Final ID: Sa3029
Prevalence and Impact of Sepsis on In-Hospital Outcomes in Children With Congenital Heart Disease in a Tertiary LMIC Center: Identifying Early, Modifiable Predictors of Poor Outcomes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Congenital heart diseases (CHD) are among the most common congenital malformations, with sepsis and lower respiratory tract infections significantly contributing to morbidity and mortality in this population. Factors such as chronic catabolic states, pulmonary over-circulation, chronic hypoxia, genetic predispositions, and the use of invasive devices heighten the risk of sepsis in children with CHD. In low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) like India, resource limitations, such as delayed diagnosis, restricted access to pediatric cardiac surgery, overburdened ICUs, and limited availability of antimicrobials and critical care support, exacerbate these risks. Despite this, data from LMIC settings remain sparse. This study aims to fill that gap by evaluating the burden and outcomes of sepsis in children with CHD admitted to a tertiary center in India.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the prevalence of sepsis and pneumonia and evaluate in-hospital outcomes related to sepsis in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease.
Methods: In this single-center retrospective study, we reviewed the records of children aged 0 to 5 years with CHD admitted with sepsis. We analyzed the prevalence of sepsis and in-hospital outcome parameters, comparing these outcomes to those of children in the same age group admitted without sepsis. Multivariate logistic regression identified predictors of mortality.
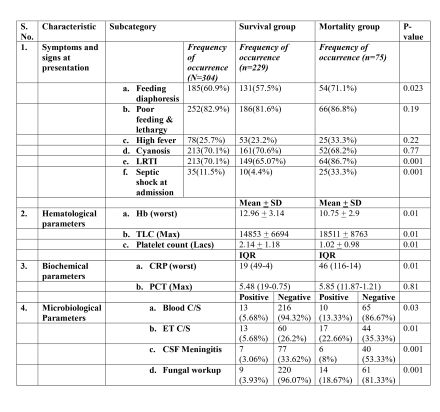
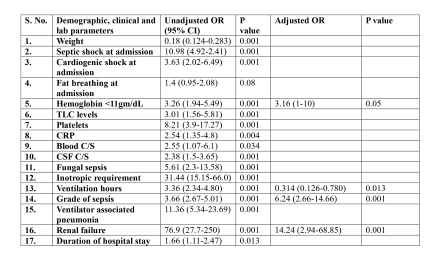
Results: A total of 913 children (median age 3 months, IQR 11) were analyzed. Sepsis was identified in 304 (33.3%) cases, with hospital-acquired sepsis in 25 (8.22%). Mortality during hospitalization was 12.4% overall, with 24.7% in infected patients compared to 6.2% in non-infected patients (p=0.001). Septic shock was associated with mortality exceeding 70%. Multivariate regression revealed that higher sepsis grade (adjusted OR 6.24, p=0.001), haemoglobin <11 gm/dL (adjusted OR 3.16, p=0.05), and renal failure (adjusted OR 14.24, p=0.001) predicted mortality.
Conclusions: Infections and sepsis account for one-third of hospitalizations among children under five with CHD. In resource-limited settings, early recognition, aggressive supportive management, and targeted interventions are urgently needed to improve outcomes in this high-risk population, including prompt antibiotic initiation, ventilatory support, and anemia management.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the prevalence of sepsis and pneumonia and evaluate in-hospital outcomes related to sepsis in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease.
Methods: In this single-center retrospective study, we reviewed the records of children aged 0 to 5 years with CHD admitted with sepsis. We analyzed the prevalence of sepsis and in-hospital outcome parameters, comparing these outcomes to those of children in the same age group admitted without sepsis. Multivariate logistic regression identified predictors of mortality.
Results: A total of 913 children (median age 3 months, IQR 11) were analyzed. Sepsis was identified in 304 (33.3%) cases, with hospital-acquired sepsis in 25 (8.22%). Mortality during hospitalization was 12.4% overall, with 24.7% in infected patients compared to 6.2% in non-infected patients (p=0.001). Septic shock was associated with mortality exceeding 70%. Multivariate regression revealed that higher sepsis grade (adjusted OR 6.24, p=0.001), haemoglobin <11 gm/dL (adjusted OR 3.16, p=0.05), and renal failure (adjusted OR 14.24, p=0.001) predicted mortality.
Conclusions: Infections and sepsis account for one-third of hospitalizations among children under five with CHD. In resource-limited settings, early recognition, aggressive supportive management, and targeted interventions are urgently needed to improve outcomes in this high-risk population, including prompt antibiotic initiation, ventilatory support, and anemia management.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian Community
Deo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan
Altered Pulmonary Arterial Hemodynamics in Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot Patients Referred for Pulmonary Valve Replacement: A Cross-Sectional 4D Flow StudyFujiwara Takashi, Kwong Michael, Fonseca Brian, Stone Matthew, Browne Lorna, Barker Alex