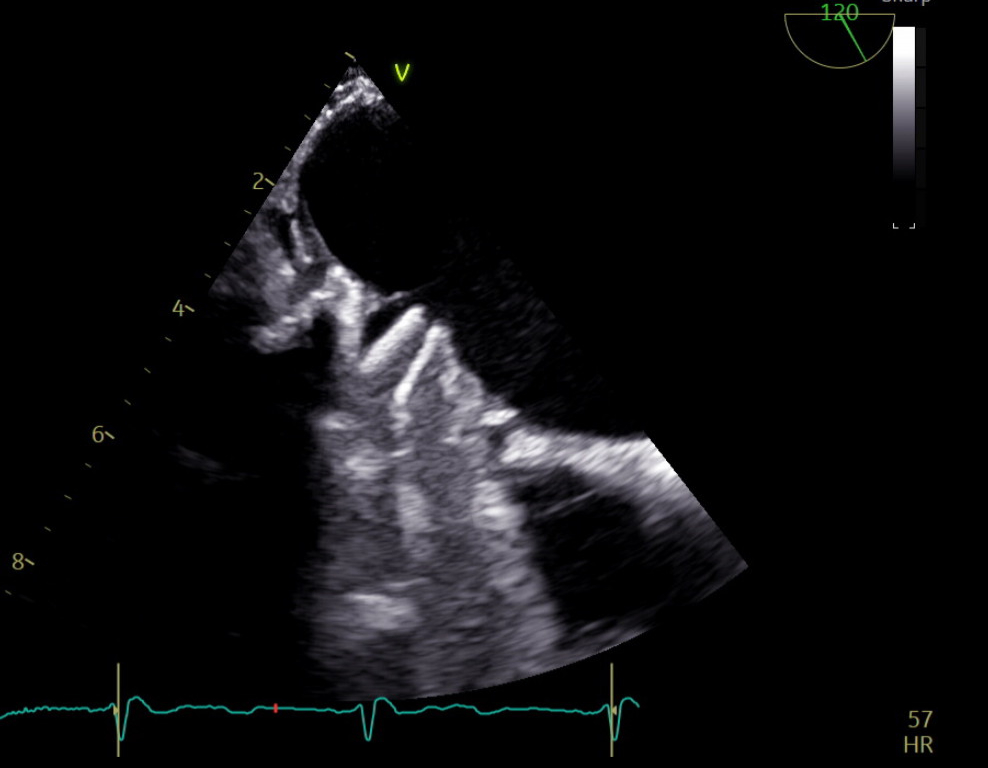
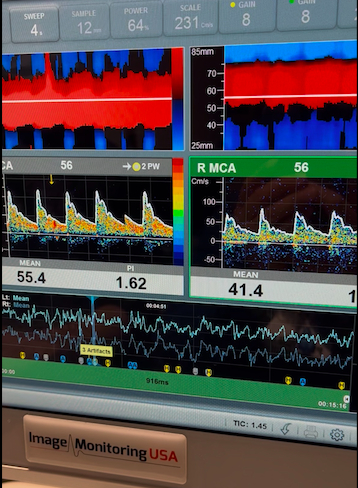
A 47-year-old female with history of thrombophilia (PAI-1 4G/4G genotype), Barlow syndrome with native leaflet repair then mechanical mitral valve (MV) replacement on warfarin, and previous stroke due to MV thromboembolism, presented with more than 24-hour onset of expressive aphasia. CT head showed showed acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in left parietal lobe with left middle cerebral artery (MCA) distal occlusion on CTA-head despite warfarin use and therapeutic INR-2.5. Within hours of admission, she had neurological deterioration and brain MRI demonstrated new left frontal-temporal intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) with cerebral herniation. She emergently received 4F-PCC/vitamin K, underwent decompression craniectomy. TTE showed MV severe stenosis. TEE (Figure 1) confirmed MV thrombus, similar embolic mechanism to prior AIS. To balance the concomitant high risks of strokes given mechanical MV thrombus requiring uninterrupted anticoagulation (AC) and ICH recurrence with AC, she was started on low-dose heparin infusion without bolus day 8. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) (Figure 2) was utilized to determine risk of cerebral embolization from MV thrombus via detection of microemboli or high-intensity transient signals (HITS) within bilateral MCA. Although patient anticoagulated with heparin, we detected 16 HITS in 15 mins of embolic monitoring suggesting high risk of recurrent ischemic stroke. AC was switched to enoxaparin at 1mg/kg twice daily and repeated TCD-emboli on day 15 showed continued AIS risk with 11 HITS even with a therapeutic anti-Xa level of 0.7 (goal 0.6-1.0). Enoxaparin dosage increased guided by emboli monitoring until HITS resolved. She was discharged to stroke rehab with plan to bridge to warfarin (INR goal 3.5-4.0) after 4 week. At one-month follow-up, she remained on warfarin 10mg daily with therapeutic INR and free of recurrent AIS or ICH.
