Final ID: Mo4062
Heart Failure-Associated SNPs Are Enriched in Estrogen-Related Receptor Binding Regions
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) are nuclear receptors essential for postnatal cardiac maturation. Our recent studies have shown that ERRs are necessary for coordinated activation of cardiomyocyte metabolic and structural gene programs through interactions with PGC-1 coactivators and cardiogenic factors such as GATA4. In heart failure (HF), ERR transcriptional programs may revert to a fetal-like state, leading to metabolic inefficiency and energy starvation.
Methods
To better understand ERRs’ role in HF, 176 SNPs from a recent HF GWAS were mapped onto the human cardiomyocyte cistrome to identify potential HF-associated variants proximal to ERRγ and/or ERRα binding regions. Overlaps were analyzed for ERR binding motifs with an 80% position-weight matrix threshold. Permutation testing was performed to determine if HF-associated variants were found more frequently than expected near ERR binding regions. Hypergeometric testing assessed whether HF-associated SNPs were enriched in ERR binding regions compared to genome-wide SNPs, with per-chromosome p-values combined using Fisher’s method. Stratified linkage disequilibrium score regression (S-LDSC) was performed to quantify whether SNPs within ERR binding regions disproportionately contributed to HF heritability compared to genome-wide averages.
Results
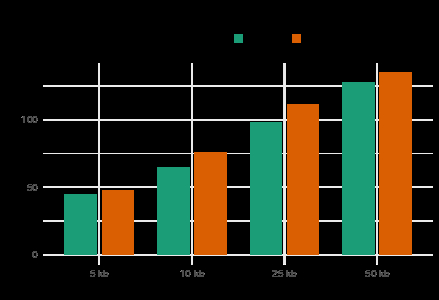
Both permutation and hypergeometric testing showed significant enrichment of HF-associated variants proximal to ERR binding regions (p < 0.05). The number of overlaps increased with the size of the flanking region, ranging from 48 at 5 kb, to 135 at 50 kb. Consensus ERR motifs were identified in 6.4% of ERRγ overlaps and 4.0% of ERRα overlaps. S-LDSC demonstrated notable HF heritability enrichment within ERRγ binding regions (enrichment score: 8.8 ± 3.0, p = 0.010), whereas ERRα showed non-significant enrichment (3.8 ± 3.3, p = 0.426), and GATA4 showed negligible enrichment (−0.4 ± 5.27, p = 0.786).
Conclusion
This computational analysis reveals significant enrichment of HF-associated SNPs in/near genomic regions containing ERR transcription factors, highlighting ERR-driven transcriptional networks as potentially important mechanisms underlying heart failure development. These results establish a platform for future functional experimental studies to determine the impact of HF-associated variants on ERR-mediated transcriptional regulatory function and additional computational analyses to clarify the precise biological roles of ERRs in HF progression.
Estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) are nuclear receptors essential for postnatal cardiac maturation. Our recent studies have shown that ERRs are necessary for coordinated activation of cardiomyocyte metabolic and structural gene programs through interactions with PGC-1 coactivators and cardiogenic factors such as GATA4. In heart failure (HF), ERR transcriptional programs may revert to a fetal-like state, leading to metabolic inefficiency and energy starvation.
Methods
To better understand ERRs’ role in HF, 176 SNPs from a recent HF GWAS were mapped onto the human cardiomyocyte cistrome to identify potential HF-associated variants proximal to ERRγ and/or ERRα binding regions. Overlaps were analyzed for ERR binding motifs with an 80% position-weight matrix threshold. Permutation testing was performed to determine if HF-associated variants were found more frequently than expected near ERR binding regions. Hypergeometric testing assessed whether HF-associated SNPs were enriched in ERR binding regions compared to genome-wide SNPs, with per-chromosome p-values combined using Fisher’s method. Stratified linkage disequilibrium score regression (S-LDSC) was performed to quantify whether SNPs within ERR binding regions disproportionately contributed to HF heritability compared to genome-wide averages.
Results
Both permutation and hypergeometric testing showed significant enrichment of HF-associated variants proximal to ERR binding regions (p < 0.05). The number of overlaps increased with the size of the flanking region, ranging from 48 at 5 kb, to 135 at 50 kb. Consensus ERR motifs were identified in 6.4% of ERRγ overlaps and 4.0% of ERRα overlaps. S-LDSC demonstrated notable HF heritability enrichment within ERRγ binding regions (enrichment score: 8.8 ± 3.0, p = 0.010), whereas ERRα showed non-significant enrichment (3.8 ± 3.3, p = 0.426), and GATA4 showed negligible enrichment (−0.4 ± 5.27, p = 0.786).
Conclusion
This computational analysis reveals significant enrichment of HF-associated SNPs in/near genomic regions containing ERR transcription factors, highlighting ERR-driven transcriptional networks as potentially important mechanisms underlying heart failure development. These results establish a platform for future functional experimental studies to determine the impact of HF-associated variants on ERR-mediated transcriptional regulatory function and additional computational analyses to clarify the precise biological roles of ERRs in HF progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Cardiac Targeting Peptide Linked to miRNA106a Targets and Suppresses Genes Known to Cause Heart Failure: Reversing Heart Failure at the Source
Lu Ming, Deng Claire, Taskintuna Kaan, Ahern Gerard, Yurko Ray, Islam Kazi, Zahid Maliha, Gallicano Ian
Adipose tissue extracellular vesicles mediate pro-arrhythmic changes in atrial cardiomyocytesLimpitikul Worawan, Garcia Contreras Marta, Betti Michael, Sheng Quanhu, Xiao Ling, Chatterjee Emeli, Gamazon Eric, Shah Ravi, Das Saumya