Final ID: MP171
The association between smoking and albuminuria in a population with a substantial burden of cardiovascular disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
According to the global burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), Egypt experiences one of the highest CVD-related mortalities. Albuminuria is recognized as a risk marker for CVD and is associated with smoking. However, the association between smoking and albuminuria is understudied in countries with very high CVD burden, such as Egypt.
Hypothesis: Self-reported smoking is associated with albuminuria regardless of the presence of prior CVD.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study involves 1,870 patients who were either admitted to or followed up at the National Heart Institute, the largest cardiac center in Egypt. The patients were asked about their diagnosed CVD and associated risk factors. CVD was defined as a history of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, or cardiac surgery. Urine samples were collected from patients in both inpatient units and outpatient clinics. The urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) was analyzed quantitatively and categorized on the 30 and 300 mg/dl cut-off. Smoking status was determined through self-reporting. The UACR categories were compared between smokers and nonsmokers among participants with and without CVD using the Chi-squared test. A multivariable linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, and diabetes was used to test the association between smoking and log-transformed UACR values stratified by history of CVD.
Results:
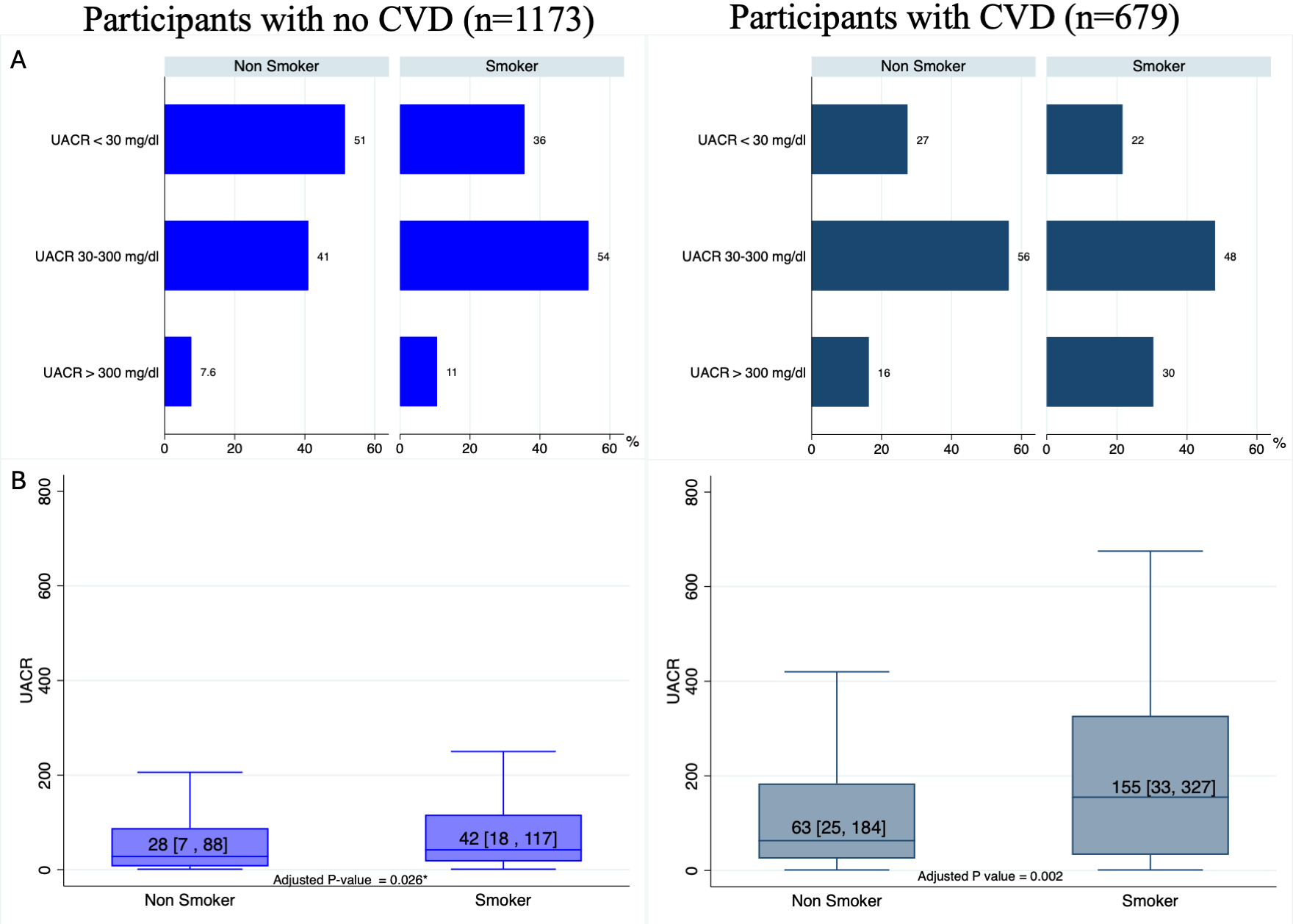
The prevalence of CVD was 37%, with a similar mean age (52 ± 13) among participants with and without CVD. Among the entire study population, 11% reported smoking, with the majority being men. The prevalence of males and smokers was 38% and 9% in participants with no CVD, respectively, in comparison to 49% and 15% in participants with CVD. The median [25th-75th percentile] of UACR was 40 [11-130] mg/dl. The prevalence of UACR >300 mg/dl tends to be higher among smokers in participants with and without CVD condition (Figure 1A), with a p-value of 0.003 and 0.008, respectively. Smoking was independently associated with higher values of UACR, regardless of the CVD condition (Figure 1B)
Conclusion:
A consistent association exists between smoking and elevated UACR in a sample of the Egyptian population, who are known to have a substantial burden of CVD.
