Final ID: MP2608
Covalent Peptidomimetic Targeting NEDD9 Regulates Pulmonary Endothelial Cell Phenotype
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction Knockout of the gene encoding SH3-domain protein NEDD9 mitigates endothelial dysfunction, vascular fibrosis and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in vivo, suggesting NEDD9 may be a therapeutic target in PAH. However, SH3 domains express flat and shallow surfaces that lack small molecule binding pockets, and, thus, are considered “undruggable”.
Hypothesis We hypothesized that a peptidyl approach leveraging the focal adhesion kinase (FAK) consensus motif, PxKPxR, which modulates NEDD9 protein-protein docking, with a warhead targeting the redox sensitive cysteine at position 18 on the flexible RT loop promotes target engagement and specificity to NEDD9.
Methods NEDD9-targeting peptides (NEDDtides) containing PxKPxR were modified with bromoacetamide as a covalent warhead, or thalidomide to engage the E3 ligase system. Crystallography and various in vitro chemical assays were used to profile NEDDtide-NEDD9 interactions, and biological effects were tested in cultured human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs).
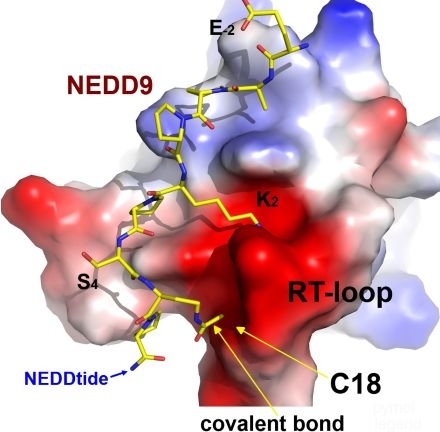
Results Isothermal titration calorimetry confirmed binding of a NEDDtide to NEDD9 SH3 domain (KD=4 μM). Compared to vehicle (V) control, transfection of HPAECs for 10 min with NEDDtide conjugated to thalidomide induced dose-dependent degradation of NEDD9 protein that was not observed for SH3 protein GBR2, which lacks an PxKPxR consensus motif (2.4±0.3 vs. 1.1±0.1 vs. 2.0±0.1 arb. units, P<0.001). To optimize potency and target specificity, we modified the NEDDtide with a reactive bromoacetamide residue. Crystallography confirmed a structural basis of interactions and covalent bond between warhead and Cys18 in NEDDtide-NEDD9 complex (Figure). Fluorescence polarization demonstrated strong affinity of the covalent peptide for the NEDD9-SH3 (IC50=4 μM). Further, incubation with a 10-fold excess of peptide led to complete labeling of NEDD9-SH3 assessed by mass spectrometry. Compared to V-treated cells, HPAECs transfection with the covalent peptide decreased cell migration by wound assay (422±35 vs. 192±30 µm, P<0.001).
Conclusion We developed a novel FAK peptidomimetic to engage the SH3 protein NEDD9. NEDDtide modification with a bromoacetamide warhead showed strong affinity to, and specificity for, NEDD9-SH3, and affected HPAEC phenotype whereas thalidomide-modified NEDDtide degraded NEDD9. This technology advances therapeutics targeting SH3 proteins with implications for diseases characterized by endothelial dysfunction including PAH.
Hypothesis We hypothesized that a peptidyl approach leveraging the focal adhesion kinase (FAK) consensus motif, PxKPxR, which modulates NEDD9 protein-protein docking, with a warhead targeting the redox sensitive cysteine at position 18 on the flexible RT loop promotes target engagement and specificity to NEDD9.
Methods NEDD9-targeting peptides (NEDDtides) containing PxKPxR were modified with bromoacetamide as a covalent warhead, or thalidomide to engage the E3 ligase system. Crystallography and various in vitro chemical assays were used to profile NEDDtide-NEDD9 interactions, and biological effects were tested in cultured human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs).
Results Isothermal titration calorimetry confirmed binding of a NEDDtide to NEDD9 SH3 domain (KD=4 μM). Compared to vehicle (V) control, transfection of HPAECs for 10 min with NEDDtide conjugated to thalidomide induced dose-dependent degradation of NEDD9 protein that was not observed for SH3 protein GBR2, which lacks an PxKPxR consensus motif (2.4±0.3 vs. 1.1±0.1 vs. 2.0±0.1 arb. units, P<0.001). To optimize potency and target specificity, we modified the NEDDtide with a reactive bromoacetamide residue. Crystallography confirmed a structural basis of interactions and covalent bond between warhead and Cys18 in NEDDtide-NEDD9 complex (Figure). Fluorescence polarization demonstrated strong affinity of the covalent peptide for the NEDD9-SH3 (IC50=4 μM). Further, incubation with a 10-fold excess of peptide led to complete labeling of NEDD9-SH3 assessed by mass spectrometry. Compared to V-treated cells, HPAECs transfection with the covalent peptide decreased cell migration by wound assay (422±35 vs. 192±30 µm, P<0.001).
Conclusion We developed a novel FAK peptidomimetic to engage the SH3 protein NEDD9. NEDDtide modification with a bromoacetamide warhead showed strong affinity to, and specificity for, NEDD9-SH3, and affected HPAEC phenotype whereas thalidomide-modified NEDDtide degraded NEDD9. This technology advances therapeutics targeting SH3 proteins with implications for diseases characterized by endothelial dysfunction including PAH.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comprehensive Single-Cell Atlas of the Human Lung in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Hong Jason, Wong Brenda, Brownstein Adam, Graves Tammy, Aldred Micheala, Dai Zhiyu, Yang Xia, Eghbali Mansoureh
Genome Wide Association Study Identifies Loci Associated with Pulmonary PressureAgrawal Vineet, Sun Yan, Brittain Evan, Hui Qin, Garry Jonah, Kundu Suman, West James, Mosley Jonathan, Kepler Joshua, Freiberg Matthew, Joseph Jacob