Final ID: MP716
Regulatory LncRNA H19 and mitophagy in hypoplastic left heart syndrome and in immature ischemic/reperfused rodent hearts
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is one of the most clinically challenging congenital heart diseases. The long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 has been identified as a key regulator of mitochondrial function and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI) in adult human and animal hearts. However, the regulation and role of H19 in immature human and animal hearts remain unknown.
Hypothesis: Upregulated H19 in HLHS and in immature ischemic/reperfused animal hearts suppresses mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway.
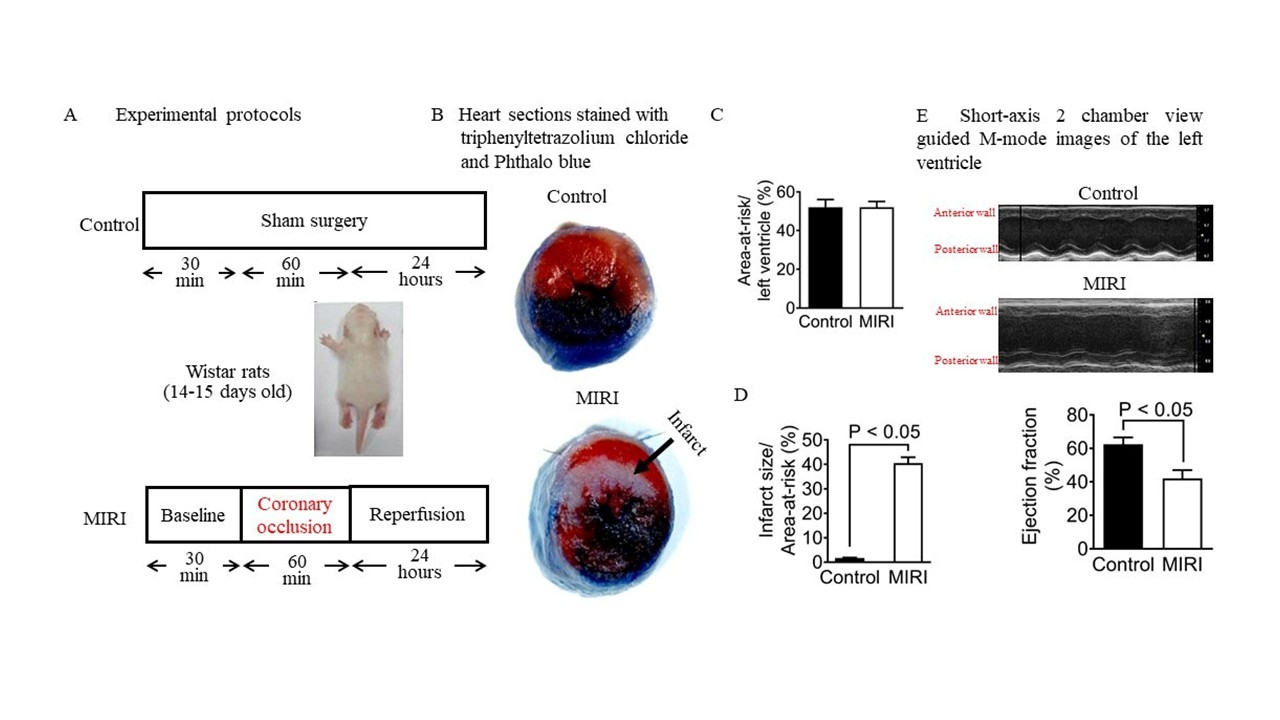
Methods: Myocardial tissues were collected from HLHS patients at the time of heart transplantation, and control tissues were obtained from donor hearts. HLHS-specific induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes were subjected to hypoxia for 3 hours followed by 24 hours of reoxygenation. MIRI was induced in 14–15-day-old Wistar rats by ligating coronary artery for 60 min, followed by 24-hour reperfusion (Fig. 1), H19 expression was measured by quantitative PCR. Myocardial tissues were examined by electron microscopy to identify autophagosomes/autolysosomes containing mitochondria. Mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin protein levels were assessed by Western blot analysis. In separate experiments, 2–3-day-old Wistar rats were injected with lentiviral vectors carrying siRNA targeting H19 or control vectors. Additionally, PINK1 knockout and C57BL/6 control mice were subjected to MIRI on a Langendorff apparatus.
