Final ID: 4366146
Adenine accumulation in Endothelial Cells Induces Cardiotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes
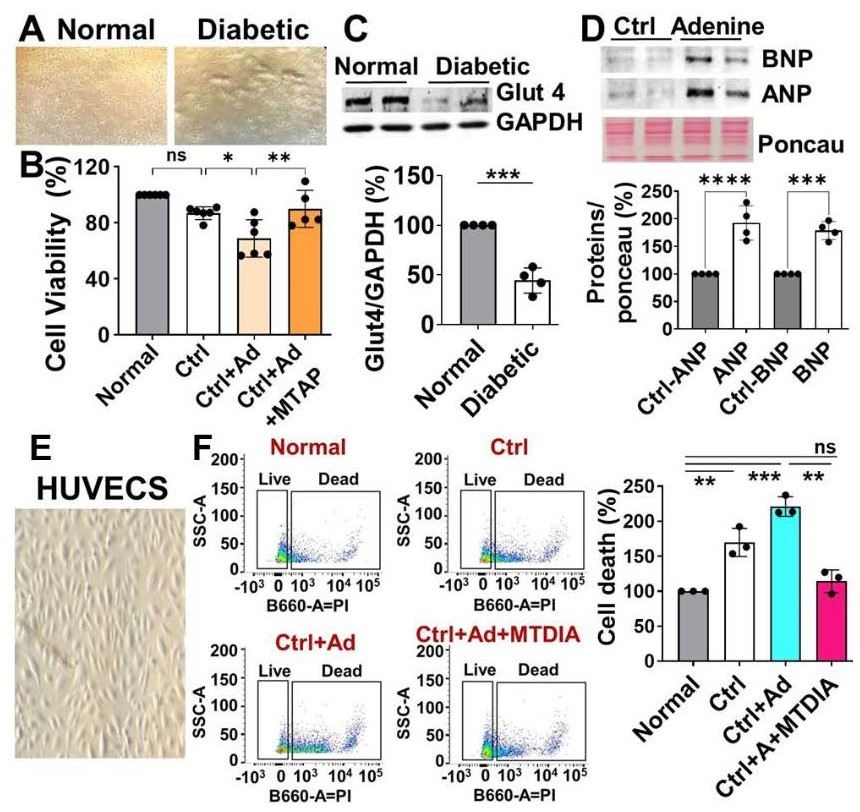
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): People living with T2DM are twice as likely to develop and die from cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks, and heart failure (HF). HF is a clinical syndrome characterized by a constellation of symptoms that are caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality. The objective of this study is to define the mechanism by which adenine accumulation in heart contributes to HF in T2DM. Human heart tissues were analyzed by spatial metabolomics to assess adenine localization across hearts from non-diabetic and diabetic patients. Multi-modal analysis was performed using auto-fluorescence (AF) to localize coronary blood vessels and overlay with H&E imaging of serial sections. H9c2 cardiomyoblasts and HUVEC cells were cultured in DPBS media supplemented with glucose (30 mM)+insulin (1 nM) for 48 h. Cells were cultured in a 5% CO2/95% humidified air atmosphere at 37 oC and at passage 4 and 8 (70-80% confluence) and treated with adenine (20 μM, 2 g/kg in vivo) or vehicle for 1h hours. Using SMART2 study, human hearts, and mouse model, after adjustment for clinical risk factors, urine adenine/creatinine ratio (UAdCR) was associated with overall incident HF. Spatial metabolomics indicated that adenine accumulation was increased in coronary artery blood vessels of diabetic human and mouse hearts (Fig. 1). Adenine treatment exacerbated the reduction in cell viability, and increased cell death (Fig. 2). Moreover, adenine administration in mice and in vitro, altered the removal of damaged mitochondria (mitophagy), and significantly decreased mitochondrial inner membrane protein (Mic60) levels. This finding was supported by the increased number of damaged mitochondria observed in human diabetic tissues with HF, and suggests alteration of cardiac bioenergetics. All these effects were reversed by the inhibitor of adenine production (MTDIA), confirming that adenine induces deleterious effects in diabetic cells. MTDIA blocked adenine accumulation in the diabetic heart (Fig. 3), and restored cardiac dysfunction, but MTDIA did not affect blood glucose and body weight. These results indicate that endogenous adenine, as reflected by the UAdCR, can predict the incidence of HF in T2DM individuals and adenine accumulation in the heart contributes to diabetes-induced HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abundance Of Long-Chain Acylcarnitines As a Key Regulator Of Metabolic Reprogramming During Postnatal Cardiac Maturation In Mice
Ramasamy Saminathan, Shrestha Pratikshya, Muthu Sakthijothi, Tran Zinnia, Velayutham Murugesan, Sundararajan Venkatesh
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian CommunityDeo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan