Final ID: Su2136
Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Inclisiran in Hyperlipidemia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background:
Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA (siRNA), inhibits hepatic PCSK9 synthesis, leading to significant LDL-C reduction. Previous meta-analyses have addressed short-term efficacy; however, recent long-term data warranted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate inclisiran’s lipid-lowering efficacy and safety in hyperlipidemic patients.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted from inception to April 2025 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing inclisiran with placebo or standard care in adults with hypercholesterolemia. Primary efficacy outcomes included percentage change in LDL-C, PCSK9, total cholesterol, apolipoprotein B (apo-B), and non-HDL-C. Safety outcomes included adverse events, cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality. Data were analyzed using a random-effects model following PRISMA guidelines. Risk ratios (RR) and weighted mean differences (WMD) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals. The protocol was registered on PROSPERO (CRD420251059229).
Results:
Eleven RCTs with 5,601 patients were included; 3,135 received inclisiran and 2,466 received placebo. Inclisiran significantly reduced:
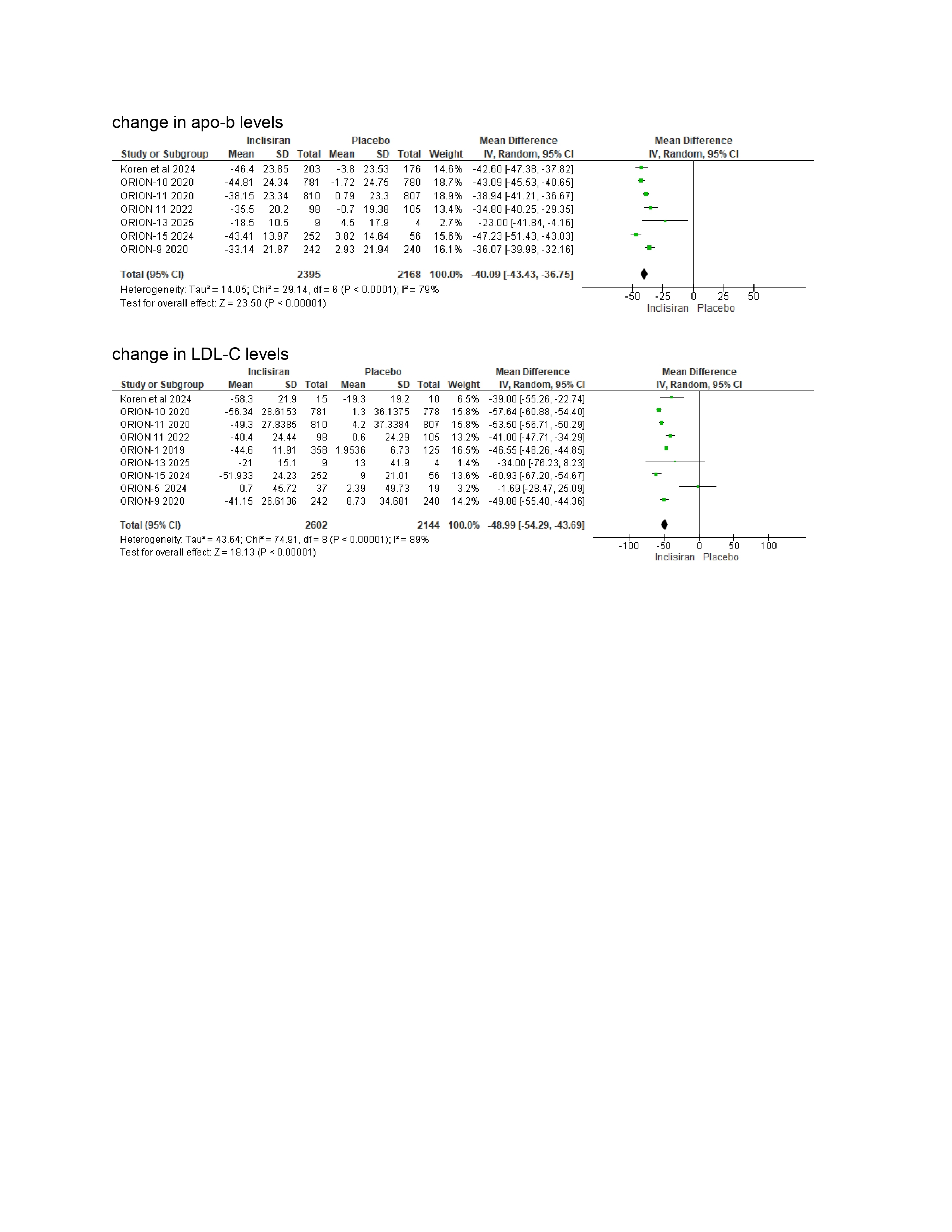
LDL-C (WMD –48.99%, 95% CI: –54.29 to –43.69)
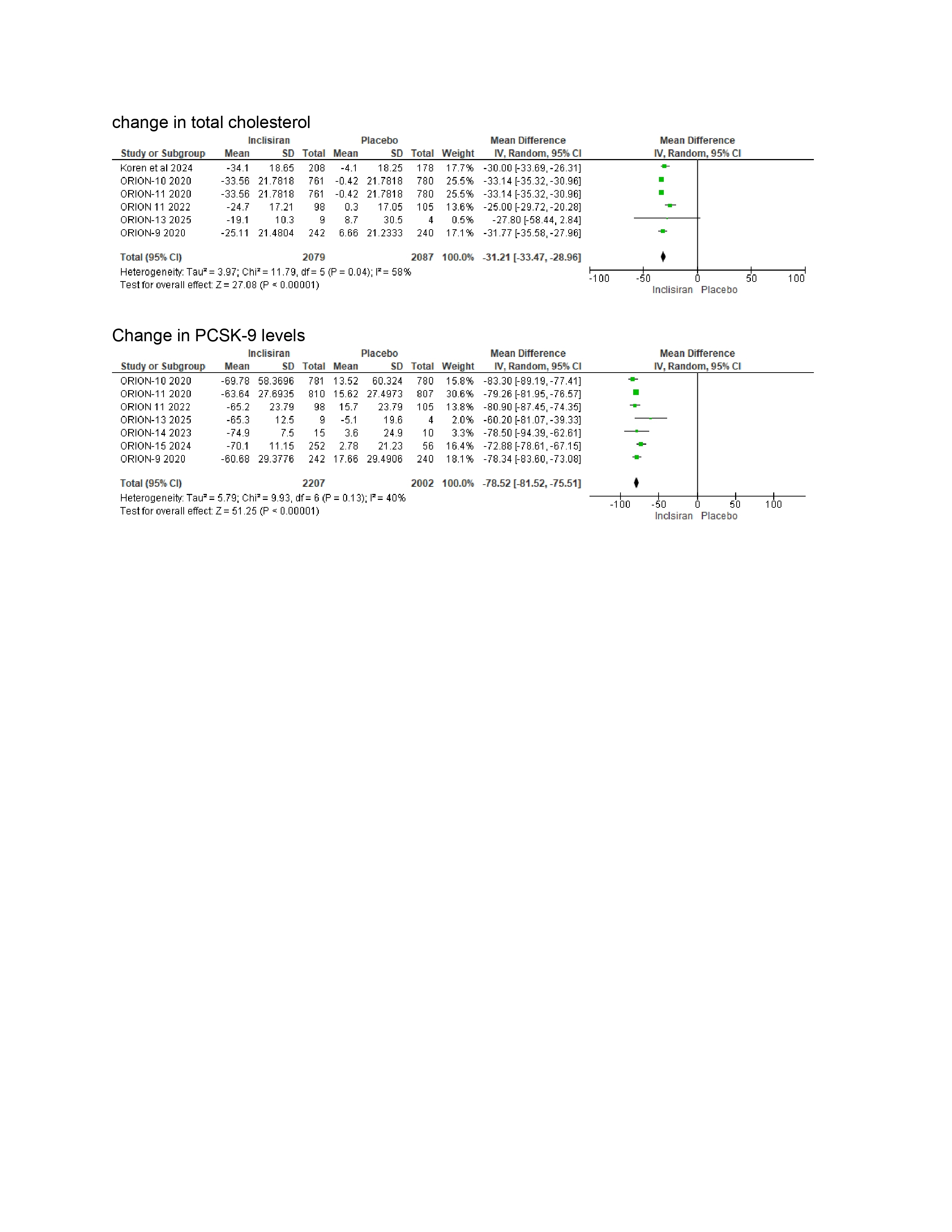