According to the global burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), Egypt experiences one of the highest CVD-related mortalities. Albuminuria is recognized as a risk marker for CVD and is associated with smoking. However, the association between smoking and albuminuria is understudied in countries with very high CVD burden, such as Egypt.
Hypothesis: Self-reported smoking is associated with albuminuria regardless of the presence of prior CVD.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study involves 1,870 patients who were either admitted to or followed up at the National Heart Institute, the largest cardiac center in Egypt. The patients were asked about their diagnosed CVD and associated risk factors. CVD was defined as a history of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, or cardiac surgery. Urine samples were collected from patients in both inpatient units and outpatient clinics. The urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) was analyzed quantitatively and categorized on the 30 and 300 mg/dl cut-off. Smoking status was determined through self-reporting. The UACR categories were compared between smokers and nonsmokers among participants with and without CVD using the Chi-squared test. A multivariable linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, and diabetes was used to test the association between smoking and log-transformed UACR values stratified by history of CVD.
Results:
The prevalence of CVD was 37%, with a similar mean age (52 ± 13) among participants with and without CVD. Among the entire study population, 11% reported smoking, with the majority being men. The prevalence of males and smokers was 38% and 9% in participants with no CVD, respectively, in comparison to 49% and 15% in participants with CVD. The median [25th-75th percentile] of UACR was 40 [11-130] mg/dl. The prevalence of UACR >300 mg/dl tends to be higher among smokers in participants with and without CVD condition (Figure 1A), with a p-value of 0.003 and 0.008, respectively. Smoking was independently associated with higher values of UACR, regardless of the CVD condition (Figure 1B)
Conclusion:
A consistent association exists between smoking and elevated UACR in a sample of the Egyptian population, who are known to have a substantial burden of CVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
ACTIVATION AND TARGETABILITY OF TYMP-IL-6-TF AXIS IN THE SKIN MICROENVIRONMENT IN UREMIC CALCIPHYLAXIS
Lotfollahzadeh Saran, Chitalia Vipul
A Loss-of-Function Missense Variant in ANGPTL3 Exerts Protective Effects Against Kidney Disease RiskZhang David, Ritchie Marylyn, Rader Daniel, Cuchel Marina