Final ID: MP921
Multi-Omics Approach Identifies SMPD1 as a Therapeutic Target Potentially Mediating Aortic Aneurysm via Ceramide Metabolism
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Aortic aneurysms (AAs), including thoracic (TAA) and abdominal (AAA) types, are associated with a high risk of dissection and rupture, with no pharmacological therapies are available to slow or prevent progression. Multi-omics strategies offer promise for discovering therapeutic targets. While prior studies based on genomic and transcriptomic data have identified lipoprotein(a) and PCSK9 as potential targets, proteomic and metabolomic analyses remain limited.
Methods
We employed two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR), summary-data-based MR (SMR) with false discovery rate correction, and Bayesian colocalization analysis with HEIDI testing to evaluate the association between plasma proteins and AA. Proteins significant in two out of three analyses were considered potential drug targets, while those significant in all three were defined as core therapeutic targets. Potential side effects of core targets were evaluated using phenome-wide association studies (PheWAS). Additional MR analyses identified AA-related metabolites, and mediation analysis via the delta method was used to assess causal pathways linking proteins and metabolites.
Results
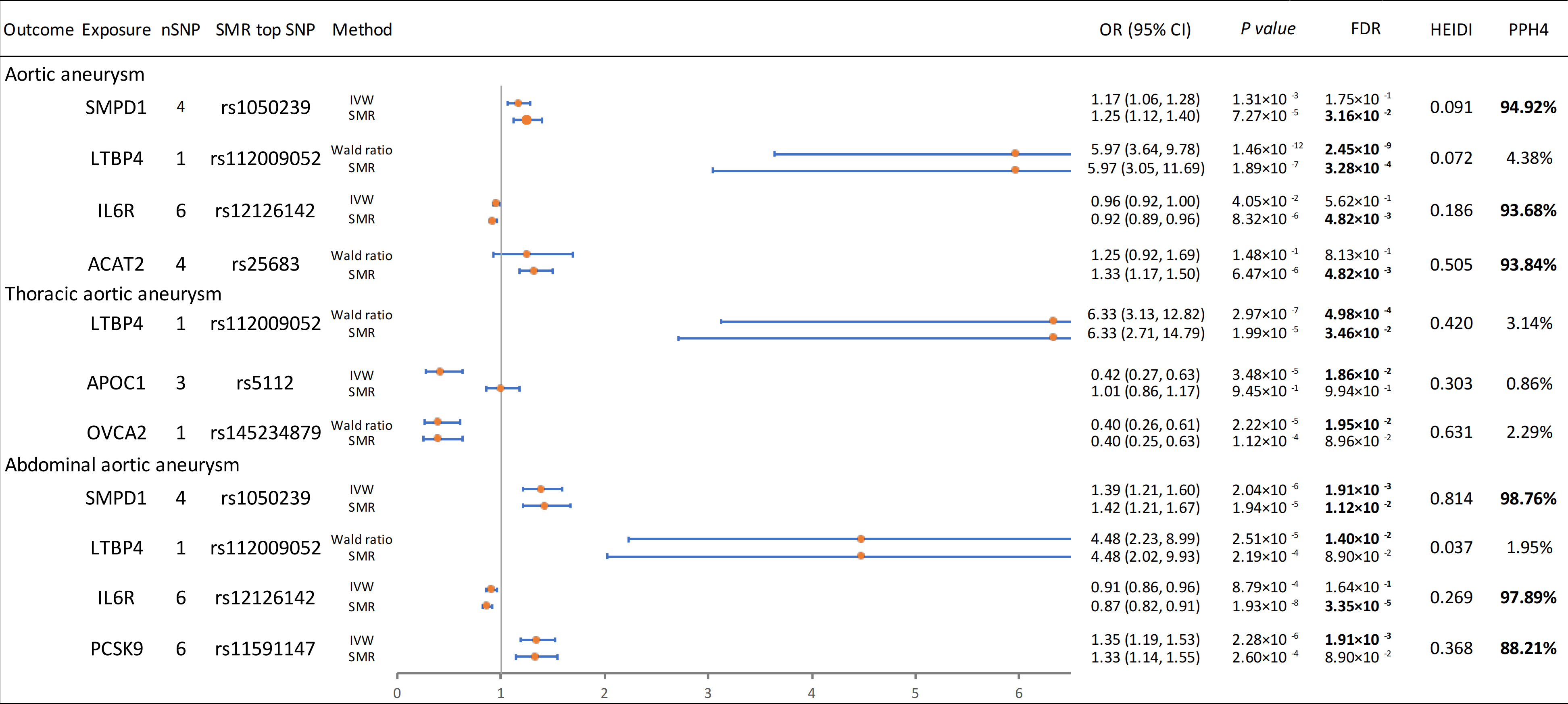
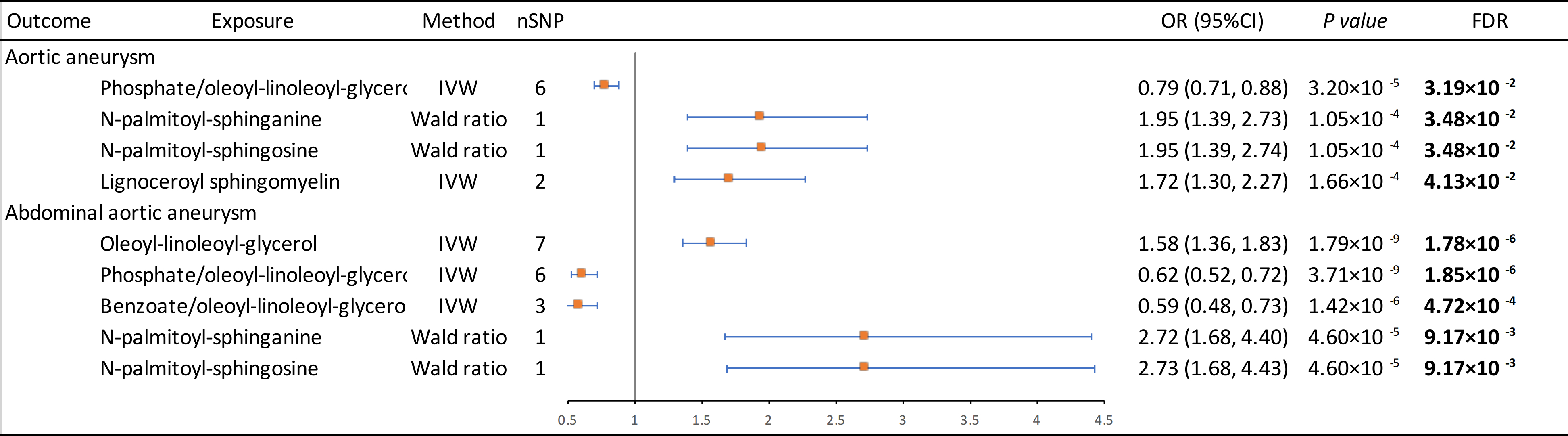
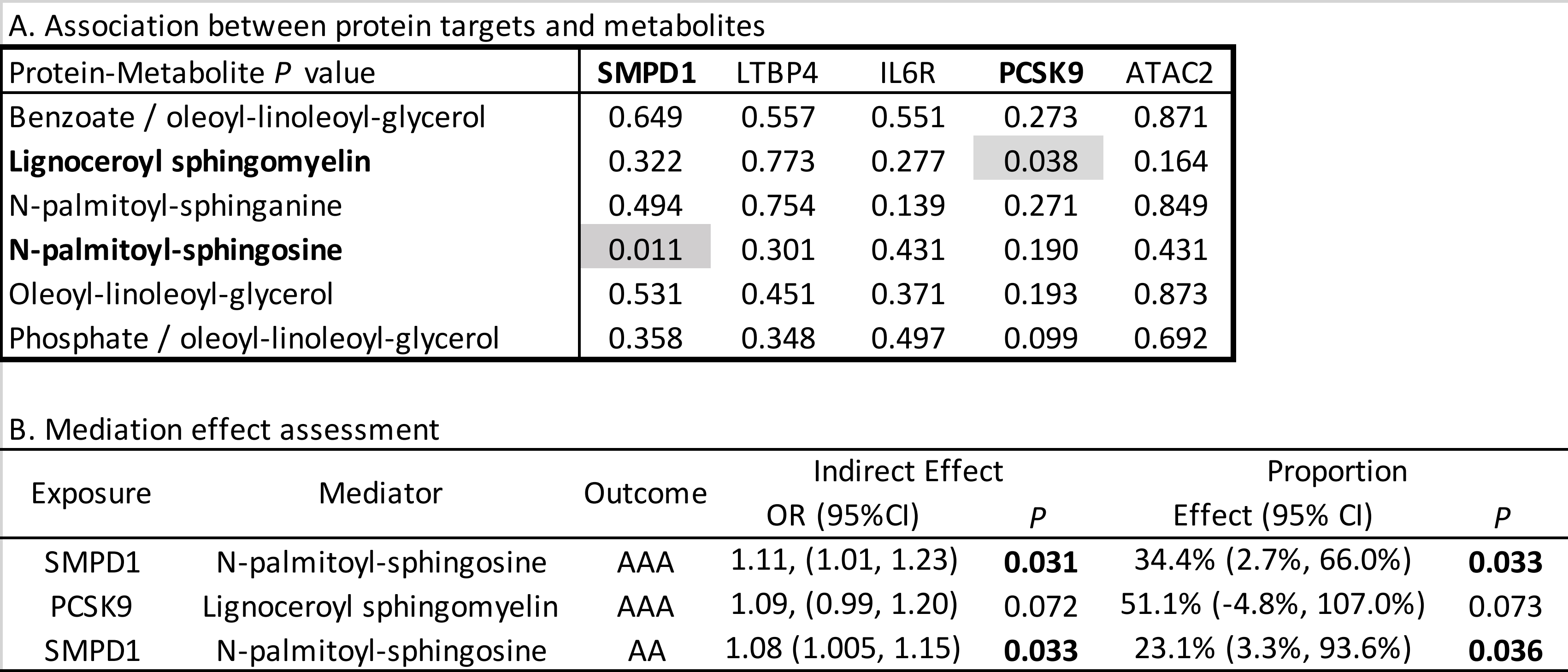
We identified five proteins as potential therapeutic targets: LTBP4 (positive association with AA, TAA), IL6R (negative association with AA, AAA), SMPD1 and ACAT2 (positive association with AA), and PCSK9 (positive association with AAA). SMPD1 emerged as a core therapeutic target for AAA, with significant associations in MR (OR = 1.39, 95% CI: 1.21–1.60, P = 2.04E-6), SMR (OR = 1.42, 95% CI: 1.21–1.67, P = 1.94E-5), and colocalization (PPH4 = 98.76%), and no adverse phenotypes detected in PheWAS. Metabolite MR further identified lignoceroyl sphingomyelin, N-palmitoyl-sphinganine, and N-palmitoyl-sphingosine as associated with AA; oleoyl-linoleoyl-glycerol, N-palmitoyl-sphinganine, and N-palmitoyl-sphingosine with AAA. Mediation analysis showed that N-palmitoyl-sphingosine significantly mediated the effect of SMPD1 on AA (effect proportion: 23.1%, 95% CI: 3.3%–93.6%) and AAA (34.4%, 95% CI: 2.7%–66.0%).