PCSK9 (WMD –78.52%, 95% CI: –81.52 to –75.51)
Total cholesterol (WMD –31.21%, 95% CI: –33.47 to –28.56)
Apo-B (WMD –40.09%, 95% CI: –43.43 to –36.75)
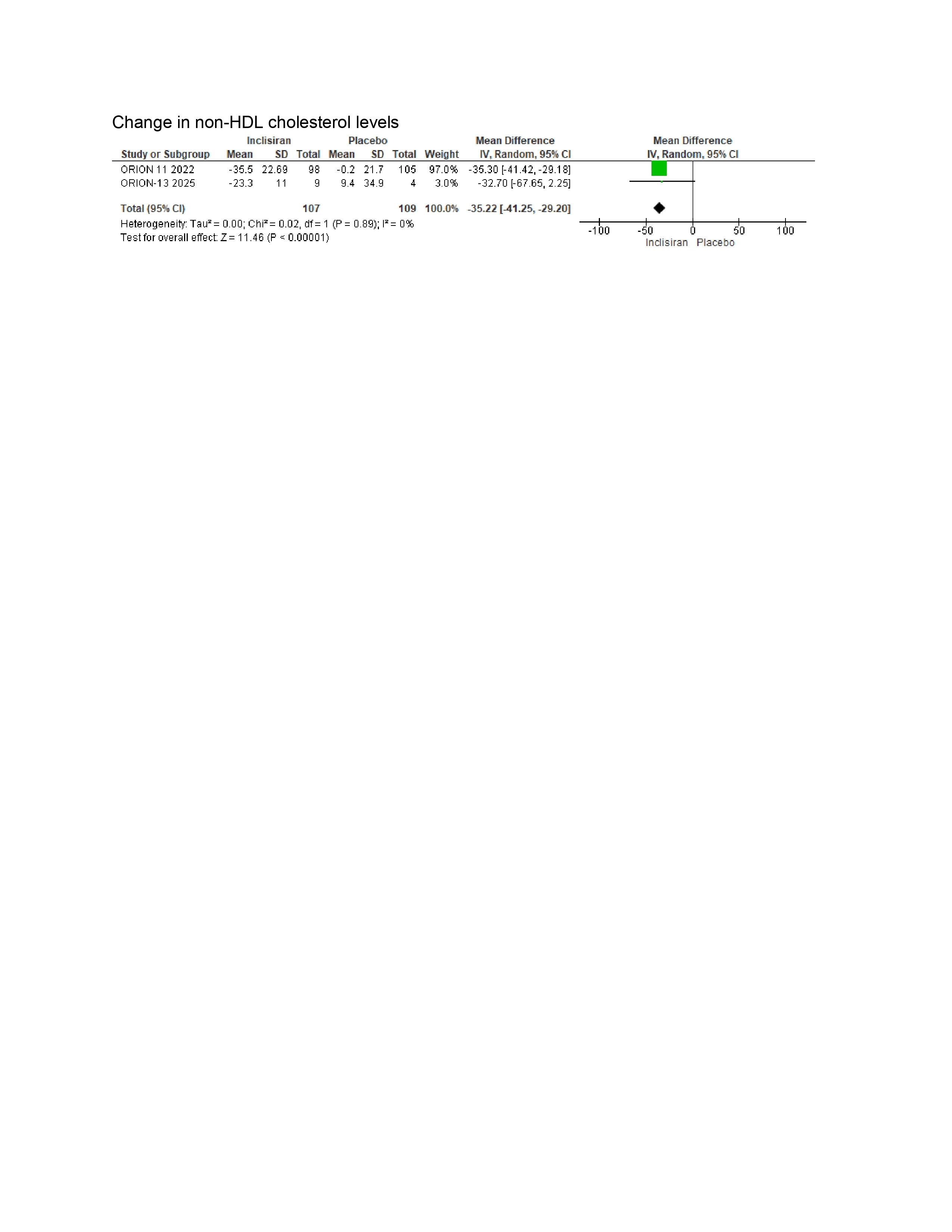
Non-HDL-C (WMD –35.22%, 95% CI: –41.25 to –29.20)
Inclisiran showed no significant impact on all-cause mortality (RR 0.94; p=0.83), cardiovascular mortality (RR 1.19; p=0.60), myocardial infarction (RR 0.85; p=0.60), stroke (RR 0.89; p=0.86), or major adverse cardiovascular events (RR 0.80; p=0.07). Total adverse events were slightly higher with inclisiran (RR 1.06; p=0.02), but serious adverse events were not significantly different (RR 0.90; p=0.36). Injection site reactions were more common with inclisiran (RR 6.45; p<0.001).
