Final ID: Sa3048
Impact of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Receiving Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Post-PCI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), combining aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor, is standard care following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). However, DAPT increases the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, prompting frequent co-prescription of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Despite their protective role, concerns exist that PPIs may diminish the efficacy of DAPT and worsen cardiovascular outcomes. This study evaluates the impact of PPI use on clinical outcomes in patients receiving DAPT post-PCI.
Research Question:
Does PPI use compromise the effectiveness of DAPT in post-PCI patients?
Methods:
A systematic search of online databases from inception to April 2025 identified eight studies (n = 12,586) assessing the impact of PPIs on aspirin and clopidogrel efficacy after PCI. Both randomized controlled trials and observational studies were included. Primary outcomes were all-cause mortality, recurrent myocardial infarction (MI), and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Secondary outcomes included cardiac death, angina, arrhythmia, heart failure (HF), revascularization, stent thrombosis, and stroke. A random-effects model was used to pool data, with results expressed as risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results:
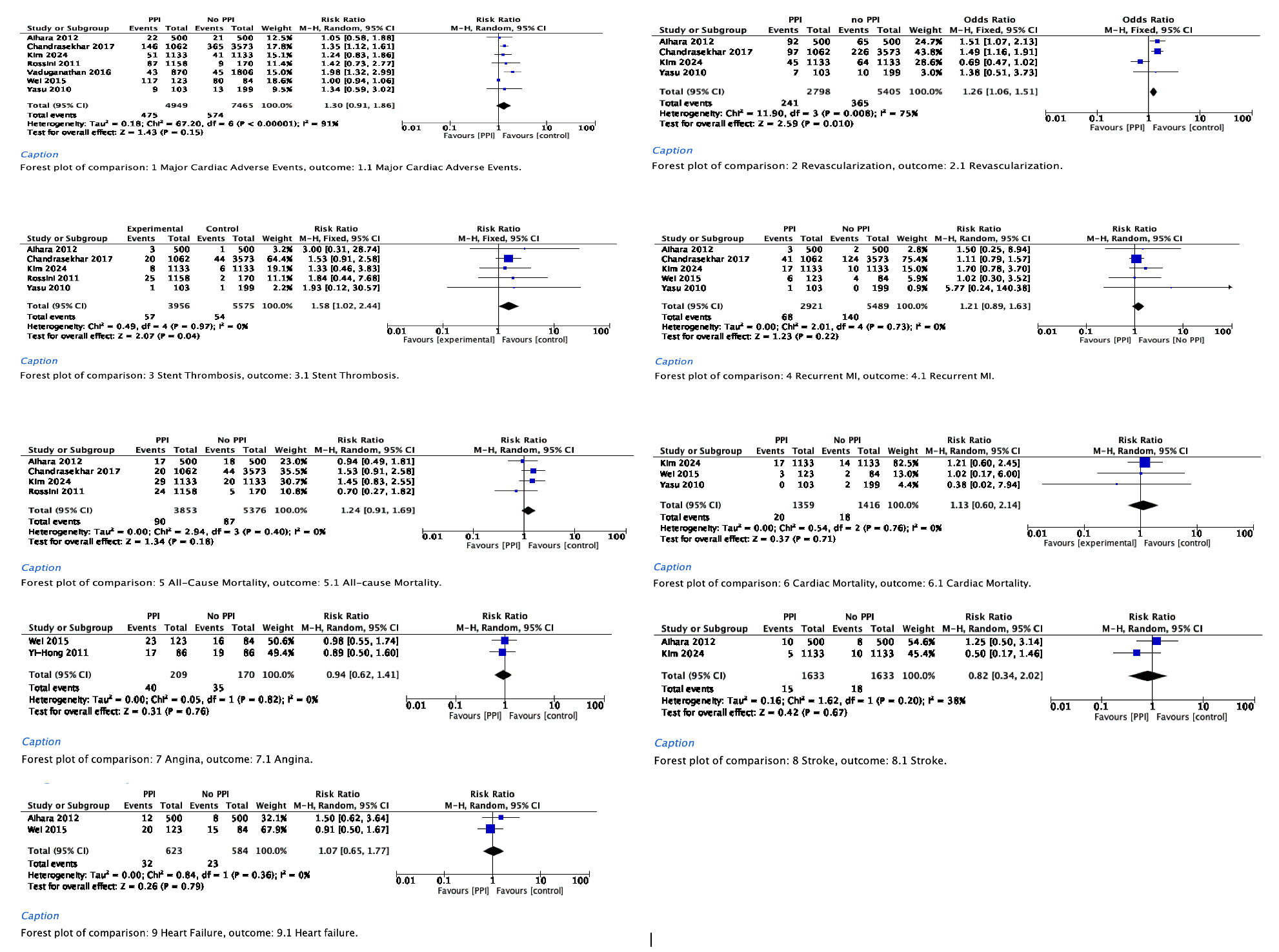
Compared to non-PPI users, PPI use was significantly associated with an increased risk of stent thrombosis (RR 1.58; 95% CI 1.02–2.44; P = 0.04) and revascularization (RR 1.26; 95% CI 1.06–1.51; P = 0.01). No significant differences were observed in MACE (RR 1.30; 95% CI 0.91–1.86; P = 0.15), all-cause mortality (RR 1.24; 95% CI 0.91–1.69; P = 0.18), cardiac death (RR 1.13; 95% CI 0.60–2.14; P = 0.71), recurrent MI (RR 1.21; 95% CI 0.89–1.63; P = 0.22), stroke (RR 0.82; 95% CI 0.34–2.02; P = 0.67), heart failure (RR 1.07; 95% CI 0.65–1.77; P = 0.79), or angina (RR 0.94; 95% CI 0.62–1.41; P = 0.76).