Discussion: Microembolic signals detected on TCD can be used as biomarkers to predict stroke risk and guide therapeutic interventions. Our patient was at risk of further ICH after decompressive hemicraniectomy but without anticoagulation she had high risk of embolic stroke from mechanical MV thrombus. TCD emboli monitoring played a pivotal role in guiding the timing of AC initiation and determining the therapeutic dose to reduce risk of both recurrent emboli and hemorrhagic complications.
A 47-year-old female with history of thrombophilia (PAI-1 4G/4G genotype), Barlow syndrome with native leaflet repair then mechanical mitral valve (MV) replacement on warfarin, and previous stroke due to MV thromboembolism, presented with more than 24-hour onset of expressive aphasia. CT head showed showed acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in left parietal lobe with left middle cerebral artery (MCA) distal occlusion on CTA-head despite warfarin use and therapeutic INR-2.5. Within hours of admission, she had neurological deterioration and brain MRI demonstrated new left frontal-temporal intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) with cerebral herniation. She emergently received 4F-PCC/vitamin K, underwent decompression craniectomy. TTE showed MV severe stenosis. TEE (Figure 1) confirmed MV thrombus, similar embolic mechanism to prior AIS. To balance the concomitant high risks of strokes given mechanical MV thrombus requiring uninterrupted anticoagulation (AC) and ICH recurrence with AC, she was started on low-dose heparin infusion without bolus day 8. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) (Figure 2) was utilized to determine risk of cerebral embolization from MV thrombus via detection of microemboli or high-intensity transient signals (HITS) within bilateral MCA. Although patient anticoagulated with heparin, we detected 16 HITS in 15 mins of embolic monitoring suggesting high risk of recurrent ischemic stroke. AC was switched to enoxaparin at 1mg/kg twice daily and repeated TCD-emboli on day 15 showed continued AIS risk with 11 HITS even with a therapeutic anti-Xa level of 0.7 (goal 0.6-1.0). Enoxaparin dosage increased guided by emboli monitoring until HITS resolved. She was discharged to stroke rehab with plan to bridge to warfarin (INR goal 3.5-4.0) after 4 week. At one-month follow-up, she remained on warfarin 10mg daily with therapeutic INR and free of recurrent AIS or ICH.
Discussion: Microembolic signals detected on TCD can be used as biomarkers to predict stroke risk and guide therapeutic interventions. Our patient was at risk of further ICH after decompressive hemicraniectomy but without anticoagulation she had high risk of embolic stroke from mechanical MV thrombus. TCD emboli monitoring played a pivotal role in guiding the timing of AC initiation and determining the therapeutic dose to reduce risk of both recurrent emboli and hemorrhagic complications.
More abstracts on this topic:
10-Year Trend Analysis of Medicare Payment in Stroke Inpatient Hospital Admission
Wong Ka-ho, Krothapalli Neeharika, Littig Lauren, Champagne Alison, Majersik Jennifer, Reddy Vivek, De Havenon Adam
A Diagnostic Pitfall: Subclavian Stenosis Mimicking Severe Aortic Stenosis on Echocardiography"Ezaldin Shady, Abdelsalam Mahmoud, Elsayed Omar, Lee Marciano