Final ID: MP732
Incidence of Spontaneous Heart Block in L-looped Ventricles
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Patients with L-looped ventricles are at risk for the spontaneous development of complete heart block; however, the incidence rate is poorly understood. The goal of this study was to quantify the incidence of spontaneous heart block in L-looped ventricles and identify risk factors for permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation.
Methodology: Patients with L-looped ventricles at Boston Children’s Hospital were identified between 01/01/1965 and 11/03/2024. For surgical heart block, logistic regression with generalized estimating equations was used to model the risk of perioperative heart block while accounting for within-subject correlation. A multistate model was used to assess the effect of VSD intervention (closure or enlargement) and presence of conduction anomalies on spontaneous risk of heart block. Incidence rates were calculated for the overall cohort as well as the subsets of patients with nodal disease (first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block or second-degree Mobitz I AV block) and infranodal disease (right bundle branch, left bundle branch, left anterior fascicular, and left posterior fascicular blocks, or intraventricular conduction delay). For the estimation of the spontaneous risk for heart block, surgical heart block events were censored at the time of the inciting surgery.
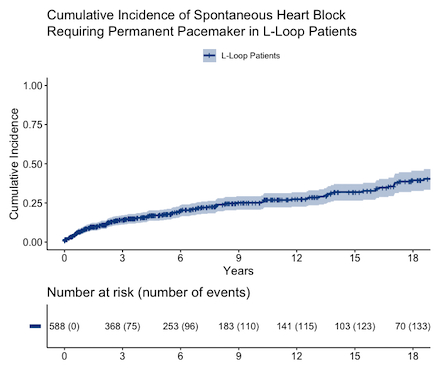
Results: There were 588 patients with L-looped ventricles between 1965-2024. Median follow-up time was 6.9 years (IQR: 3.0-14.9 years). The overall incidence of spontaneous heart block was 3.2%/year (149 events / 4611 person-years) (Figure 1). VSD intervention did not affect the spontaneous risk for complete heart block. However, patients with nodal disease had higher incidence of PPM at 18.2%/year (31 events / 170 person-years; OR: 11.3, 95% CI: 6.7-19.2, p < 0.001) compared to 2.6%/year in patients with normal conduction (88 events / 3340 person-years). Conversely, the presence of intraventricular conduction disturbances was not associated with PPM. Finally, VSD intervention was associated with an increased risk of PPM implantation (ARVSD: 11.7%, ARNo VSD: 1.8%; OR: 7.1, 95% CI: 3.5-14.1, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The risk for surgical heart block is high with VSD intervention in patients with L-loop ventricles. Beyond this, the baseline incidence of spontaneous heart block in patients with L-looped ventricles is 3.2%/year, and patients with first-degree AV block or second-degree Mobitz I AV block are at substantially higher risk than those with normal conduction.
Methodology: Patients with L-looped ventricles at Boston Children’s Hospital were identified between 01/01/1965 and 11/03/2024. For surgical heart block, logistic regression with generalized estimating equations was used to model the risk of perioperative heart block while accounting for within-subject correlation. A multistate model was used to assess the effect of VSD intervention (closure or enlargement) and presence of conduction anomalies on spontaneous risk of heart block. Incidence rates were calculated for the overall cohort as well as the subsets of patients with nodal disease (first-degree atrioventricular (AV) block or second-degree Mobitz I AV block) and infranodal disease (right bundle branch, left bundle branch, left anterior fascicular, and left posterior fascicular blocks, or intraventricular conduction delay). For the estimation of the spontaneous risk for heart block, surgical heart block events were censored at the time of the inciting surgery.
Results: There were 588 patients with L-looped ventricles between 1965-2024. Median follow-up time was 6.9 years (IQR: 3.0-14.9 years). The overall incidence of spontaneous heart block was 3.2%/year (149 events / 4611 person-years) (Figure 1). VSD intervention did not affect the spontaneous risk for complete heart block. However, patients with nodal disease had higher incidence of PPM at 18.2%/year (31 events / 170 person-years; OR: 11.3, 95% CI: 6.7-19.2, p < 0.001) compared to 2.6%/year in patients with normal conduction (88 events / 3340 person-years). Conversely, the presence of intraventricular conduction disturbances was not associated with PPM. Finally, VSD intervention was associated with an increased risk of PPM implantation (ARVSD: 11.7%, ARNo VSD: 1.8%; OR: 7.1, 95% CI: 3.5-14.1, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The risk for surgical heart block is high with VSD intervention in patients with L-loop ventricles. Beyond this, the baseline incidence of spontaneous heart block in patients with L-looped ventricles is 3.2%/year, and patients with first-degree AV block or second-degree Mobitz I AV block are at substantially higher risk than those with normal conduction.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adipose tissue extracellular vesicles mediate pro-arrhythmic changes in atrial cardiomyocytes
Limpitikul Worawan, Garcia Contreras Marta, Betti Michael, Sheng Quanhu, Xiao Ling, Chatterjee Emeli, Gamazon Eric, Shah Ravi, Das Saumya
Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) as career? Examining encouraging and discouraging factors around the globe in the Global ACHD Survey.Bravo-jaimes Katia, Elizari Maria Amalia, Valdez Ramos Miriam, Cupido Blanche, Zentner Dominica, Almasri Murad, Phillips Sabrina, Mcleod Christopher, Burchill Luke, Bullock-palmer Renee, Windram Jonathan, Srour Mhd Osama, Jenkins Petra, Luna-lopez Raquel, Tutarel Oktay, Kandavello Geetha, Guerrero Carlos, García Cruz Edgar, Ackerman Judith