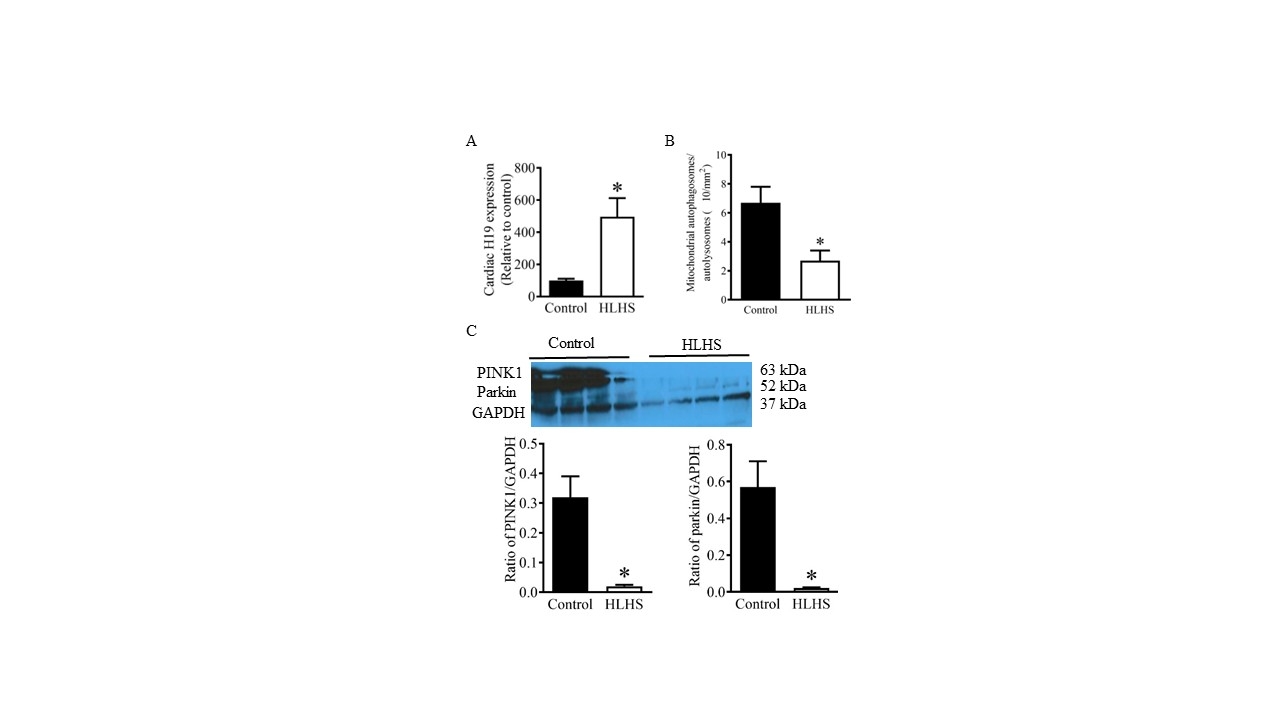
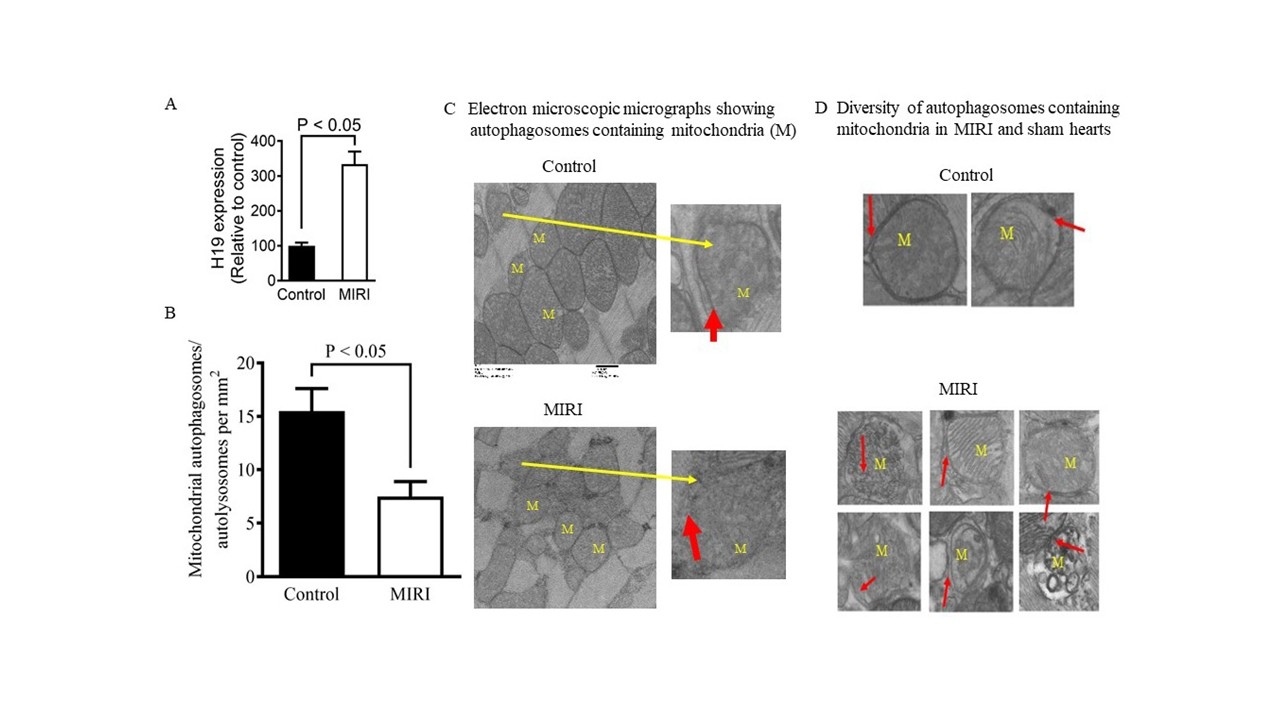
Results: H19 expression was upregulated and mitophagy was decreased in cardiac tissues from HLHS patients compared to controls, accompanied by reduced mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin expression (Fig. 2). In iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, hypoxia/reoxygenation induced lactate dehydrogenase release and H19 expression and decreased PINK1 and Parkin expression. In rats, MIRI resulted in an infarct size of 40 ± 2% of the area-at-risk (n = 10), accompanied by elevated H19 expression, reduced mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin levels, and suppressed mitophagy (Fig.3). H19 knockdown reduced infarct size (decreased lactate dehydrogenase release in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes), increased mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin levels, and enhanced mitophagy in ischemic/reperfused hearts. Compared to C57BL/6 controls, PINK1 knockout mice exhibited significantly reduced ±dP/dt and decreased mitophagy two hours after reperfusion.
Conclusions: Upregulated H19 exacerbates MIRI by suppressing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in immature hearts.
Hypothesis: Upregulated H19 in HLHS and in immature ischemic/reperfused animal hearts suppresses mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway.
Methods: Myocardial tissues were collected from HLHS patients at the time of heart transplantation, and control tissues were obtained from donor hearts. HLHS-specific induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes were subjected to hypoxia for 3 hours followed by 24 hours of reoxygenation. MIRI was induced in 14–15-day-old Wistar rats by ligating coronary artery for 60 min, followed by 24-hour reperfusion (Fig. 1), H19 expression was measured by quantitative PCR. Myocardial tissues were examined by electron microscopy to identify