Final ID: Mo2011
Explainable Machine Learning for Risk Stratification of Major Adverse Cardiac Events Using Clinical and Imaging Data
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Accurate prediction of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) is critical for guiding cardiovascular care. Traditional risk scores such as the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) and PREVENT rely solely on clinical variables and may underutilize valuable imaging data. With increasing availability of coronary artery calcium (CAC) CT scans, there is a growing opportunity to leverage multimodal data and interpretable machine learning (ML) models for enhanced risk stratification.
Research Questions
Can an interpretable ML model incorporating clinical, medication, ECG, and CAC CT-derived features outperform traditional clinical risk scores (PCE, PREVENT) in predicting MACE? Which features contribute most outcome prediction?
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, 7,828 asymptomatic individuals without known cardiovascular disease underwent CAC CT between 2010–2023 for risk stratification. A total of 52 features were used for model development, including 16 clinical variables, 7 medication variables, 15 ECG-derived parameters, and 14 CT-derived imaging features (including Agatston score, CAC volume and density, and cardiac chamber volumes). An XGBoost model was trained using stratified 10-fold cross-validation with hyperparameter optimization via grid search. Model performance was evaluated by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and compared against the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE), PREVENT score, and total CAC score. Feature importance was assessed using total gain.
Results/Data
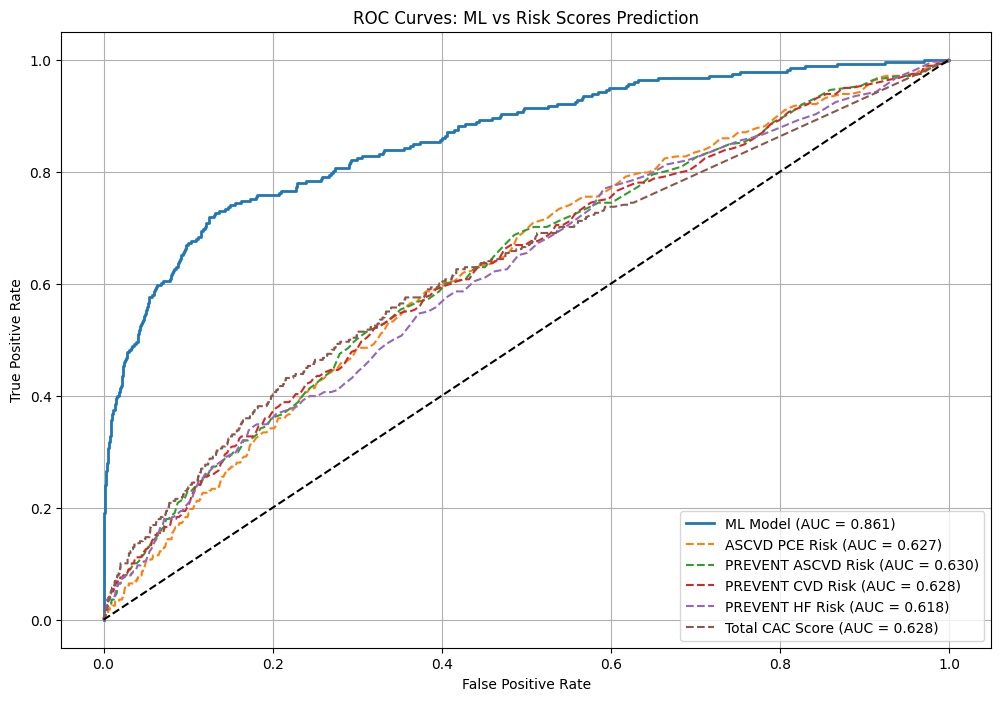
The mean age was 57.9 years; 44.6% were women and 11.5% were Black. The overall MACE rate was 4.6%. Non-zero CAC was observed in 56.6% of participants, with a median CAC score of 44.2 (IQR 5.3, 145) among those with calcifications. The ML model achieved an AUROC of 0.861 for MACE prediction, outperforming the PCE (AUROC = 0.627), PREVENT (AUROC = 0.630), and total CAC score alone (AUROC = 0.628). The most informative predictors included the PREVENT and PCE risk scores, CAC in the left anterior descending artery, total CAC volume, myocardial and right atrial volumes, and regional CAC scores.
Conclusion
An interpretable ML model incorporating clinical and imaging features significantly outperformed traditional risk scores in predicting MACE. Key imaging and clinical variables were identified as principal contributors to risk, demonstrating the potential of interpretable ML to augment cardiovascular risk stratification.
Accurate prediction of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) is critical for guiding cardiovascular care. Traditional risk scores such as the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) and PREVENT rely solely on clinical variables and may underutilize valuable imaging data. With increasing availability of coronary artery calcium (CAC) CT scans, there is a growing opportunity to leverage multimodal data and interpretable machine learning (ML) models for enhanced risk stratification.
Research Questions
Can an interpretable ML model incorporating clinical, medication, ECG, and CAC CT-derived features outperform traditional clinical risk scores (PCE, PREVENT) in predicting MACE? Which features contribute most outcome prediction?
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, 7,828 asymptomatic individuals without known cardiovascular disease underwent CAC CT between 2010–2023 for risk stratification. A total of 52 features were used for model development, including 16 clinical variables, 7 medication variables, 15 ECG-derived parameters, and 14 CT-derived imaging features (including Agatston score, CAC volume and density, and cardiac chamber volumes). An XGBoost model was trained using stratified 10-fold cross-validation with hyperparameter optimization via grid search. Model performance was evaluated by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and compared against the Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE), PREVENT score, and total CAC score. Feature importance was assessed using total gain.
Results/Data
The mean age was 57.9 years; 44.6% were women and 11.5% were Black. The overall MACE rate was 4.6%. Non-zero CAC was observed in 56.6% of participants, with a median CAC score of 44.2 (IQR 5.3, 145) among those with calcifications. The ML model achieved an AUROC of 0.861 for MACE prediction, outperforming the PCE (AUROC = 0.627), PREVENT (AUROC = 0.630), and total CAC score alone (AUROC = 0.628). The most informative predictors included the PREVENT and PCE risk scores, CAC in the left anterior descending artery, total CAC volume, myocardial and right atrial volumes, and regional CAC scores.
Conclusion
An interpretable ML model incorporating clinical and imaging features significantly outperformed traditional risk scores in predicting MACE. Key imaging and clinical variables were identified as principal contributors to risk, demonstrating the potential of interpretable ML to augment cardiovascular risk stratification.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-CVD vs. PREVENT for Predicting Incident Heart Failure: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
Naghavi Morteza, Mirjalili Seyed Reza, Atlas Kyle, Zhang Chenyu, Reeves Anthony, Azimi Amir, Wong Nathan
AI-CVD: Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Opportunistic Screening of Coronary Artery Calcium Computed Tomography Scans for Predicting CVD Events and All-Cause Mortality: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)Naghavi Morteza, Yu Ruilin, Branch Andrea, Ma Ning, Roy Sion, Nasir Khurram, Molloi Sabee, Fayad Zahi, Mcconnell Michael, Kakadiaris Ioannis, Zulueta Javier, Reeves Anthony, Maron David, Shah Prediman, Williams Kim, Abela George, Levy Daniel, Wong Nathan, Atlas Kyle, Zhang Chenyu, Atlas Thomas, Henschke Claudia, Yankelevitz David, Budoff Matthew, Fan Wenjun