Conclusion:
Inclisiran significantly reduces LDL-C, PCSK9, total cholesterol, apo-B, and non-HDL-C, confirming strong lipid-lowering efficacy. It is generally well tolerated, with a slightly higher incidence of mild injection site reactions but no increase in serious adverse events. Longer-term studies are needed to assess its effect on cardiovascular outcomes.
Background:
Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA (siRNA), inhibits hepatic PCSK9 synthesis, leading to significant LDL-C reduction. Previous meta-analyses have addressed short-term efficacy; however, recent long-term data warranted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate inclisiran’s lipid-lowering efficacy and safety in hyperlipidemic patients.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted from inception to April 2025 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing inclisiran with placebo or standard care in adults with hypercholesterolemia. Primary efficacy outcomes included percentage change in LDL-C, PCSK9, total cholesterol, apolipoprotein B (apo-B), and non-HDL-C. Safety outcomes included adverse events, cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality. Data were analyzed using a random-effects model following PRISMA guidelines. Risk ratios (RR) and weighted mean differences (WMD) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals. The protocol was registered on PROSPERO (CRD420251059229).
Results:
Eleven RCTs with 5,601 patients were included; 3,135 received inclisiran and 2,466 received placebo. Inclisiran significantly reduced:
LDL-C (WMD –48.99%, 95% CI: –54.29 to –43.69)
PCSK9 (WMD –78.52%, 95% CI: –81.52 to –75.51)
Total cholesterol (WMD –31.21%, 95% CI: –33.47 to –28.56)
Apo-B (WMD –40.09%, 95% CI: –43.43 to –36.75)
Non-HDL-C (WMD –35.22%, 95% CI: –41.25 to –29.20)
Inclisiran showed no significant impact on all-cause mortality (RR 0.94; p=0.83), cardiovascular mortality (RR 1.19; p=0.60), myocardial infarction (RR 0.85; p=0.60), stroke (RR 0.89; p=0.86), or major adverse cardiovascular events (RR 0.80; p=0.07). Total adverse events were slightly higher with inclisiran (RR 1.06; p=0.02), but serious adverse events were not significantly different (RR 0.90; p=0.36). Injection site reactions were more common with inclisiran (RR 6.45; p<0.001).
Conclusion:
Inclisiran significantly reduces LDL-C, PCSK9, total cholesterol, apo-B, and non-HDL-C, confirming strong lipid-lowering efficacy. It is generally well tolerated, with a slightly higher incidence of mild injection site reactions but no increase in serious adverse events. Longer-term studies are needed to assess its effect on cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparative Study of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Prediction: Conventional QRISK3 vs. Enhanced Machine Learning Models Combined with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Algorithm
Harmadha Wigaviola Socha Purnamaasri, Wang Dennis, Masood Mohsin
Clinical outcomes associated with utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in heart failure patients in the United StatesLoghin Andrei, Bashir Zubair, Saxena Ritika, Gaalema Diann, Chatila Khaled, Khalife Wissam, Albaeni Aiham