Conclusion:
PPI use in patients on DAPT post-PCI does not significantly affect MACE, mortality, or recurrent MI risk. However, it is linked to higher risks of stent thrombosis and revascularization. These findings highlight important clinical considerations regarding PPI co-prescription in this population. While PPIs are vital for GI protection, clinicians must balance this benefit against potential cardiovascular risks. Individualized decisions should weigh GI bleeding risk, and further large-scale randomized trials are needed to guide optimal post-PCI management.
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), combining aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor, is standard care following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). However, DAPT increases the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, prompting frequent co-prescription of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Despite their protective role, concerns exist that PPIs may diminish the efficacy of DAPT and worsen cardiovascular outcomes. This study evaluates the impact of PPI use on clinical outcomes in patients receiving DAPT post-PCI.
Research Question:
Does PPI use compromise the effectiveness of DAPT in post-PCI patients?
Methods:
A systematic search of online databases from inception to April 2025 identified eight studies (n = 12,586) assessing the impact of PPIs on aspirin and clopidogrel efficacy after PCI. Both randomized controlled trials and observational studies were included. Primary outcomes were all-cause mortality, recurrent myocardial infarction (MI), and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Secondary outcomes included cardiac death, angina, arrhythmia, heart failure (HF), revascularization, stent thrombosis, and stroke. A random-effects model was used to pool data, with results expressed as risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results:
Compared to non-PPI users, PPI use was significantly associated with an increased risk of stent thrombosis (RR 1.58; 95% CI 1.02–2.44; P = 0.04) and revascularization (RR 1.26; 95% CI 1.06–1.51; P = 0.01). No significant differences were observed in MACE (RR 1.30; 95% CI 0.91–1.86; P = 0.15), all-cause mortality (RR 1.24; 95% CI 0.91–1.69; P = 0.18), cardiac death (RR 1.13; 95% CI 0.60–2.14; P = 0.71), recurrent MI (RR 1.21; 95% CI 0.89–1.63; P = 0.22), stroke (RR 0.82; 95% CI 0.34–2.02; P = 0.67), heart failure (RR 1.07; 95% CI 0.65–1.77; P = 0.79), or angina (RR 0.94; 95% CI 0.62–1.41; P = 0.76).
Conclusion:
PPI use in patients on DAPT post-PCI does not significantly affect MACE, mortality, or recurrent MI risk. However, it is linked to higher risks of stent thrombosis and revascularization. These findings highlight important clinical considerations regarding PPI co-prescription in this population. While PPIs are vital for GI protection, clinicians must balance this benefit against potential cardiovascular risks. Individualized decisions should weigh GI bleeding risk, and further large-scale randomized trials are needed to guide optimal post-PCI management.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anomalous Origin Of Left Circumflex Artery From Right Pulmonary Artery Resulting In Heart Failure: A Rare Vascular Steal Phenomenon
Chander Yogesh, Bhardwaj Rajeev, Nandal Rajesh, Mittal Saurav, Pruthi Taniya, Singh Subeg
Achieving Guidelines within a 24-Hour Movement Paradigm and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in United States AdultsBoudreaux Benjamin, Xu Chang, Dooley Erin, Hornikel Bjoern, Munson Alexandra, Shechter Ari, Palta Priya, Gabriel Kelley, Diaz Keith