Final ID: Sa4095
Fluidic Shear Stress Has Opposing Effects on Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) is a significant route of internalization for macromolecules and membrane receptors in eukaryotic cells such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VE-cadherin, transferrin, integrins, and pathogens like COVID-19. During CME, the coat protein clathrin is recruited to form vesicles at the plasma membrane. Two opposing models to describe this process have been proposed, constant curvature and constant area. Recently we and others observed a spectrum of vesicle formation dynamics in fibroblast cells, supporting a flexible model. It has been shown that pressure, squeezing, and stress reduce the number of CME events in fibroblast cells. However, vascular endothelial cells live with pressure and the sheer force from blood flow, as well as mechanical force from vasodilation and vasoconstriction. It has been reported fluid sheer stress (FSS) results in morphological and transcriptional changes as well as actin rearrangement in HUVECs (Human umbilical vein endothelial cells), but how these environmental conditions impact CME in vascular endothelial cells remains unknown.
Our lab developed Simultaneous Two-wavelength Axial Ratiometry (STAR) microscopy to bridge the gap between static EM and dynamic fluorescence microscopy. STAR achieves dynamic nanoscale resolution in the axial z-direction allowing us to study real-time dynamics of clathrin coated pit formation in living cells. We hypothesized CME dynamics in vascular endothelial cells can be promoted under flow but are suppressed by increased membrane tension.
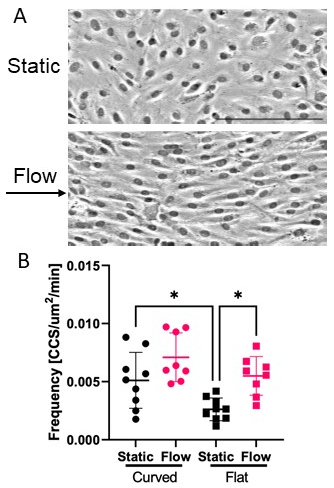
We applied STAR to HUVECs cultured under flow. Surprisingly, we observed increased CME dynamics when HUVECs were cultured under 10 dyne/cm2 FSS but imaged in static conditions, compared with those cultured and imaged statically. Next, we conducted transferrin uptake experiments to test if flow during the experiment has an impact on internalization. HUVECs were cultured under 10 dyne/cm2 FSS flow and transferrin uptake was performed for 20 min in either flow or static culture. We found increased transferrin uptake in the static experimental group. This indicates flow may have opposing effects. The fluid flow itself it can suppress CME, possibly through physical forces. While the protein expression and morphological changes from being grown under flow can promote CME. Future work will investigate how CME responds to different rates of FSS and identify changed of protein expression patterns that may drive changes in CME.
Our lab developed Simultaneous Two-wavelength Axial Ratiometry (STAR) microscopy to bridge the gap between static EM and dynamic fluorescence microscopy. STAR achieves dynamic nanoscale resolution in the axial z-direction allowing us to study real-time dynamics of clathrin coated pit formation in living cells. We hypothesized CME dynamics in vascular endothelial cells can be promoted under flow but are suppressed by increased membrane tension.
We applied STAR to HUVECs cultured under flow. Surprisingly, we observed increased CME dynamics when HUVECs were cultured under 10 dyne/cm2 FSS but imaged in static conditions, compared with those cultured and imaged statically. Next, we conducted transferrin uptake experiments to test if flow during the experiment has an impact on internalization. HUVECs were cultured under 10 dyne/cm2 FSS flow and transferrin uptake was performed for 20 min in either flow or static culture. We found increased transferrin uptake in the static experimental group. This indicates flow may have opposing effects. The fluid flow itself it can suppress CME, possibly through physical forces. While the protein expression and morphological changes from being grown under flow can promote CME. Future work will investigate how CME responds to different rates of FSS and identify changed of protein expression patterns that may drive changes in CME.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiac Output Assessment from Intrinsic Frequencies of a Single Carotid Pressure Waveform in a Large Community-Based Population: The Framingham Heart Study
Niroumandi Soha, Wei Heng, Wolfson Aaron, Vaidya Ajay, Pahlevan Niema
A Phase 2a randomized controlled trial of once-daily versus twice-daily remote ischemic conditioning in vascular cognitive impairment (TRIC-VCI)Ganesh Aravind, Mccreary Cheryl, Sahlas Demetrios, Sharma Mukul, Swartz Richard, Smith Eric, Barber Philip, Black Sandra, Corbett Dale, Field Thalia, Frayne Richard, Hachinski Vladimir, Ismail Zahinoor, Mai Lauren