autophagosomes/autolysosomes containing mitochondria. Mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin protein levels were assessed by Western blot analysis. In separate experiments, 2–3-day-old Wistar rats were injected with lentiviral vectors carrying siRNA targeting H19 or control vectors. Additionally, PINK1 knockout and C57BL/6 control mice were subjected to MIRI on a Langendorff apparatus.
Results: H19 expression was upregulated and mitophagy was decreased in cardiac tissues from HLHS patients compared to controls, accompanied by reduced mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin expression (Fig. 2). In iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, hypoxia/reoxygenation induced lactate dehydrogenase release and H19 expression and decreased PINK1 and Parkin expression. In rats, MIRI resulted in an infarct size of 40 ± 2% of the area-at-risk (n = 10), accompanied by elevated H19 expression, reduced mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin levels, and suppressed mitophagy (Fig.3). H19 knockdown reduced infarct size (decreased lactate dehydrogenase release in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes), increased mitochondrial PINK1 and Parkin levels, and enhanced mitophagy in ischemic/reperfused hearts. Compared to C57BL/6 controls, PINK1 knockout mice exhibited significantly reduced ±dP/dt and decreased mitophagy two hours after reperfusion.
Conclusions: Upregulated H19 exacerbates MIRI by suppressing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in immature hearts.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylation of mitochondrial LCAD and SOD2 promotes metabolic dysfunction, oxidative stress, multi-organ damage and hypertension
Dikalov Sergey, Nogueira Marina, Polosukhin Vasiliy, Gius David, Milne Ginger, Dikalova Anna
Brd4-mediated 3D chromatin architecture determines old donor heart preservation qualityGao Wenbin, Sicim Huseyin, Tang Paul, Lei Ienglam