Conclusion
This study identifies five plasma proteins and four metabolites as potential therapeutic targets for AA. To our knowledge, this is the first study to highlight SMPD1 as a core therapeutic target for AAA, likely acting through ceramide metabolism involving N-palmitoyl-sphingosine. These findings offer novel mechanistic insights into AAA and suggest promising directions for drug development.
Aortic aneurysms (AAs), including thoracic (TAA) and abdominal (AAA) types, are associated with a high risk of dissection and rupture, with no pharmacological therapies are available to slow or prevent progression. Multi-omics strategies offer promise for discovering therapeutic targets. While prior studies based on genomic and transcriptomic data have identified lipoprotein(a) and PCSK9 as potential targets, proteomic and metabolomic analyses remain limited.
Methods
We employed two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR), summary-data-based MR (SMR) with false discovery rate correction, and Bayesian colocalization analysis with HEIDI testing to evaluate the association between plasma proteins and AA. Proteins significant in two out of three analyses were considered potential drug targets, while those significant in all three were defined as core therapeutic targets. Potential side effects of core targets were evaluated using phenome-wide association studies (PheWAS). Additional MR analyses identified AA-related metabolites, and mediation analysis via the delta method was used to assess causal pathways linking proteins and metabolites.
Results
We identified five proteins as potential therapeutic targets: LTBP4 (positive association with AA, TAA), IL6R (negative association with AA, AAA), SMPD1 and ACAT2 (positive association with AA), and PCSK9 (positive association with AAA). SMPD1 emerged as a core therapeutic target for AAA, with significant associations in MR (OR = 1.39, 95% CI: 1.21–1.60, P = 2.04E-6), SMR (OR = 1.42, 95% CI: 1.21–1.67, P = 1.94E-5), and colocalization (PPH4 = 98.76%), and no adverse phenotypes detected in PheWAS. Metabolite MR further identified lignoceroyl sphingomyelin, N-palmitoyl-sphinganine, and N-palmitoyl-sphingosine as associated with AA; oleoyl-linoleoyl-glycerol, N-palmitoyl-sphinganine, and N-palmitoyl-sphingosine with AAA. Mediation analysis showed that N-palmitoyl-sphingosine significantly mediated the effect of SMPD1 on AA (effect proportion: 23.1%, 95% CI: 3.3%–93.6%) and AAA (34.4%, 95% CI: 2.7%–66.0%).
Conclusion
This study identifies five plasma proteins and four metabolites as potential therapeutic targets for AA. To our knowledge, this is the first study to highlight SMPD1 as a core therapeutic target for AAA, likely acting through ceramide metabolism involving N-palmitoyl-sphingosine. These findings offer novel mechanistic insights into AAA and suggest promising directions for drug development.
More abstracts on this topic:
CC-Chemokine Receptor 2 Inhibition Prevents Monocyte/Macrophages Recruitment in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
Elizondo Benedetto Santiago, Zaghloul Mohamed, Arif Batool, Bredemeyer Andrea, Lavine Kory, Gropler Robert, Liu Yongjian, Zayed Mohamed
ADP-Ribosylation In a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis: a Potential Novel Link Between Dyslipidemia and Inflammation in Cardiovascular DiseaseDelwarde Constance, Mlynarchik Andrew, Perez Katelyn, Campedelli Alesandra, Sonawane Abhijeet, Aikawa Elena, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Masanori, Santinelli Pestana Diego, Kasai Taku, Kuraoka Shiori, Nakamura Yuto, Okada Takeshi, Decano Julius, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Ge Rile